File
advertisement

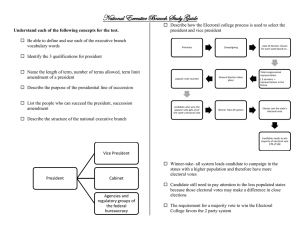
Aim: How doe the electoral college system operate? Electoral College System In US presidential elections, the Electoral College is the group of electors who actually cast ballots for the President. When a voter casts a ballot for a presidential candidate, he or she is actually voting for a slate of electors from their state who will cast their ballots for their candidate. What does this say about the actual election of the President??? Indirect election- The people technically DO NOT vote for the President!!!!!!! The actual electoral college meets in December to vote for the President!!! How it operates A candidate needs 270 votes to win in the Electoral College. If a candidate doesn’t get a MAJORITY, THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES PICKS THE PRESIDENT!!!!! This has happened 2 x Each state gets a number of electors that is equal to the total Senators and House of Representatives from that state. Someone can win by winning just the 11 largest states. Nebraska and Maine award votes by congressional district vote totals. They can divide their Electoral votes, and are not "winner-take-all." For example, if McCain wins the overall vote in Nebraska, he gets 2 votes. If Obama can win 1 of the 3 districts within Nebraska, and McCain wins the other 2 districts, then McCain would get 4 electoral votes, and Obama would get one electoral vote. Elected officials at the federal level are not eligible to be Electors (people who vote in the Electoral College.) WHY???? We have had 18 presidents who have been elected by majority in the Electoral College who did NOT receive at least 50 percent of the popular vote. More than 150 "faithless" electors have decided not to vote for the candidate that they pledged to elect. 4x the winner of the popular vote DID NOT BECOME THE PRESIDENT More than half of the states have laws that punish an elector who is "faithless." However, these punishments have never been enforced, and the punishments are as little as a $500 fine. Who does it help?? Where should the candidate campaign. Which states??? Battleground states!!! Big or small states??? Small states!!! Cuz at least they are worth some points!! Aim: How is the Constitution flexible? Constitutional Flexibility Why would we set up a Constitution that is flexible and vague? to fit the changing times People change There was no internet, in 1789, so can the federal government make a law dealing with the internet?? Yes!!,, there are communication and commerce parts to the Constitution, so we adjust it to the “new” versions of commerce and communication Elastic Clause Congress can make any laws it feels is “necessary and proper” dfdfd Amendments Change to the Constitution 2/3rds of Congress/3/4 of states 27 total amendments 1st 10 is Bill of Rights Judicial Review Supreme Court decides if a law is unconstitutional Comes from McCulloh v Maryland case and Marbury vs. Madison dfd Unwritten Constitution http://www.socialstudieshelp.com/Lesson_ 19_Notes.htm Cabinet Committee System PAC’s/Pressure Groups Political Parties Judicial Review