Effectiveness of Training
advertisement

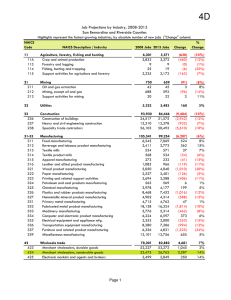
EFFECTIVENESS OF TRAINING Group 5 Effectiveness of Training What is “effectiveness of training”? Effectiveness means producing an intended result. Training is the systematic development of the knowledge, skills and abilities required by an individual to perform adequately a given task or job. It is the evaluation of how well a training program instills the K.S.A.s an employee needs to perform job oriented tasks. http://vimeo.com/5168056 Basic overview of Training Approaches Analyze (Needs Assessment) Design Implement Evaluate Analyze (Needs Assessment) Training Needs can be assessed by analyzing three major human resource areas: 1. The organization as a whole- Organizational Analysis 2. The job characteristicsJob Analysis 3. The individual- Person Analysis Analyze (Needs Assessment) Organizational Analysis- consists of environmental trends, organizational goals, and current resources: technology, financial, and human. This analysis will provide some benchmarks against which the effectiveness of a training program can be evaluated. Analyze (Needs Assessment) An internal audit will help point out areas that may benefit from training. A skills inventory will help the organization determine what skill are available now an what skills are needed for future development. Analyze (Needs Assessment) Job analysis is where training begins. To be able to effectively train an employee the trainer must understand what the employee’s task and working conditions. These are separated into job context and job content. Job Context: contacts, and working conditions, physical and personal demands. Job content: What a worker does, purpose of action, tools and equipment used in process, expected performance levels, training needed. Person Analysis When training-needs analysis focuses on the individual, it is called person analysis. Training needs here emphasize who needs training. (typically conducted through performance appraisal) DESIGNING THE TRAINING PROGRAM Once training needs have been determined, the next step is designing the learning environment. Four related areas are particularly important: 1. Instructional Objectives 2. Trainee Readiness and Motivation 3. Principles of Learning 4. Characteristics of Instructors Implementing the Program A major consideration in choosing among various training methods is determining which ones are appropriate for the KSAs to be learned. A wide variety of methods are available for training personnel at all levels. Training Methods On-the-job training Off-the-job training Orientations Lectures Role Playing/ Simulation Audiovisual Methods Job Rotation Apprenticeships Internships/ Assistantships Programmed Learning Laboratory Training On-the-Job Training On-the-job training focuses on the acquisition of skills within the work environment generally under normal working conditions. Is the oldest form of training. Is still the predominant form of job training in the United States, particularly for non-managerial employees. On-the-job training is a significant investment considering that roughly 30% of a new worker's time is spent in on-the-job training during the first 90 days of employment. On the Job Training On-the-Job Training Benefits Demonstrate how to complete a task. Review important points. Demonstrate task again. Let workers perform easier parts of the task. Help workers perform the entire task. Allow workers to perform the entire task, while being monitored. Allow workers to perform the task on their own. Detriments The training may not be rigorous, efficient or systematic Trainees may be given boring and repetitive tasks Some workers may not be good at teaching their own skills; they may pass on bad work practices as well as good ones The needs of the trainee may be subordinated to other priorities Untrained workers can make mistakes and create hazards. Effective on the job training Lists all the info/skills the trainees need to learn to perform. Sets learning Objectives. Ensures trainee has observed a competent worker . Has been informed the purpose of job related duties and tasks. Gives the trainee opportunity to perform the tasks and give feedback. Orientation Orientation effectively integrates the new employee into your organization and assists with retention, motivation, job satisfaction, and quickly enabling each individual to become contributing members of the work team. New employee orientation is usually performed by the Human Resources department Orientation Job Orientation Includes: Company History Core Values and Beliefs Vision Company Mission Benefits http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nPgSZ0RfCNo Structure Evaluation Why Measure Training Effectiveness? Many training programs fail to deliver the expected organizational benefits. Having a well constructed measuring system in place can help one determine where the problem lies. The most well- known and used model for measuring the effectiveness of training programs was developed by Donald Kirkpatrick in the late 1950s, The Kirkpatrick Model. The Kirkpatrick Model Kirkpatrick Model Continued Level 1 Reaction Level 3 Behavior • participant questionnaire, informal comments from participants, focus group sessions with participants. • self- assessment questionnaire, onthe–job observation, customers reports, peers, and participant’s manager. Level 2 Learning Level 4 Results • pre- and post- test scores, on-the-job assessments, supervisor reports. • financial reports, quality inspections, interview with sales managers. Phillip’s Model Results of Ineffective Training Poor job performance Low job satisfaction Safety hazards and injuries Lower customer satisfaction Legal repercussions Waste of Resources High Cost Low Return Advantages of Effective Training Improved Quality of Work Better Team Performance Increased Productivity Increased Sales Improved Employee Health Improved Safety Record Increased Customer Retention Increased Employee Morale and Retention