project management skills
advertisement

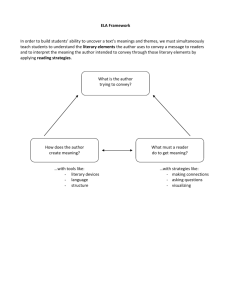
IT Project Management, Project Failure and Success Introduction Projects operate in a broad organizational environment. Project managers need to use systems thinking: Taking a holistic view of a project and understanding how it relates to the larger organization. Senior managers must make sure projects continue to support current business needs. 1 PROJECT Project – a [temporary] sequence of unique, complex, and connected activities having one goal or purpose and that must be completed by specific time, within budget, and according to specification Project management – the process of scoping, planning, staffing, organizing, directing, and controlling the development of an acceptable system at a minimum cost within a specified time frame. 2 Poor Expectations Management: Scope creep – the unexpected and gradual growth of requirements during an information systems project. Feature creep– the uncontrolled addition of technical features to a system. 3 The art of project management Technological change Customer and management expectations Documentation and communication Time and resource constraints Managing people Organizational change and complexity Contractors and vendors Methodologies and tools Systems development life cycle 4 A Systems View of Project Management The term systems approach emerged in the 1950s to describe a holistic and analytical approach to solving complex problems. Three parts include: Systems philosophy: View things as systems, which are interacting components that work within an environment to fulfill some purpose. Systems analysis: Problem-solving approach. Systems management: Address business, technological, and organizational issues before making changes to systems. 5 MEASURES OF SUCCESS The resulting information system is acceptable to the customer. The system was delivered ‘on time.’ The system was delivered “within budget.” The system development process had a minimal impact on ongoing business operations 6 CAUSES OF PROJECT FAILURE Lack of organization’s commitment to the system development methodology Failure to establish upper-management commitment to the project Taking shortcuts through or around the system development methodology Failure to adapt to business change Insufficient resources 7 Poor expectations management Premature commitment to a fixed budget and schedule Poor estimating techniques Over optimism Inadequate skills people management 8 FUNCTIONS OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT Scoping – setting the boundaries of the project, understand context and complexity of the project Planning – identifying the tasks required to complete the project Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition 9 PROJECT MANAGEMENT SKILLS: Management skills Leadership skills Technical skills Conflict management skills Customer relationship Risk and change management 10 PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS Initiating project Planning project Executing project Closing down project The environment is one of the continual change and problem solving. 11 Overcoming project team difficulties Promote team work Convey concepts in meetings/ workshops Use joint problem solving/ brainstorming Encourage feedback Identify roles and responsibilities for each team member Convey common understanding of the project Master schedules and critical path Be visible and available as Project Manager 12 13