SCIENCE 10 Unit 1: FIELD TRIP Part I: Biomes, Climatograms and
advertisement

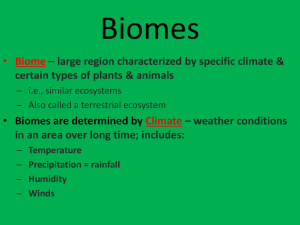
SCIENCE 10 Unit 1: FIELD TRIP Part I: Biomes, Climatograms and Biotic and Abiotic Factors Complete Questions 1-3 at red gate entrance, then 4-6 at first lookout. 1. Location: ______________________________________ Type of Ecosystem: ______________________________ 2. Describe as many characteristics of this environment as you can. Use the sign board and group the characteristics as abiotic and biotic components; be specific regarding names of organisms. 3. The largest and most predominant biome of Canada is the ________________________. The area we are in however is not a biome but an ecosystem. Explain the difference. 4. Examine the climatograms of all the major biomes from Chapter 1 in your textbook. Pick the one you think most closely depicts this environment and copy that climatogram in the space below. Be sure to include labeled axes and a title for the graph 5. Give a minimum of three (3) observations about this environment that support your choice of climatograph above. 6. Identify 3 things discussed in chapter one that not only influence the distribution of major biomes but would also explain why we see different ecosystems, like this here, within a major biome. 7. What is biodiversity? Does Kalamalka Provincial Park seem like an environment with a high biodiversity, explain why or why not? Part II: PHOTO SCAVENGER HUNT 1. Take photos to illustrate the following: a) Adaptations: take a photo of one living organism, plant, animal or fungi. Think about the structural, physiological, and behavioural adaptations we discussed in class and identify one that your organism has to help it survive in this environment. Image Explanation b) Food webs/ chains: Take a photo of each of the following: a producer, one type of consumer, and a detrivore. Explain why you’ve selected the organism for that trophic level. Image Explanation c) Ecological succession: Vernon was, at one time, scraped clean by massive glaciers! It was bare rock (omg)! Glaciers are no longer agents of change in this region, give one example a current natural agent of change in this area. ____________________________________ d) Since glaciers have left the area 10’s of thousands of years ago we are likely only to see secondary succession in this region. Describe secondary succession. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ e) Include two photos indicating a pioneer species and a climax community. Describe the image and state two reasons why the image you’ve taken is a good representation. Image f) Explanation Human Influences: Give two ways you think humans impact this environment one positive and one negative. Image Explanation g) Invasive species: in several locations, invasive species are dominating the area. Find and take a picture of a NATIVE species and an INVASIVE SPECIES, explain what makes a species ‘invasive’. (HINT: The sign boards will be helpful for this activity) Image Explanation h) Find and take a picture of two organisms living in a symbiotic relationship. Classify it as commensalism, parasitism, or mutualism and explain. Image Explanation Part III: Examining Diversity Procedures: 1. Using your string map out an area 1m 2 of flat ground (a quadrant) that has a good cover of dead leaves, twigs, moss and grasses. 2. Measure the temperature 1m above the plot, at the ground level and underneath the litter. The thermometer must be in the shade during all readings. Allow 2 min for the thermometer to set before reading a temperature. Record the temperatures in a table. 1 m above Temp ( Ground level Below litter ) a. Which region has the highest and lowest temperatures? 3. At one corner of the plot, use the shovel and or your hand to remove a soil core of at least 20cm. Strata soil (layers) are usually visible and consist of humus, topsoil and a number of subsoil layers. Make a sketch of the core and label thickness, color, hardness and water content. a. Beside your diagram identify several abiotic and biotic factors that influence the characteristics and development of the soil described above. 4. Have each member of your group mark off a 25cm X 25cm square (a nested quadrant) within your original plot. In each nested quadrant, count as many organisms, plant and animal, as you can by removing layers of soil. Record your data in the table below. Quadrant Number of Plants Number of Animals Answer any one of the questions below. 5. In a short paragraph below define biodiversity and reflecting back on your response to #7, in part I, and all the activities and data collected today, write a short paragraph indicating whether or not you feel this ecosystem has a high biodiversity and whether or not it is an environment worth protecting. Give reasons supporting your response. 6. Think back to everything we discussed and hopefully, you’ve learned. Regardless of whether you go on in science or not identify at least three things you currently do or things you would change that would have a positive impact on Sustaining Earth’s Ecosystems. 7. Out of all the various activities we’ve done in this unit identify your two favorite and one least favorite. Out of all the topics/concepts we’ve discussed identify 3 that you’ve enjoyed learning about and explain what it is you liked about those topics.