The term endothermic describes a process or
advertisement

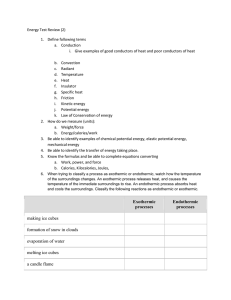
The term endothermic describes a process or reaction in which the system absorbs energy from its surroundings in the form of heat. The intended sense is that of a reaction that depends on taking in heat if it is to proceed. The opposite of an endothermic process is an exothermic process, one that releases, "gives out" energy in the form of heat. Thus in each term (endothermic & exothermic) the prefix refers to where heat goes as the reaction occurs. Endothermic Reaction Examples An endothermic reaction is any chemical reaction that absorbs heat from its environment. Here's a list of examples of endothermic reactions. You can use these when asked to cite an example or to get ideas to set up a demonstration of an endothermic reaction or process. e.g: photosynthesis (chlorophyll is used to react carbon dioxide plus water plus energy to make glucose and oxygen) Endothermic Processes These examples could be written as chemical reactions, but are more generally considered to be endothermic or heat-absorbing processes: melting ice cubes melting solid salts evaporating liquid water converting frost to water vapor (melting, boiling, and evaporation in general are endothermic processes) forming a cation from an atom in the gas phase splitting a gas molecule separating ion pairs cooking an egg baking bread Examples of Endothermic and Exothermic Processes Photosynthesis is an example of an endothermic chemical reaction. In this process, plants use the energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This reaction requires 15MJ of energy (sunlight) for every kilogram of glucose that is produced: sunlight + 6CO2(g) + H2O(l) = C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) EXOTHERMIC REACTION : An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of light or heat. It is the opposite of an endothermic reaction. The term exothermic ("outside heating") describes a process or reaction that releases energy from the system, usually in the form of heat, but also in a form of light (e.g. a spark, flame, or flash), electricity (e.g. a battery), or sound (e.g. explosion heard when burning hydrogen). After an exothermic reaction, more energy has been released to the surroundings than was absorbed to initiate and maintain the reaction. An example would be the burning of a candle, wherein the sum of calories produced by combustion (found by looking at radiant heating of the surroundings and visible light produced, including increase in temperature of the fuel (wax) itself, which with oxygen, have become hot CO2 and water vapor,) exceeds the number of calories absorbed initially in lighting the flame and in the flame maintaining itself. An exothermic reaction is a chemical or physical reaction that releases heat. It gives out energy to its surroundings. The energy needed for the reaction to occur is less than the total energy released. Some examples of exothermic processes are: Explosions are some of the most violent exothermic reactions Condensation of rain from water vapor Combustion of fuels such as wood, coal and oil Mixing water and strong acids Mixing alkalis and acids The setting of cement and concrete Exothermic processes Endothermic processes making ice cubes melting ice cubes formation of snow in clouds conversion of frost to water vapor condensation of rain from water vapor evaporation of water a candle flame forming a cation from an atom in the gas phase mixing sodium sulfite and bleach baking bread rusting iron cooking an egg burning sugar producing sugar by photosynthesis forming ion pairs separating ion pairs Combining atoms to make a molecule in the gas phase splitting a gas molecule apart mixing water and strong acids mixing water and ammonium nitrate mixing water with an anhydrous salt making an anhydrous salt from a hydrate crystallizing liquid salts (as in sodium acetate in chemical handwarmers) melting solid salts nuclear fission reaction of barium hydroxide octahydrate crystals with dry ammonium chloride mixing water with calcium chloride reaction of thionyl chloride (SOCl2) with cobalt(II) sulfate heptahydrate