2. monetary policy
advertisement

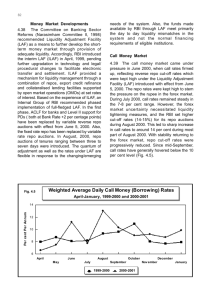
MONETARY POLICY - 2013-14 SECOND QUARTER REVIEW Dr. Raghuram Rajan, the Reserve Bank Governor has announced the second quarter review which can be summed up as pragmatic, modest and in the right direction. The policy attempts a judicious balance across multiple objectives by taking several steps to tackle inflation and ensuring economic growth. The reduction in Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate by 25 basis points coupled with enlarged liquidity provided through term repo window will ensure a significant decline in cost of borrowings for the banks. The policy stance and measures in this review are intended to curb mounting inflationary pressures and manage inflation expectations in a situation of weak growth. The measures announced will help strengthen the environment for growth by fostering macroeconomic and financial stability. The Reserve Bank will closely monitor inflation risk while being mindful of the evolving growth dynamics. MACRO TARGETS: Financial Year 2014, GDP growth estimate revised downward to 5 per cent. Growth likely to pick up in second half on good show in exports and agriculture Wholesale inflation expected to be higher than current levels; Retail inflation to hover around 9 per cent. Normalcy will restored in the forex market only when OMCs fully return to the market for their demand. MONETARY MEASURES: On the basis of an assessment of the current and evolving macroeconomic situation, following monetary measures have been announced: REPO RATE: The policy Repo rate under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) has been increased by 25 basis points from 7.50 per cent to 7.75 per cent with immediate effect. REVERSE REPO RATE: The Reverse repo rate determined with a spread of 100 bps points below the repo rate, stands at 6.75%. MARGINAL STANDING FACILITY (MSF): The MSF rate reduced by 25 basis points from 9.0 per cent to 8.75 per cent with immediate effect. BANK RATE: The Bank Rate stands reduced to 8.75 per cent with immediate effect. With these changes, the MSF rate and the Bank Rate are recalibrated to 100 basis points above the repo rate. CASH RESERVE RATIO: The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) of scheduled banks has been retained at 4% of their net demand & time liabilities (NDTL). TERM REPOS: The liquidity provided through term repos of 7-day and 14-day tenor has been increased from 0.25% of net demand and time liabilities (NDTL) of the banking system to 0.5% with immediate effect. MONETARY POLICY STANCE: a) As steps to contain the CAD started taking effect in an improving external environment, volatility in the foreign exchange market ebbed and it became possible to unwind the exceptional liquidity tightening measures. Keeping in view the need to infuse liquidity into the system to normalise liquidity conditions, term repos will now be conducted for a total notified amount equivalent to 0.5% of NDTL of the banking system. In addition, the MSF rate will be reduced by 25 basis points. b) With the more recent upturn of inflation, and with inflation expectations remaining elevated anticipating the pass-through of exchange rate depreciation and ongoing adjustment in administered fuel prices, it is important to break the spiral of rising price pressures in order to curb the erosion of financial saving and strengthen the foundations of growth. It is in this context that the LAF repo rate has been increased by 25 basis points. c) With the reduction of the MSF rate and the increase in the repo rate in this review, the process of re-aligning the interest rate corridor to normal monetary policy operations is now complete. ASSESSMENT: The policy decisions are based on a detailed assessment of the global and domestic macroeconomic situation. The outlook for global growth has improved modestly and the prospect of delay in the taper of the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases has brought calm to financial markets. Domestically, while industrial activity has weakened, strengthening export growth, signs of revival in some services along with the expected pick-up in agriculture could increase the real GDP growth from 4.4 per cent in Q1 to a central estimate of 5% for the year as a whole. The revival of large stalled projects and the pipeline cleared by the Cabinet Committee on Investment may stimulate investment and overall activity towards the close of the year. On inflation, both wholesale and consumer price inflation are likely to remain elevated in the months ahead, warranting an appropriate policy response. The RBI have calibrated liquidity management to the system’s requirements. The measures provide liquidity through overnight LAF repos, through export credit refinance and through 7day and 14-day term repos. This is coupled with greater flexibility in managing reserve requirements. On the external sector, a perceptible narrowing of the trade deficit coupled with policy interventions have brought some calm to the foreign exchange market, but normalcy will be restored only when the demand for dollars from public sector oil marketing companies is fully returned to the market. DEVELOPMENTAL AND REGULATORY POLICIES: The RBIs developmental measures over the next few quarters are based on five pillars. These are: Clarifying and strengthening the monetary policy framework. Strengthening banking structure through new entry, branch expansion, encouraging new varieties of banks, and moving foreign banks into better regulated organizational forms. Broadening and deepening financial markets and increasing their liquidity and resilience so that they can help absorb risks entailed in financing India’s growth. Expanding access to finance to small and medium enterprises, the unorganized sector, the poor, remote and underserved areas of country through measures to foster financial inclusion. Improving the system’s ability to deal with corporate distress and financial institution distress by strengthening real and financial restructuring as well as debt recovery. COMMENTS: The policy announcements has been on expected lines. By reducing the MSF by .25%, the cost of funds is likely to dip immediately. One measure that brings unexpected relief to the bank is the ability to borrow more from the new term repo window. Banks have seen a sharp spike in their borrowing costs in recent months, with MSF rates rising and the repo borrowings capped at Rs. 40,000 crore. Banks borrowed as much as 60% of their requirements from the more expensive MSF window. But in the beginning of Oct. RBI opened a new window for banks to source funds the 7- and 14 day term repos, this has been a marginally cheaper option with cut-off rates at 8.8%. By borrowing close to Rs. 20,000 crore from this window. Banks were able to minimize recourse of MSF and reduce their average costs by 10-15 basis points. By doubling the sums that banks can source from term repos to Rs. 40,000 crore, the RBI has handed banks a savings of another 10-15 basis points on costs. Overall, cost of funds has come down by 80 bps from August. This will indeed lead to incremental savings for banks. The policy significance lies in the announcement of the five-points development plan that will inform future policies of the RBI covering critical areas of monetary policy framework, banking structure, financial markets, financial inclusion and financial distress. GLOBAL OUTLOOK: The outlook for global growth has improved modestly, with fiscal concerns abating in the US and lead indicators of activity firming up in the Euro area and the UK. In emerging and developing economies, the prospect of delay in the taper of the Federal Reserve’s bond purchases has brought calm to financial markets, and capital flows have resumed. Nevertheless, headwinds to growth from domestic constraints continue to pose downside risks, and vulnerabilities to sudden shifts in the external environment remain. OUTLOOK FOR INDIA: INDUSTRIAL GROWTH: In India, industrial activity has weakened, with a contraction in consumer durables and tepid growth in capital goods reflecting the ongoing downturn in both consumption and investment demand. Strengthening export growth and signs of revival in some services, along with the expected pick-up in agriculture, could support an increase in growth in the second half of 2013-14 relative to the first half, raising real GDP growth from 4.4 per cent in Q1 to a central estimate of 5.0 per cent for the year as a whole. The revival of large stalled projects and the pipeline cleared by the Cabinet Committee on Investment may stimulate investment and overall activity towards the close of the year. With many large entities holding back on payments, liquidity pressures are building up on small and medium enterprises leading to financial distress. Remedies partly lie in the speed-up of government and public sector payments, and on measures to channel credit to small and medium enterprises. EXTERNAL SECTORS: As regards the external sector, the improvement in export performance over the last two months, coupled with the contraction in non-oil import demand, has enabled a perceptible narrowing of the trade deficit with favourable implications for the current account deficit going forward. Policy interventions have bridged the external financing gap. These factors have brought some calm to the foreign exchange market. However, normalcy will be restored to the exchange market only when the demand for dollars from public sector oil marketing companies is fully returned to the market. INFLATION: Inflation measured by the wholesale price index (WPI) rose in Sept for the fourth month in succession. The pass-through of rupee depreciation into prices of manufactured products is acting, along with elevated food and fuel inflation, to offset possible dis-inflationary effects of low growth. While food price pressures may ease with the arrival of the kharif harvest and the usual seasonal moderation, overall WPI inflation is expected to remain higher than current levels through most of the remaining part of the year, warranting an appropriate policy response. Retail inflation measured by the consumer price index (CPI) has also risen sharply across food and non-food constituents, including services, keeping inflation expectations high. Notwithstanding the expected edging down of food inflation, retail inflation is likely to remain around or even above 9% in the months ahead, absent policy action. LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT: Liquidity management has been calibrated to the system’s requirements arising from the sharp pick-up in credit relative to deposit growth and festival-related demand for currency. Liquidity up to 0.5 per cent of bank-wise NDTL is available through overnight LAF repos. Furthermore, export credit refinances of up to 50% of eligible export credit outstanding amounts to approximately 0.5% of system-level NDTL. To provide market participants with additional access to primary liquidity, as well as greater flexibility in managing reserve requirements, term repos of 7-day and 14-day tenor have been introduced to provide liquidity equivalent to 0.25 per cent of NDTL. As a result of the measures taken by the RBI to ease liquidity, the average drawal on the MSF has declined significantly from about Rs.1.4 trillion in mid-Sept to Rs.0.4 trillion by midOctober, and money market rates have fallen by 125 basis points. Going forward, however, the more durable strategy for mitigating mismatches between the supply of, and demand for, funds is for banks to step up efforts to mobilise deposits. DEVELOPMENTAL AND REGULATORY POLICIES: The Reserve Bank’s developmental measures over the next few quarters will be built on five pillars. These are: a) Clarifying and strengthening the monetary policy framework. b) Strengthening banking structure through new entry, branch expansion, encouraging new varieties of banks, and moving foreign banks into better regulated organisational forms. c) Broadening and deepening financial markets and increasing their liquidity and resilience so that they can help absorb the risks entailed in financing India’s growth. d) Expanding access to finance to small and medium enterprises, the unorganised sector, the poor, and remote and underserved areas of the country through measures to foster financial inclusion. e) Improving the system’s ability to deal with corporate distress and financial institution distress by strengthening real and financial restructuring as well as debt recovery. BASEL III - COUNTERCYCLICAL CAPITAL BUFFER: As part of the Basel III capital framework, an internal Working Group (Chairman: Shri B. Mahapatra) was constituted to operationalise the countercyclical capital buffer framework in India. RBI proposes to place the draft report of the group on the Reserve Bank’s website by end-November 2013 for inviting comments/suggestions from various stakeholders. DOMESTIC SYSTEMICALLY IMPORTANT BANKS: The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision provided a framework for dealing with domestic systemically important banks (D-SIBs) in Oct 2012. The D-SIBs framework is principle based and provides broad guidance to national authorities on assessment of the systemic importance of banks and additional capital requirements of D-SIBs. RBI proposes place a draft of the framework for DSIBs on the RBIs website by end-Nov. 2013. STRESS TESTING: The Reserve Bank had issued guidelines on stress testing which required banks to have a sound stress testing policy which will determine liquidity risk, interest rate risk, credit risk and foreign exchange risk under stressed scenarios. Drawing from the BCBS principles on the subject and subsequent global developments, RBI proposes to issue updated guidelines on stress testing by endNov 2013. UNHEDGED FOREIGN CURRENCY EXPOSURES: Unhedged foreign currency exposures of corporates are a cause for concern as they pose a risk to individual corporates as also to the entire financial system. Based on feedback received from industry participants, RBI proposes to issue final guidelines on unhedged foreign currency exposures by end-December 2013. INTEREST ON RUPEE SAVINGS/TERM DEPOSITS: As per extant instructions, banks are required to pay interest on savings deposits and term deposits at quarterly or longer intervals. As all commercial banks are now on core banking platforms, RBI has decided to give banks option to pay interest on savings deposits and term deposits at intervals shorter than quarterly intervals. LICENSING OF NEW BANKS: In terms of the guidelines for licensing of new banks in the private sector, applications will be screened by the RBI to ensure prima facie eligibility, and thereafter, the applications will be referred to a High Level Advisory Committee. The HLAC will devise its own procedures for screening the applications and submit its recommendations to the Reserve Bank for consideration. The decision to issue an in principle approval for setting up of a bank will be taken by the RBI whose decision in this regard will be final. The HLAC has been set up under the Chairmanship of Dr. Bimal Jalan, former Governor of the RBI. FOREIGN BANKS IN INDIA: The RBI released a Discussion Paper on the presence of foreign banks in India on Jan 21, 2011 factoring in the lessons from the crisis which favoured a subsidiary mode of presence from a financial stability perspective. Taking into account the feedback received from stakeholders, a scheme of subsidiarisation of foreign banks in India, guided by the two cardinal principles of reciprocity and single mode of presence, is being finalised. The Wholly Owned Subsidiaries (WOSs) would be given near-national treatment, including in the opening of branches. While it will not be mandatory for existing foreign banks (i.e., banks set up before August 2010) to convert into WOSs, they will be incentivised to convert into WOSs by the attractiveness of the nearnational treatment. The initial minimum paid-up voting equity capital or net worth for a WOS shall be Rs.5 billion. RBI proposes to issue the Scheme by mid-Nov 2013. RETAIL INFLATION INDEXED SECURITIES: The Union Budget, 2013-14 proposed to introduce instruments that will protect savings from inflation and provide an alternative to gold as an investment avenue for individuals. Inflation indexed securities for retail investors of 10-year tenor would be linked to the new (combined) consumer price index. Eligible investors would consist of individuals, hindu undivided families (HUFs), trusts and charitable institutions. The rate of interest on these securities would comprise of a fixed rate plus inflation. Interest would be compounded half-yearly and paid cumulatively at redemption. These securities will be distributed through banks to reach out to the masses. Accordingly, RBI proposes to launch Inflation Indexed National Saving Securities (IINSSs) for retail investors in Nov/Dec 2013 in consultation with the Govt. INTEREST RATE FUTURES CONTRACTS: In order to develop the money and government securities markets, RBI has decided to introduce cash settled 10-year Interest Rate Futures (IRF) contracts. Product design and operational modalities are being discussed with all stakeholders, including market bodies and stock exchanges, and after taking into account their feedback, the RBI, in consultation with the SEBI, would issue guidelines by mid-Nov 2013 and the product is expected to be launched by the exchanges by end-Dec 2013. CREDIT ENHANCEMENTS IN CORPORATE BONDS: The corporate bond market in India currently lacks sufficient depth and liquidity. As a result, corporates have significant dependence on bank financing. Therefore, RBI has proposed to allow banks to offer partial credit enhancements to corporate bonds by way of providing credit facilities and liquidity facilities to the corporates, and not by way of guarantee. MARGINAL STANDING FACILITY: With a view to facilitating settlement of electronic funds transfers as well as to reduce unnecessary volatility in reserve maintenance, RBI has decided to revise the timing of MSF operations. With effect from Nov 5, 2013 the settlement will be conducted between 7.00 pm and 7.30 pm instead of between 4.45 pm and 5.15 pm. REPO FACILITY FOR MUTUAL FUNDS: On July 17, 2013 the RBI had opened a special repo window for mutual funds with a view to enabling banks to meet the liquidity requirements of mutual funds. With the normalisation of exceptional measures and taking into consideration the improvement in liquidity conditions since then, RBI has decided to close this window with immediate effect. SERVICES / FACILITIES FOR EXPORTERS: Some recommendations of the Technical Committee on Services / Facilities to Exporters (Chairman: Shri G. Padmanabhan) such as an increase in the limit of e-commerce transactions and extending the time period for submission of documents under project exports, simplification of reporting requirement of forward contracts booked over-the-counter (OTC) and extending the limit for exporters to cancel and rebook the forward contracts have been accepted and necessary guidelines have been issued. Other recommendations are being analysed in coordination with government agencies/other stakeholders for implementation. GENERAL CREDIT CARD SCHEME: The coverage of the General Credit Card (GCC) Scheme is being revised to enhance credit linkage of individuals to all non-farm entrepreneurial activities within the overall priority sector. It is expected that the revised scheme will give a fillip to flow of credit to small businesses and low income households. BANKING SERVICES IN UNBANKED VILLAGES: State Level Bankers’ Committees are mandated to prepare a roadmap covering all unbanked villages of population less than 2000 and to notionally allot these villages to banks for providing banking services. Accordingly, about 4,90,000 unbanked villages have been identified and allotted to various banks to be covered by March 2016. SHORT-TERM CO-OPERATIVE CREDIT STRUCTURE: In Jan 2013, the RBI constituted an Expert Committee (Chairman: Dr. Prakash Bakshi) on the short-term co-operative credit structure. The recommendations taken up for implementation include, improvement of governance and management of rural cooperatives, moving to Core Banking Solutions (CBSs) and setting up of a Working Group to examine human resources requirement of rural co-operative banks following the transition of state co-operative banks and district central co-operative banks to CBS. CHARGES LEVIED FOR SENDING SMS ALERTS: With a view to ensuring reasonableness and equity in the charges levied by banks for sending SMS alerts to customers, banks are advised to leverage the technology available with them and the telecom service providers to ensure that such charges are levied on all customers on actual usage basis. GIRO BASED PAYMENT SYSTEM: Following the report of the Committee for Implementation of GIRO Based Payment System highlighting the need for an electronic bill payment system based on a GIRO model for payment of dues of essential services, insurance premia, utility payments, taxes, university fees, examination fees and the like, a GIRO Advisory Group (Chairman: Prof. Umesh Bellur) has been constituted with representation from banks and other stakeholders. The Group is expected to submit its report by end-December 2013. ACCESS TO MOBILE BANKING: A Technical Committee (Chairman: Shri B. Sambamurthy) has been constituted to examine various options / alternatives, including the feasibility of encrypted SMSbased funds transfer using an application which can run on any type of handset, for expansion of mobile banking in the country. The Committee is expected to submit its report by end-December 2013. SECURITY AND RISK MITIGATION MEASURES: The Reserve Bank has advised banks to put in place by end-June 2013 security features in order to secure card transactions and the electronic banking infrastructure. A review of banks’ preparedness in this regard indicates that technical glitches are hampering the transition to desired environment. Accordingly, a one-time extension has been granted to stakeholders. PREPAID PAYMENT INSTRUMENTS: In order to further popularize prepaid payment instruments (PPIs) and facilitate remittance of funds by people not having bank accounts, a pilot is being planned with select nonbank PPI issuers to study the technological and operational feasibility of allowing cash pay-out (remittance) from PPIs issued by non-bank entities using Aadhaar based biometric authentication. The broad technical, operational and functional parameters of the pilot are being finalised in consultation with participants and the pilot is expected to go live before end-March 2014. NBFCS - RESTRUCTURING GUIDELINES: The Reserve Bank’s Working Group (Chairman: Shri B. Mahapatra) reviewed prudential guidelines on restructuring of advances by banks and financial institutions and relevant guidelines to banks have been issued. As NBFCs are also part of the financial institutions that lend to the sectors where restructuring benefits are now available, either as part of a consortium or otherwise, it has been decided to review the extant instructions on restructuring for NBFCs and issue guidelines in the matter by end-Nov 2013. FSLRC: RBI has proposed to implement the recommendations of the FSLRC pertaining to consumer protection and capacity building. All instructions relating to consumer services/consumer protection would be consolidated and will be placed on the RBI’s website as a single group of instructions by end-March 2014 and they will be examined for gaps, if any further, a Committee will be set up by the RBI to examine capacity building, including basic and job specific knowledge requirements and examine whether a system of formal certification is warranted for certain job descriptions within the Reserve Bank and in the financial entities and market segments regulated by it. The Reserve Bank will examine its own public facing services and institute time-bound response guidelines where feasible and not already in place. Such guidelines will be placed on the Reserve Bank’s website by January 2014. CURRENCY MANAGEMENT: Banks were advised to explore the possibility of meeting the growing demand for banknotes and coins in the country through Business Correspondents (BCs) and consider engaging the services of Cash in Transit (CIT) entities to address last mile connectivity issues. Instructions have been issued permitting banks to include distribution of banknotes and coins in the scope of activities which may be undertaken by BCs/CITs. Banks have also enhanced their capacity to take over the retail function of distribution of notes and coins and adjudication of mutilated notes. They have so far identified 805 bank branches for the purpose. Correspondingly, the distribution level across the Reserve Bank’s counters has decreased by 61% and 64% for notes and coins, respectively, and the adjudication of notes by 51%. COUNTERFEIT BANKNOTES: In view of t he recommendation of the Department-related Parliament Standing Committee (DPSC) to introduce a scheme of incentives in order to encourage banks to report counterfeit notes detected by them, instructions were issued to banks on the procedure to be followed and compensation to banks for detection of counterfeit notes and penalty for non-detection / reporting thereof. SNIPPETS Bhattacharya has taken over charge as the first woman chairperson of State Bank of India. announced as the next chief of the Indian Air Force after Air Chief Marshal NAK Browne retires on Dec. 31, 2013. Commissioned into the IAF in Dec. 1974 in the ‘Fighter Stream’, Air Marshal Raha is currently posted as the IAF vice-chief. has taken the Charge as the Chairman and Managing Director of Corporation Bank. -SX CHAIRMAN: Former Union Home Secretary G.K. Pillai has been appointed as Chairman of MCXSX. Further, former acting Chairman of the LIC, Thomas Mathew T., has been appointed as the Vice-Chairman. election to the UN Board of Auditors with its nominee Shashi Kant Sharma, the Comptroller and Auditor General, garnering the largest number of votes. Sharma won 124 votes out of the total 186 cast in the General Assembly's Fifth Committee on Administrative and Budgetary questions. The closest contender was from Philippines, which got 62 votes. AN OF RAILWAY BOARD: Arunendra Kumar has been appointed as Chairman of Railway Board. Zealand author won the Man Booker Prize 2013 for her second novel entitled ‘The Luminaries’, published by Granta. R TERESA AWARD 2013: Former Miss Universe Sushmita Sen conferred with the Mother Teresa Memorial International Award by NGO The Harmony Foundation for her efforts towards achieving social justice in Mumbai. agricultural scientist M.S. Swaminathan selected for the Indira Gandhi Award for National Integration for the year 2012. India Award for the year 2013. -50 WOMEN BUSINESS LEADERS: Four Indians led by ICICI Bank CEO Chanda Kochhar have made to Fortune magazine's global list of top-50 women business leaders. Kochhar has been ranked fourth, followed by National Stock Exchange chief Chitra Ramkrishna at 17th, Axis Bank's Shikha Sharma at 32nd and HSBC's Naina Lal Kidwai at 42nd place among the Indians on the international list of most powerful women in business. The list is topped by Brazilian energy giant Petrobras' CEO, Maria Das Gracas Foster. -year old Srishti Rana has made the country proud by winning the coveted Miss Asia Pacific 2013 title outclassing 49 other contestants in Korea. Srishti was being crowned by the reigning Miss Asia Pacific World 2012 Himangini Singh Yadu from India. jana, a pension and life insurance fund scheme for blue-collar Indian workers in UAE launched. Haryana to introduce Union National Vocational Qualitative Framework (NVQF) Scheme. The scheme has been implemented by the All India Technical Education Council and the National Skill Development Council. launched the e-KYC initiative to facilitate paperless banking to Aadhaar card holders at Mumbai. With this step, Axis Bank became the first bank to allow customers to open an account with just their Aadhaar number. to start an aviation venture with Tata Sons. The joint venture called TATA SIA will be having initial foreign investment of 49 million US dollars. released a commemorative postage stamp on the Golden Jubilee of Bhakra Dam. Bangalore topped the list of best business destinations in India as per the study done by Global Initiative for Restructuring Environment and Management. Kohli became fastest century scorer (in 52 balls) of India on 16 October 2013 in One day International (ODI) held at Jaipur. He was the seventh fastest century scorer in ODI in the world. the Eradication of Poverty was observed on 17 October 2013 to promote people’s awareness of the need to eradicate poverty and destitution worldwide, particularly in developing countries. ranked at 63rd Position global hunger index report 2013. -ETIHAD DEAL APPROVED BY SEBI: Jet-Etihad deal has been approved by SEBI. Jet Airways had proposed to sale 24 percent stake to Abu Dhabi-based Etihad. The Jet-Etihad deal was announced in April 2013 and because of objections from regulators the deal was stuck half-way. firm Reliance Jio Infocomm has bagged a unified licence, which allows a licensee to provide a host of telephony services by acquiring spectrum from the market. Reliance Jio migrated to the new regime from having an internet service licence by paying Rs 1,673 crore mainly to provide voice services. RBI’s Governor Raghuram Rajan, India would not run to IMF (International Monetary Fund) for money for next five years and maybe even beyond. According to Rajan, India is facing some issues in the financial markets but is away from any crisis-like situation. India has a debt of 66% of GDP, 90% of which is denominated in rupees. External debt was 22% of GDP and reserves at 15% of GDP. RBI will shortly issue Rs. 10 denomination Bank notes incorporating "Rs." symbol on the obverse and reverse, without inset letter in both the numbering panels, in the Mahatma Gandhi Series-2005 bearing the signature of Dr. Raghuram G. Rajan, Gov. RBI, and the year of printing '2013' printed on the reverse of the Banknote. Mahindra Bank (KMB) has announced the launch of Kotak Multi Currency World Travel Card. The prepaid card is designed to offer global convenience with higher security. The card has multicurrency- wallet functionality with the option to load/reload multiple currencies on a single card from the 8 predefined currencies offered by the bank. Customers can lock exchange rates before travel thereby to escape exchange rate fluctuation. has been ordered to pay about $2.46 billion in a class action lawsuit - the biggest ever securities fraud class action trial. The company fraudulently misled investors about its predatory lending practices, the quality of its loans and its financial accounting from March 23, 2001, through October 11, 2002. POLICY GUIDELINES LAF – REPO AND REVERSE REPO RATES As announced in the Second Quarter Review of Monetary Policy 2013-14, RBI has decided to increase the Repo rate under the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) by 25 basis points from 7.50% to 7.75 % with immediate effect. Consequent to the change in the Repo rate, the Reverse Repo rate under the LAF will stand automatically adjusted to 6.75 per cent with immediate effect. MARGINAL STANDING FACILITY RATES As announced in the Second Quarter Review of Monetary Policy 2013-14, RBI has decided to reduce the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate by 25 basis points from 9.00 percent to 8.75 per cent with immediate effect. Consequent to this change, Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate is recalibrated to 100 basis points above the policy repo rate under the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF). MSF -REVISION IN TIMINGS The Reserve Bank of India has decided to revise the timings of Marginal Standing Facility (MSF). The MSF will now be available between 7.00 pm and 7.30 pm instead of the existing timings of 4.45 pm to 5.15 pm. The change in timings will take effect from November 5, 2013. BANK RATE Since the MSF has been reduced, the Bank Rate stands adjusted by 25 basis points from 9% to 8.75% with effect from October 29, 2013. Further, all penal interest rates on shortfall in reserve requirements, which are specifically linked to the Bank Rate, also stand revised. STANDING LIQUIDITY FACILITIES In the Second Quarter Review of Monetary Policy, the Repo rate under the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) has been increased by 25 basis points from 7.50 per cent to 7.75 per cent. Accordingly, the Standing Liquidity Facilities provided to banks under Export Credit Refinance (ECR) and to Primary Dealers (PDs) (collateralised liquidity support) from the RBI would be available at the revised repo rate, i.e., at 7.75 per cent with effect from October 29, 2013. TERM REPO UNDER LAF As announced in the Second Quarter Review of Monetary Policy 2013-14, RBI has decided to increase the quantum of liquidity to be provided through term repos of 7-day and 14-day tenor from the existing 0.25 per cent to 0.50 per cent of net demand and time liabilities (NDTL) of the banking system with immediate effect. FDI – DEFINITION OF ‘GROUP COMPANY’ RBI has reviewed the extant FDI policy and has decided to incorporate the definition for ‘group company’ as under; Group Company’ means two or more enterprises which, directly or indirectly, are in position to: a) Exercise twenty-six per cent, or more of voting rights in other enterprise; or b) Appoint more than fifty per cent, of members of board of directors in the other enterprise. SMERA RATINGS LIMITED (SMERA) As per the extant guidelines, M/s. SME Rating Agency of India Limited has been accredited for the purpose of risk weighting the banks' claims for capital adequacy purposes along with other credit rating agencies (CRAs). The agency has now changed its name to SMERA Ratings Limited. SEBI has issued the necessary Certificate of Registration. However, there is no change in the rating symbols of the CRA subsequent to change in name. SETTLEMENT OF CLAIMS IN RESPECT OF MISSING PERSONS IN UTTARAKHAND DISASTER In the aftermath of Uttarakhand Natural Disaster during June 2013, the Govt. has devised a procedure for Registration of Death of missing persons and issue of ‘Death Certificate’ in Natural Calamities affected areas in Uttarakhand. Further, banks are advised to settle the claims in respect of missing persons, covered by the circular, without insisting on production of any documentation other than: a) The ‘Death Certificate’ issued by the Designated Officer under MHA Circular b) Letter of indemnity. KNOWLEDGE PLUS BIOMETRICS The term "Biometrics" is derived from the Greek words bio (life) and metric ( to measure). A biometric system is essentially a pattern recognition system which makes a personal identification by determining the authenticity of a specific physiological or behavioral characteristic of the user. Biometric characteristics can be divided in two main classes: fingerprint, face recognition, DNA, hand and palm geometry, iris recognition. rhythm, gait, and voice. Some researchers have coined the term Behavio metrics for this class of biometrics. Voice recognition is mainly based on the study of the way a person speaks, and therefore is commonly classified as behavioral. A Biometric system can operate in the following two modes: – A one to one comparison of a captured biometric data with a stored template to verify individual‘s identity. It can be in conjunction with a smart card, username or ID number. – A one to many comparisons of the captured biometric data against a biometric database in attempt to identify an unknown individual. TYPES OF BIOMETRICS BERTILLONAGE: It is the first type of biometrics. It was created by an anthropologist named Alphonse Bertillon in 1890. He based his system on the claim that measurement of adult bones does not change after the age of 20. The method consisted of identifying people by taking various body measurements like a person’s height, arm length, length and breadth of the head, the length of different fingers, etc. using calipers. However, the methodology was unreliable as non-unique measurements allowed multiple people to have same results. FINGERPRINT RECOGNITION: Image of a person's fingertips is taken and characteristics like whorls and arches, with the patterns of ridges, furrows, and minutiae recorded. FACE RECOGNITION: This technique records face images through a digital video camera and analyses facial characteristics like the distance between eyes, nose, mouth, and jaw edges. These dimensions broken into facial planes and retained in a database are used for comparison. FACIAL THERMOGRAMS: This uses infrared heat scans to identify facial characteristics. This non-intrusive technique is light-independent and not vulnerable to disguises. Even plastic surgery, cannot hinder the technique. To prevent a fake face or mold from faking out the system, many systems now require the user to smile, blink, or move in a way that is human before verifying. This technique is gaining support as a potential tool for averting terrorism, law enforcement areas and also in networks and automated bank tellers. VOICE RECOGNITION: This combines physiological and behavioral factors to produce speech patterns that can be captured by speech processing technology. Inherent properties of the speaker like fundamental frequency, nasal tone, cadence and inflection are used for speech authentication. IRIS RECOGNITION: This analyzes features like rings, furrows, and freckles existing in the coloured tissue surrounding the pupil. The scans use a regular video camera and works through glasses and contact lenses. HAND GEOMETRY: This involves the measurement and analysis of the human hand. Features like length and width of the fingers, aspect ratio of the palm or fingers, width of the palm, thickness of the palm etc., are computed. HAND VASCULAR PATTERN IDENTIFICATION: This uses a non-harmful near infrared light to produce an image of one's vein pattern in their face, wrist, or hand, as veins are relatively stable through one's life. It is a non-invasive, computerized comparison of shape and size of subcutaneous blood vessel structures in back of a hand. The vein "tree" pattern is sufficiently idiosyncratic to function as a personal code that is extremely difficult to duplicate or discover. RETINA RECOGNITION: This technology uses infrared scanning and compares images of the blood vessels in the back of the eye, the choroidal vasculature. The eye’s inherent isolation and protection from the external environment as an internal organ of the body is a benefit. Retina scan is used in high-end security applications like military installations and power plants. SIGNATURE RECOGNITION: This is an instance of writer recognition, which has been accepted as irrefutable evidence in courts of law. The way a person signs his name is known to be a characteristic of that individual. Approach to signature verification is based on features like number of interior contours and number of vertical slope components. Signatures are behavioral biometric that can change with time, influenced by physical and emotional conditions of the signatories