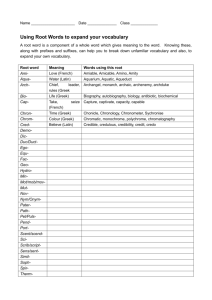
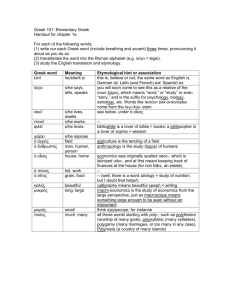
Greek & Hellenistic Culture Greek Art sculpts 38 foot statue of
advertisement

Greek & Hellenistic Culture Greek Art _________________ sculpts 38 foot statue of Athena in the _____________________ Values of Greek classical Art: _______________, ________________, _____________________ - faces of Greek sculptures are serene, never _____________, laughing or showing ______________ Greek statues – Some examples are: ______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Greek Drama/Tragedy Theatres express ____________________________ and tribute to the _____________. _________________- features a tragic hero with extraordinary abilities and a ______________________to be their downfall; Ex. Aeschylus- The Oresteia; Sophocles– Oedipus the King, Antigone; Euripedes- Medea Greek Drama/Comedy ____________________- scenes filled with __________or _________ about customs, politics, people or ideals Aristophanes- The Birds, Lysistrata Greek Architecture Draw the 3 order of Greek columns in the boxes Doric Ionic Corinthian Greek Philosophy Philosophers- means “___________________________________________________” ___________________- word comes from sophos (wisdom). Travel around ________________ teaching wisdom, rhetoric and the art of _____________________. _____________________ (469-399 B.C.) -- Was NOT a Sophist, believed that there are ____________________ standards of truth and justice; his teaching method__________________________ people; he made enemies by exposing ignorance; brought to trial for “_______________________________________________” and “neglecting the city’s ___________.” _______________ (427-347 B.C.) -- Founder of the ____________________ in Athens; most famous work: ________________________; vision of a perfectly governed society made up of: farmers and artisans, warriors, ruling class, a philosopher __________ _______________________ (384-322 B.C.) -- Founds a school in Athens called the ________________; balance between reasons and desires is to live ________________________; he influenced _________________________ (life in moderation); his famous pupil was _________________________ Philip II King of ____________________________ --Region north of Greece; transformed _________________ into trained ____________ Goals: 1.) ___________________________________________________2.) ______________________________ Accomplishments: Conquered Greece but ______________________ had local control and were ___________ under Philip’s leaders; declared war on ______________, a common enemy At height of career, he was _________________________ Alexander the Great Philip’s _______; became King of ____________________; Aristotle was his ______________ where he learned philosophy, art, science; learned __________________ lessons from the Macedonian army; his goal was to continue his father’s work and defeat _______________and create a huge _________________ Alex’s timeline -- What did he do and how did he do it? crushed _________________________________________________ conquered the ___________________________________ conquered __________________ moved east, conquering territory until he reached the ___________________________ founded new cities (______________________) and rebuilt old ones married a _______________princess and ordered his generals to marry _________________________ blending of __________________ (Hellenism) seen as _________________ -- chivalrous and noble ___________________________ Wanted more- No army could ________________ him; pushed men to ___________but his troops are exhausted so they _______________________; at the age of ______, died of a ________________ Legacy -- Mixing of Greek, Egyptian, Persian, and Indian traditions – called ______________________ Culture Hellenistic Culture _____________, _________________, _______________, and _______________ cultures blended together Formed by Alexander the Great; the city of ___________________ in Egypt became the center for ________________, was an _________________________ community; known for its many ________________, libraries, temples, art galleries, gardens Art Statues honored the ___________, commemorate heroes, everyday people; more _______________ and _________________________than Greek art The Colossus of _____________ - 7 wonders of the Ancient World, toppled by an ___________________ Hellenistic Science, Math, and Technology Math – Focused on ____________________ - proofs and logical explanations - Pythagoras - created ________________________________ (a2+b2=c2) - Aristarchus - proved planets ________________ around the sun - Eratosthenes - calculated earth’s ________________________ to within 1% - Euclid - geometry, book called the __________________, still used in geometry courses today - Archimedes - calculated ____ Science – Astronomy (applying logical thinking and geometry) - Aristarchus: __________________________ theory (heliocentric theory) - Ptolemy: ____________________________ theory (geocentric theory) - Aristotle: All earthly bodies composed of ___________________ -- fire, water, earth, & air corresponding attributes: hot & cold, wet & dry Tend to be _________________ to other elements of its kind (explain why objects fall, steam rises) Taxonomy - Observation to _________________ creatures Medicine You could learn to understand and treat _______________ by using careful _________________________ and _________________ thought. - __________________________ - dismissed the notion that magic or spirits caused or cured disease. Cartography - Map making The earth is a _______________ Accepted world was round, but most figured world much _______________ (though with some exceptions) Impact of Greek Thought on Medieval Europe Philosophy, math and science ______________________ and preserved by __________ scholars Many documents lost or ______________________ from Greek to Arabic to Latin to Spanish to French ________________________ believed the ancients foremost authority on science- couldn’t _______________