3.2.2 Digestive sytem Questions
advertisement

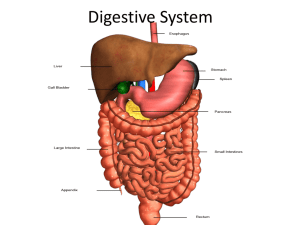
Project 3.2.2 and Project 3.2.3: Student Resource Sheet Use the information found below to guide your research and to design your model. Take notes, answer questions, and complete sketches in your laboratory journal. 1. Oral cavity, pharynx, (must also include accessory organs such as salivary glands, tongue, and teeth) What is the oral cavity and what does it contain? What is the function of the salivary glands? What is the function of the tongue? What is a bolus? Where are the soft and hard palate located and what are their functions? What mechanical and chemical digestion occurs in the oral cavity? What mechanisms are in place to make sure food does not “go down the wrong tube” and into the windpipe? 2. Esophagus and Stomach What is peristaltic movement and how does it function in the esophagus? Does any digestion of food occur in the esophagus? What are the primary functions of the stomach? What is chyme and how does the stomach mix this material? What role does the stomach play in decontaminating the incoming food matter? What cells in the stomach function to form enzymes and acids? Why doesn’t gastric juice digest the inside of the stomach? What are sphincters and how are they related to the stomach? What mechanical and chemical digestion occurs in the stomach? 3. Small Intestine and Large Intestine What are the three sections of the small intestine and what role does each section play in digestion or absorption? The three sections are the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum is the first part of digestion. The jejunum is where the inside walls absorb nutrients. The ileum absorbs bile acids. What is the pH within the small intestine and how is this pH maintained? The pH is 6. This pH is maintained by bicarbonate ions secreted by the pancreas that neutralize the acidic pH of the food and create an alkaline pH. Where do bile and pancreatic enzymes enter the small intestine? At the duodenum. How does food move through the intestines? Via peristalsis (the involuntary contraction of the intestines). What enzymes act inside the small intestine and what are the functions of these enzymes? Amylase, lactase, lipase, and protease act inside the small intestine. The amylase breaks down starch when you chew food and converts it into © 2014 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Human Body Systems Project 3.2.2 and Project 3.2.3 Student Resource Sheet – Page 1 smaller carbohydrates. Lactase breaks down a sugar called lactose (found in milk) into smaller sugars for absorption. Lipase digests fats. Protease breaks down proteins. What is the function of the large intestine in relation to digestion? Also know as the colon, it removes water from the remaining indigestible food matter. What are the three sections of the large intestine and what roles does each play in digestion or absorption? The three sections are the ascending colon, transverse colon, and descending colon. The ascending colon carries feces from cecum to the transverse colon. The transverse colon reclaims water from the fecal material and the descending colon stores the food remains that will be discarded. How does the large intestine help maintain a water balance in the body? The large intestine absorbs water out of fecal matter. 4. Pancreas, Liver and Gallbladder What are the size and the location of the pancreas? It is 6 inches and it is behind the stomach. What are the different functions of the pancreas, and how is the pancreas directly related to digestion? The pancreas has an exocrine function that helps in digestion and an endocrine function that regulates blood sugar. How does the pancreas connect to the rest of the digestive system? It connects to the duodenum. What enzymes are produced by the pancreas and what are their functions? Lipase, protease, and amylase. Lipase breaks down fat, protease breaks down proteins, and amylase breaks down carbs. How is insulin related to the digestive system? It is needed for the glucose to be taken up by the cells. What is the size of the liver and where is it located? It is about 3 pounds and located to the right of the stomach. How does the liver function in relation to digestion? The liver produces bile for the breakdown of food. What are other functions of the liver in the body? It converts glycogen to glucose. What is the relationship between the liver and the gallbladder? The gallbladder stores bile from the liver. What is the function of bile and where does it enter the digestive tract? Bile is needed for the breakdown of food and it enters at the stomach. © 2014 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Human Body Systems Project 3.2.2 and Project 3.2.3 Student Resource Sheet – Page 2