Project
advertisement

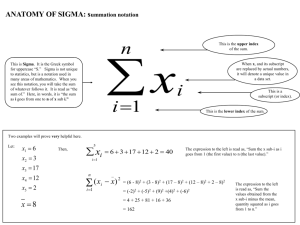
Team 5: Catherine Pellow, Ryan Fettinger, Tyler Schroeder, Radha Patel, Jonathan Yulan, Minsu Kim Problem Cost of raw material increased $20 million in planned cost Raise list price By how much? Too much = lose customers Too little = pointless to implement Pricing practices are hard to change Project Acme appointed a manager for Six Sigma steps (DMAIC) Define Measure Analyze Improve Control Define Clarify problem Acme manager defined defect Transaction invoiced at lower price than set Narrow scope One product line Propose charter Collect data, carry out analysis, ensure support Measure Gather data and prepare it for analysis Mapped the price agreement process Pricing process with 6 main steps Quality of input data assessed Analyze Guide discussion to ensure tasks are performed Used a Cause-and-Effect Diagram Standard statistical analysis Improve Recommend modifications to existing processes (process adjustments) Graduated discount approvals Exception codes Control Creates controls to allow company to sustain changes (quality assurance) Set up monthly reviews Used control charts The Payoff The initial goal of generating half a million dollars in incremental revenue in the first year was completed within three months. The average transaction price for the pilot product line went up by slightly more than the list prices. With the help of the list price increase and the Six Sigma it resulted in $5.8 million dollars in incremental sales in the first six months. The Payoff The Six Sigma approach drastically reduced the friction in the Pricing-Sales relationship. Since their recent success Acme is rolling out the Six Sigma pricing across the entire corporation. Other companies operating in competitive environments can also benefit from Acme’s experience as they look for ways to exercise price control without alienating customers. Which Steps Matter? • The Cause and Effect Matrix is one of the basic tools of any Six Sigma project. • It is a vital way to judge the impact of each step on the customer in order to identify the underlying problems and their causes. 1) List the customers requirements 2) Rate the importance of each requirement 3) Describe each step 4) List all of the inputs 5) Multiply the importance rating by the effect score, then add across F What Are We Doing? Acme's Six Sigma team mapped the company's pricing process The formal process comprised of six main steps The Cause and Effect Matrix is a systematic way to judge the impact of each step on the process's customers as a prelude to prioritizing underlying problems and identifying their causes. The Six Sigma Process The Six Sigma Pricing Process The process got bogged down as pricing analysts rooted around for information they should have already obtained from the sales staff What Are We Really Changing? Our analysis showed that the higher the list price, the deeper the mean discount tended to be. This was showed to be true especially for large transactions Without doubt, Six Sigma emphasizes the importance of linking financial gains to projects undertaken. Why it Should Change This suggested that improve average prices by differentiating the pricing guidelines for transactions of different sizes precluding deep discounts Sources http://www.isixsigma.com/new-to-sixsigma/getting-started/what-six-sigma/ http://web.ebscohost.com.ezaccess.libra ries.psu.edu/ehost/detail?vid=3&hid=12 &sid=59cb3746-94ac-4d5b-9585aaad30eb6af1%40sessionmgr13&bdata =JnNpdGU9ZWhvc3QtbGl2ZQ%3d%3d #db=buh&AN=16951608 Terms Six Sigma Scope Defect DMAIC Quality Cause-and-Effect Diagram Process Adjustments Process Control Charts Quality Assurance