Migration
advertisement

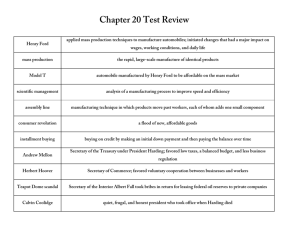
Objectives: Content: Analyze 5 paintings from Jacob Lawrence’s Great Migration Series. Language: List key instruments in jazz music. The Great Migration Migration • Migration is the process of moving from one location to another. • Immigration is a kind of migration! Great Migration Facts • Who: 500,000 African Americans • What: Migrated from the South to the North • Where: Large cities such as New York, Chicago, Detroit, Cleveland, and St. Louis Great Migration Facts • When: The Great Migration happened between 1910 and 1920, especially during World War I. • Chicago’s (Illinois) African American population grew from 44,000 in 1910 to 110,000 in 1920. • Cleveland’s (Ohio) African American population grew from 8,000 to 34,000. Reasons for Leaving the South 1. Jobs in the South were scarce (very few) and low paying. ▫ African Americans could earn a lot more money in the North 2. African Americans faced discrimination and violence in the South. The South was still dealing with the effects of the Civil War, including Jim Crow laws 3. African Americans moved to northern cities and the Midwest in search of better job opportunities. ▫ WWI almost completely stopped immigration from Europe ▫ The northern industries needed African Americans to work ▫ World War I also increased the demand for goods. This increase in demand meant an even greater need for jobs! Problems • African Americans also faced discrimination and violence in the North and Midwest ▫ White workers hated the labor competition ▫ White homeowners were upset that overcrowded black neighborhoods overflowed into white neighborhoods Harlem Renaissance Harlem Renaissance • African American artists, writers, and musicians based in Harlem (NYC) revealed the freshness and variety of African American culture. • Popularity of these artists spread beyond Harlem to the rest of society. Jacob Lawrence • Jacob Lawrence was a painter who chronicled the experience of the Great Migration north through art • Migration Series “Migration Series” Langston Hughes • Langston Hughes was a poet who combined the experiences of African and American cultural roots • “Ballad of the Landlord” “Merry-Go-Round” Where is the Jim Crow section On this merry-go-round, Mister, cause I want to ride? Down South where I come from White and colored Can’t sit side by side. Down South on the train There’s a Jim Crow car. On the bus we’re put in the backBut there ain’t no back To a merry-go-round! Where’s the horse For a kid that’s black? Duke Ellington • Jazz Musician • Pianist and Composer • “It Don’t Mean a Thing” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qDQpZT3GhDg • What do you see, hear? What does the song make you feel? Sad, Happy, etc? Louis Armstrong • Jazz Musician • Singer and Trumpet Player • “What a Wonderful World” http://youtu.be/2nGKqH26xlg • What do you see, hear? How does the music make you feel? Happy, sad, etc? Bessie Smith • Blues singer • “Nobody Knows You When You’re Down and Out” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6MzU8xM99Uo • What do you see, hear? How does the music make you feel? Happy, sad, etc? Warm Up • On a separate piece of paper, choose either a school day or a weekend day and list what you do from wake up to sleep. ▫ My morning: Alarm Bathroom Get dressed, fix hair Daughter announces her clock is green Get children dressed for daycare/school Eat breakfast Pack children’s lunch/daycare bag Shoes Brush teeth and brush children’s hair Coats and get into the car (with light on in the garage) Drive to daycare/school Call Dad/my husband Objectives: Content: Determine which daily activities would not be possible without the advances in the 1920s. Language: Use words or sketches to describe the results of Prohibition. Changing American Life 1920’s Changes • The following developments changed American life and the standard of living 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Transportation Factory and labor productivity Electrification Communication Prohibition Daily Activities • As you learn about each advancement, think about your list from the beginning of class. • Cross off any activity that would change if those item(s) had not been developed. Airplane • The Wright Brothers invented the first airplane in 1903. • The first flight happened in North Carolina https://youtu.be/RriKI7u72Xs • By 1920s, first commercial airports appear Automobile • While others used it before, Henry Ford has been credited with perfecting the assembly line. • Henry Ford used the assembly line to produce his Model T cars faster and cheaper. • Led to the rise of mechanization machines do the job instead of a person Results of Improved Transportation • Greater mobility • Creation of jobs • Growth of transportationrelated industries (road construction, oil, steel, automobile) • Movement to suburban areas Electricity • Thomas Edison perfected the light bulb • Electricity changed American Life ▫ Washing machines, electric stoves, and water pumps saved a lot of time and labor ▫ Electric lighting made it possible to do work into the night • Improved communication powered by electricity Innovations • Telephones were more readily available ▫ Increased speed of communication • Development of motion pictures (movies) ▫ First silent and then with sound http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DfGs2Y5WJ14 &feature=related • Guglielmo Marconi has been credited with inventing the radio ▫ Focused on wireless telegraphy • Radio provided a new kind of entertainment Broadcasting • David Sarnoff was a pioneer in the broadcast industry first with bringing radio to the masses and then later television • Founded the National Broadcasting Company (NBC) Daily Activities Wrap Up • How many things would you be able to do from your list without the assistance of technology? • Are you surprised? Why or why not? Prohibition Prohibition Review • The temperance movement worked to ban alcohol • Prohibition was imposed by a constitutional amendment (18th Amendment) that made it illegal to manufacture, transport, and sell alcoholic beverages. • Prohibition can be used to describe the law that banned alcohol OR the period in US History when alcohol was illegal The Results of Prohibition • Speakeasies were created as places for people to drink alcoholic beverages. • Bootleggers smuggled illegal alcohol and promoted organized crime • Organized crime – groups of people conducting illegal activities to make a profit. ▫ Al Capone was the most famous “American Gangster” https://youtu.be/VzfWQ7TRF8w • Prohibition was repealed in 1933 with the passage of the 21st amendment. Warm-Up: 1. Who are your favorite singers, bands, or rappers? 2. Why do you like them? Objectives: • Content: Compare and contrast Jazz and Popular styles. • Language: List the major contributions of Copland, Gershwin, O’Keefe, Fitzgerald, and Steinbeck. Culture of the 1920s and 1930s Aaron Copland • Composer and conductor who wrote uniquely American music • Populist style • “Fanfare for the Common Man” http://www.youtube.com/wa tch?v=cr6CnG5dmvM George Gershwin • Composer and pianist who wrote uniquely American Music • Classical and popular styles • “I Got Rhythm” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vI pNepgmCQA American Idol: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RlEpSQeRmOQ Georgia O’Keeffe • An artist known for urban scenes and, later, paintings of the Southwest Urban Scenes Southwest Themes “Black Mesa Landscape” F. Scott Fitzgerald A novelist who wrote about the Jazz age of the 1920s The Century: http://viewpure.com/RN7ftyZigYs • Wrote a novel called The Great Gatsby http://youtu.be/os2gKtW9aZk John Steinbeck • A novelist who portrayed the strength of poor migrant workers during the 1930s http://youtu.be/MYOmjQO_UMw (Dust Bowl) • Wrote a novel called The Grapes of Wrath