homeostasis + water balance
advertisement

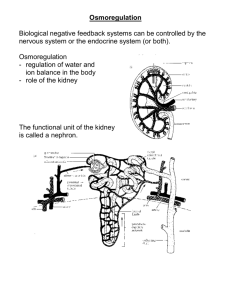
Who’s urine? MATCH UP! Normal diet Drunk plenty of water Has been exercising but not drunk anything Title - Homeostasis Learning Objective To be able to explain how our bodies control water content. Learning Outcome • Homeostasis involves making sure that our bodies have the correct levels of 4 key things. • Can you name two of them? What is Homeostasis? Homeostasis involves maintaining a constant environment in the body • Homeostasis makes sure our body has the correct levels of; Temperature Water Carbon dioxide Oxygen B2 : How does the body control water balance? In Out Food and drink Breath Our bodies need a balanced water level to keep the Water madeconcentration in respiration Sweat internal of our cells at the correct level for them to work properly. Faeces Urine The kidneys Kidneys do two main jobs: 1. Remove waste urea from the blood. 2. Keep a balance of other chemicals in the blood – including water. How kidneys work Filtering all small molecules from the blood. Reabsorbing all of the glucose. Reabsorbing as much salt as the body needs. Reabsorbing as much water as the body needs. Excreting the remaining urea, excess water and salt as urine, which is stored in the bladder. Water balance The concentration of blood plasma is monitored as it passes through the brain. If the blood is too dilute then kidneys excrete more water in the urine. If the blood is too concentrated then kidneys excrete less water in the urine. The amount of water in the blood depends on: external temperature, exercise, intake of fluids and salts. ADH and water balance. The concentration of urine is controlled by a hormone called ADH (anti-diuretic hormone). It is released into the bloodstream by the pituitary gland. Blood too concentrated – detected in brain ADH secreted by pituitary gland ADH causes kidneys to reabsorb more water to blood Water Balance Normal blood concentration Blood too dilute – detected in brain Normal blood concentration ADH not secreted by pituitary gland kidneys reabsorb less water to blood TITLE: Controlling Water Content Outcomes: create a think board on homeostasis and water balance. Which hormone controls water content in the body? How do the Kidneys help keep water in the body balanced? Where is it released from? (C) What 3 main things can effect the concentration of urine? (D) Draw a flow diagram of how the Explain in as much detail as possible (use as concentration of urine is controlled by a many science key words as you can) how hormone Alcohol and Ecstasy affect ADH production (B) (A) True/False Quiz! • • • • • • Your urine is always the same. FALSE The pituitary gland monitors blood plasma. TRUE TRUE Homeostasis maintains a constant internal environment. The liver helps balance water and waste in the body. FALSE Alcohol suppresses ADH production. TRUE Dehydration Ecstasy increases ADH production. TRUE Drowning Which is the odd one out? bacteria virus fungus B2 past EXAM questions! • I will be round to mark them as you go ready to put into your progress folder. ALL must do 2 exam questions SOME will do more so can pick their highest grade for progress folder FEW will do all exam questions for a PRIZE! Exam Question (hard) 3 marks – pick from the following • number of bacteria after 2 hours is 12 800 (or 1.28 x 104), which is a sufficient number to cause food poisoning • idea that if conditions were not optimum the actual number may be lower than this • idea that not enough data/evidence/information, or would need to measure more things, to conclude that person will definitely get food poisoning • idea of immune response against bacteria or toxins / acid in stomach destroying bacteria or toxins Testing Urine • Draw the following table in your books neatly. Sample Protein Sugar A B C • Test the 3 urine samples for protein and for sugar using the equipment available. • EXTENSION: explain in as much detail as possible what homeostasis is and how water content is controlled in the body. Drug Trials • Outcomes: create a Powerpoint on the use of drug trials in medical science. Include information on the following: - Laboratory testing on human cells [C] - Laboratory testing on animals [C-B] - Human clinical trials [A] - ‘blind trails’ (you’ll need to know what a placebo is) - ‘double blind trials’ - ‘open label trials’ Homeostasis • How hot do you think our core body temperature is? • 370c How do we maintain our body temperature in hot environment Red cheeks Hairs lie flat Sweating Controlling body temperature • If the body temperature gets too high, the blood flows closer to the skin. • This is the reason why we get red cheeks. Sweating • • When your body is hot, sweat glands are stimulated to release sweat. The liquid sweat turns into a gas. Sweating The skin Effects of overheating • Being to hot is dangerous. • If too much water is lost through sweating, the body becomes d_ h _d_ a _ _d. • This can lead to heat stroke and even death. How do we maintain our body temperature in a cold environment? Shiver Hairs stand on end Respire more Respire more Effects of being too cold • If the body temperature fall too low, sweating stops and the muscles begin to s _ _ ver. • Hypothermia is when the body temperature falls too far below 37oc. • This causes unconsciousness and sometimes death Body temperature readings • Where on the body can body temperature readings be taken from? ANUS MOUTH SKIN SURFACE FINGER EAR Task • Complete the worksheet. • If you need help put your hand up.