The Neuron
advertisement

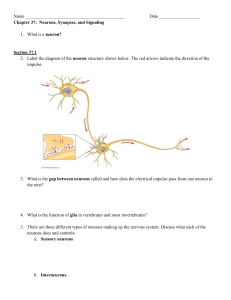
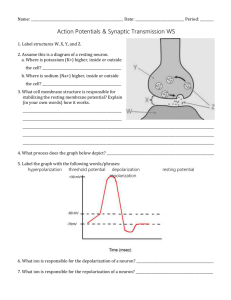
The Neuron Basic Constitution • The major features: soma (the cell body), dendrites (the receiving end) and axon (the outgoing end) • Neurons differ in size, shape and physiological properties Bipolar neuron e.g., retina, olfactory bulb Unipolar neuron Invertebrates Multipolar neuron pyramidal cell Neuronal State: Membrane Potential • Membrane potential: the difference between electric potentials within the cell body and its surrounding. Speciality of Membrane • Permeability of the membrane • Ions types: Potassium, Sodium, Calcium and Chloride • Ion channel types: – – – – – – – Leakage channel: always open Voltage-gated channel: sensitive to the size of membrane potential Neurotransmitter -gated channel: sensitive to the binding of neurotransmitters Ion bump : generating concentration difference for ions within and outside the cell And others Resting potential •Ion pump generates concentration difference of ions; Under natural force, ions diffuse from high to low concentrations •Positive charged ions (cations) leak through leakage channels, but the membrane is not permeable to the anions binding to cations; A electrical potential is generated. •A balance is reached when the electrical force matches diffusion force Neuronal Interaction • Chemical synapses and neurotransmitters • Synapses: the contact sites between neurons •Pre- and post- synaptic neurons •Action potential triggers the release of neurotransmitter •Neurotransmitters drift across the synaptic cleft •Neurotransmitter-gated channels open, generating electrical current (or postsynaptic potential (PSP)) •Dependent on the sign of PSP, synapses are clarified as excitatory and inhibitory ones. Action potential: •Membrane potential increases due to external input. •When its value is larger than a threshold, voltage-gated channels are open, ions influx and efflux the cell. •Voltage-gated channels are closed very quick, leading to an electrical pulse. Summary of Neural Signaling Mechanism •Resting potential -Special permeability of the membrane for ions -Ion bump account for the concentration gradient of ions -Leakage channel only for cations -A balance between electric and diffusion force •Basic synaptic mechanism -Action potential triggers the release of neurotransmitter at the axon terminal of pre-synaptic neuron -Neurotransmitter drift across the synaptic cleft -Neurotransmitter opens the neurotransmitter-gated channels, generating PSP at the post-synaptic neuron •The mechanism for generating action potential? -The increase of membrane potential triggers the opening of voltage-gated channels The Profile of Action Potential • Rising phase (Depolarization): A sharp increase of the membrane potential to a positive value • Falling phase (de-polarization): Followed the rising phase quickly, a sharp decrease in the membrane potential, which even overshoot the resting potential • Returning phase: The membrane potential gradually returns to the resting value The minimal mechanism • Rising phase (depolarization): – The membrane voltage change triggers the opening of voltagegated sodium channels – The influx of sodium depolarizes the neuron (up to V=+35mV) • Falling phase (de-polarization): – The sodium channels become inactive at around 1ms after their opening – Meanwhile, the potassium channels open—the efflux of potassium ions overshoots the resting potential (down to V=80mV). • Returning phase – The hyper-polarization causes the close of potassium and sodium channels – Ion bump may be called to retain the concentration gradients of potassium and sodium ions The status of channels The opening of Na+ channel Inactive of Na+ channel; Opening K+ channel Closing of Na+ & K+ channels The opening of leakage channel Review Questions: 1. Name 3 types of neurons. 2. What is a membrane potential? 3. What ion channels/pumps are responsible for keeping the resting membrane potential? 4. What ion channels/pumps are responsible for generating the action potential? 5. By which ways are the neurons repolarized? 6. What is meant by the absolute refractory period? Name 1,2,3,4,5,6 and 7 What is “A” & “B” ?