Worksheet 24 - Iowa State University
advertisement

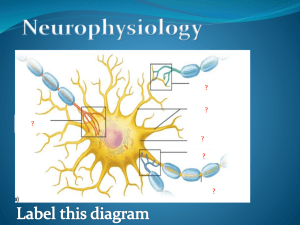
Neuroscience 1 Week 14.1 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Natalie Course: BIOL 212 Date: 4/13/14 Chapter: 41 1. What change in membrane potential will occur if the cell becomes less negative relative to surrounding solution? 2. Which type of potential can vary in strength? Which is elicits an all or nothing response? 3. Which potential comes first: graded or action? 4. What are the two types of gated channels? Describe them. 5. What are the five steps in an action potential sequence? 6. Draw a picture labeling the steps and the refractory period. (include = signs if needed) 7. Rearrange these steps in the correct order. Action potential, graded potential depolarizes cell membrane, voltage gated Na+ channels become inactivated, threshold potential, voltage gated Na+ channels open, refractory period, voltage gated K+ channels open, voltage gated K+ channels close, voltage gated Na+ channels close, hyperpolarization 8. How does a signal travel all the way down an axon? 9. How is backward conduction prevented? 10. Where does myelination occur? Is it continuous? 11. If one axon had only 3 nodes of Ranvier and another had 10, which one would send an action potential faster? (drawing a picture may help) 12. What is a synapse? 13. In a chemical synapse, where is the neurotransmitter kept? What causes this to be released?