Southwest Asia & North Africa: Geography, Religion, Conflict
advertisement
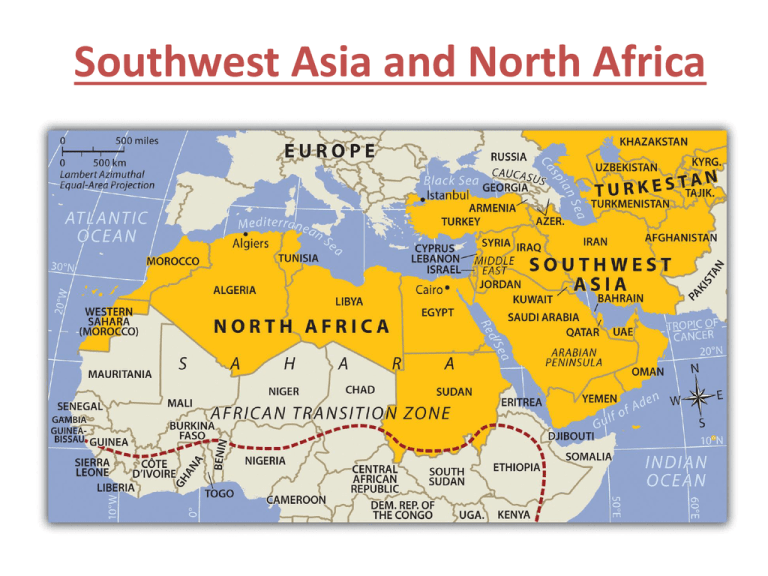
Southwest Asia and North Africa Southwest Asia • Also called the Middle East • Is a land bridge that connects Asia, Africa, and Europe. • The most distinctive land form is the Arabian peninsula. The Anatolian peninsula which is occupied by the country of Turkey is another important landform. Southwest Asia and North Africa Satellite Images at night Wadi • Is a riverbed that remains dry except during the rainy season. Hindu Kush • Are very high mountains in Afghanistan. These mountains landlocked Afghanistan and made contact with the outside world very difficult. Zagros Mountains • Isolate Iran from the rest of Southwest Asia. Elburz Mountains • Cut off east access to the Caspian Sea by Iran. Taurus Mountains • Separate Turkey from the rest of Southwest Asia. Tigris and Euphrates Rivers • Are two of the regions most important rivers.They supported several ancient river valley civilizations in an area called the Fertile Crescent. Today it flows through Turkey, Syria, and Iraq. The valley of these rivers are fertile and are good for agriculture. Jordan River • Starts at Mount Hermon and then forms the natural border between Jordan and Israel. Dead Sea • Is a landlocked salt lake. It is so salty that nothing but bacteria can live in its water. It is also 1349 feet below sea level making it the lowest place on the exposed crust of the earth. The Arabian Peninsula Ch.22 Section 1 Colonial Powers • Much of Southwest Asia fell under the control of Britain and France. • The region was valuable to colonial powers because of the Suez Canal, a link between Asia and Europe, and because oil was discovered there after 1932. Oil • *The most abundant resource in Southwest Asia. • One-half of the worlds oil reserves are located in Southwest Asia. • These large reserves have made the region important because so many countries like the U.S., depend on its oil. http://www.traileraddict.com/clip/the-kingdom/opening-sequence OPEC • The organization of Petroleum exporting countries, known as OPEC. • The purpose of OPEC is to help members control worldwide oil prices. •*The most powerful factor in defining the Middle East and North Africa is RELIGION. Religion has led to many conflicts in the region. •The three main religions in the region are Islam, Christianity and Judaism. •All three religions consider Jerusalem to be a holy city. •*The holy book of Islam is the Qur’an. The holy book of Judaism is the Torah. The holy book of Christianity is the Bible. •*Islamic fundamentalists are trying to remove Western influences and other religions from the region. Christianity •Christianity is the most popular religion in the world with over 2 billion adherents. 42 million Britons see themselves as nominally Christian, and there are 6 million who are actively practising. •Christians believe that Jesus was the Messiah promised in the Old Testament. •Christians believe that Jesus Christ is the Son of God. •The Christian holy book is the Bible, and consists of the Old and New Testaments. •Christians believe that God sent his Son to earth to save humanity from the consequences of its sins. •One of the most important concepts in Christianity is that of Jesus giving his life on the Cross (the Crucifixion) and rising from the dead on the third day (the Resurrection). •Christians believe that there is only one God, but that there are three elements to this one God: God the Father God the Son The Holy Spirit Judaism •Judaism is the original of the three Abrahamic faiths, which also includes Christianity and Islam •there were around 13.1 million Jewish people in the world in 2007, most residing in the USA and Israel •Judaism originated in the Middle East over 3500 years ago •Judaism was founded by Moses, although Jews trace their history back to Abraham. •Jews believe that there is only one God with whom they have a covenant. •Judaism has a rich history of religious text, but the central and most important religious document is the Torah. •Spiritual leaders are called Rabbis. •Jews worship in Synagogues Prophet Muhammad • Founder of Islam. Mecca • Muhammad lived part of his life in the city of Mecca. • Mecca located in Saudi Arabia is the holiest city of Islam. The 5 pillars of Islam • There are certain rules that all Muslims are required to follow: they are the 5 Pillars • 1. Faith • 2. Prayer five times a day • 3. Charity • 4. fasting • 5. hajj or Pilgrimage to Mecca Islam Adherents to the Islamic religion make up around 20% of the world’s population (1 billion). It is the world’s second largest religion. It is interesting to note that the four nations with the largest number of Muslims are outside the Middle East: Indonesia – approx. 165 million (88%) Pakistan – approx. 110 million (97%) Bangladesh – approx. 97 million (85%) India – approx. 90 million (10%) Mosque • Is an Islamic place of worship. Theocratic • This means religious leaders controll the government. • Rulers relied on religious law for running the country. • Today Iran is ruled by religious leaders. Change To Urban Life • *Population growth, overuse of land and water resources has led millions of people to abandon villages and moving to the cities (Urbanization). • Technical skills are needed for many jobs today. Foreign workers are brought in to fill those jobs. Religious Duties • Women cover their heads, hair, and sometimes faces. • Women’s roles have expanded in some countries. • Muslims are expected to perform religious duties. Arabic Culture •*Arab culture refers to the culture in Arab countries of West Asia and North Africa, from Morocco to the Persian Gulf. Examples •Language, literature, art, architecture, music, spirituality, philosophy, Loyalty to family The Eastern Mediterranean Jerusalem • Is the capital of Israel. • *It is a holy city for the Jews, Christians, and Muslims. Western Wall • This was the 2nd temple of King Solomon built in 538B.C. The only portion left today is the Western Wall. Modern Jews pray at this site. Christians • Jerusalem was the site of the crucifixion of Jesus. • Jerusalem was under Muslim control in the Middle Ages. • During this time the Christians started the Crusades to liberate these lands. Muslims • To Muslims it is the 3rd most important city. • The shrine Dome of the Rock, is where Muslims believe the prophet Muhammad rose into heaven. Muslims are credited with preserving much of the learning from the ancient world and diffusing it to much of the known world. Zionism • The holy land was called Palestine in the 1800s. The British controlled the land. • In the mid-1800s a movement called Zionism had begun. Its goal was to create a Jewish homeland in Palestine. Creating The State of Israel • The 1947, the UN divided Palestine into two states- one for Arabs and one for Jews. Israel • Israel became a nation on May 14, 1948. •*Israel treats women more as equals to men than any other country in the region. •*Many countries like Saudi Arabia (Mecca) require that women wear clothing that covers their faces because of their Islamic believes. •*Israel also has more ethnic diversity than any other country in the Middle East because of immigration from around the world. Hostilities • In 1948, Arab countries invaded Israel and Jewish troops fought back. • The 1948 war was the beginning of hostilities that continue today. •One of the conflicts in Southwest Asia is setting the boundary between Israel and Palestine. •*Some of the problems are Jewish settlements, control of Jerusalem, and the location of aquifers. •*Many different groups of people have controlled Jerusalem including the Romans, Hebrews, and Muslims. Gaza Strip • Another area of Palestinians is the Gaza Strip. This is a territory along the Mediterranean Sea, just northeast of the Sinai Peninsula. Israel has occupied it since 1967. PLO • The land designated for the Palestinian Muslims was under Israeli control. • In the 1960s the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) was formed to regain the land for the Palestinian Arabs. Yasser Arafat • Was chairman of the PLO from 1969 until his death in 2004. Palestinian Refugees • The creation of Israel produced large numbers of Palestinian refugees. • Refugees struggle to find food and shelter. • Providing education and services for them is difficult for many poor countries like Jordan. Civil Wars • Civil wars in Lebanon and Cyprus have caused huge economic problems. • Lebanon, a more developed nation, was hit hard by a civil war that lasted from 1975 to 1976. The conflict widened to include other nations, and in 1982 Israel invaded Lebanon. Some Israeli troops remained until 2000. Modern Infrastructure • This region has great potential for development. They have a good climate and are well located for connections to international markets. • What many countries lack is infrastructure that would support a growing economy. The Northeast Mesopotamia • “Land between two rivers” (Tigris and Euphrates) • Several of the world’s ancient civilizations were in this region. • They grew up along the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. Babylon, Assyria and Chaldea, all built empires in Mesopotamia, the land between the Rivers. • Is largely corresponded with modern day Iraq, and portions of Syria, Turkey, and Iran Iraq Population Density Kurds • The Kurds are a stateless nation. They live in areas of Iraq, Iran and Turkey. They have been in conflict with all these countries and because of this conflict it prevents them from getting a homeland. •*There are two main branches of the Islamic religion, Shia and Sunni. 85% of Muslims are Sunni and can be found in countries like Syria, Saudi Arabia, and Pakistan. Shia Muslims are found mainly in Iran and parts of Iraq. • After the death of the prophet Muhammad, Muslims split into two groups Sunni and Shi’ite. • About 85% of all Muslims are Sunni. • Sunni Muslims agree with the position taken by many of the Prophet's companions, that the new leader should be elected from among those capable of the job. Sunni Shi’ite • Most Iranian are Shi’ites. • Shia Muslims believe that following the Prophet Muhammad's death, leadership should have passed directly to his cousin/son-in-law Ali (the father of his grandsons Hasan ibn Ali and Hussein ibn Ali) • Ali was married to Fatimah, Muhammad's daughter. Reforming Economies • Turkey and Iran are making progress in modernizing their economies. • Turkey wants to be a member of the European Union but they have been reluctant to accept them because of their human rights record and fights with Greece over territory. • Major obstacles are political problems and devastating wars. •*The Gulf War of 1991 was the result of Iraq attacking Kuwait because of oil that they take from the same reserve pool. Afghanistan has had many conflicts since the 1970’s. This led to Taliban, extremist Sunni Muslims, coming to power. Their interpretation of Islam meant that women were excluded from civil rights and were treated poorly. Taliban • The Taliban in Afghanistan wanted to preserve traditional ways. • They imposed rigid rules on society. • The rules included restrictions on clothing, appearance of women in public and listening to music or T.V. • In 2002, troops led by the U.S. toppled the Taliban regime. Kurdistan Kurds are an ethnic group that has not historically had a country of their own. The Kurds have people in the countries of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Syria. A Region of Conflict Issues in North Africa and the Middle East ©2012, TESCCC World Geography Unit 8, Lesson 4 Reasons for Conflict ©2012, TESCCC Israeli-Palestinian Conflict • • • • • • • • • • • 1948 the state of Israel was created through a United Nations charter War with Arabs nations followed immediately 1967 Israel takes control of Jerusalem, West Bank, and Gaza strip at the end of the Six-Day War 1974- The Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) is recognized by the UN as the legitimate representative of the Palestinians 1978 Camp David Accords set up Palestinian self-rule in the West Bank 1978 First Palestinian Intifada (resistance movement, ended in stalemate) 1993 Oslo Accords allow Palestinians to establish self-rule in West Bank and Gaza Strip 2001 election of Ariel Sharon as Prime Minister (waged battle against terror groups) 2003 Israel starts building a fence along the West Bank 2004 Yasser Arafat dies (leader of PLO) 2012- Peace talks end without progress ©2012, TESCCC A refugee camp in Israel ©2012, TESCCC ©2012, TESCCC Women in the Middle East • Unequal status (due to Islamic law) • Family life (marriage, divorce, child custody, inheritance)- husband is considered the head of the family and given greater legalstanding than his wife • Gender-based violence • Nations including Kuwait, UAE, and Bahrain permit women to participate in government • Working outside the home and access to higher education (is not allowed in some areas) • Wearing of the veil (hijab) ©2012, TESCCC ©2012, TESCCC Water Issues Conflicts over Natural Resources • Water is the most important natural resource and the most likely to cause conflict in the future • The ]Dead Sea is evaporating and shrinking • Land rights and aquifers (North Africa) • Distributing the waters of the Nile- areas outside of Egypt (Aswan High Dam) ©2012, TESCCC Oil Wealth • War- Desert Storm (Kuwait) • Effects of Modernization (desalinization) • Industrialization (malls, airports, land reclamation) ©2012, TESCCC Arab Spring • • • • • • • • • • Dec. 2010- A Tunisian vendor sets himself on fire in protest of police brutality Jan. 2011- Thousands take to the streets in Tunisia demanding better living conditions Jan. 2011- Tunisian president steps down and flees to Saudi Arabia Jan. 2011- Thousands take to the streets in Jordan in protest of high fuel prices Jan. 2011- Algerians protest outside the parliament building Jan. 2011- “Day of Rage” in Egypt as tens of thousands take the streets in protest demanding the ousting of then President Mubarak Feb. Mubarak dismisses his government and surrenders power (ending almost 30 years in control) March 2011- no fly zone contention in Libya April 2011- protesters killed in Syria October- Gaddafi killed (ending 42 years of power) ©2012, TESCCC ©2012, TESCCC Climate and Vegetation Water • *The most valuable resource in the region. • *Most influential in the pattern of human settlement. • In some areas water is so scarce that it must be guarded and carefully used. • Efforts to conserve water have been part of the culture of the region for thousands of years. Desert • Deserts spread across the region. The most famous desert is Rub al-Khali. Known as the empty quarter. It is called this because it is said that no one comes out of it. It covers much of the Arabian peninsula. Oasis • An area of the desert where vegetation is found because water is available. Negev Desert • Located in Israel. It produces crops through extensive irrigation. Salt Flats • In Iran, high mountains block the rain, and dry winds increase the evaporation. Winds evaporate the moisture in the salty soil. As a result chemical salts remain, that create a salt flat. Semiarid Lands • These are located on the edge of the desert and have a semi-arid climate. They have warm to hot summers but receive enough rain to support grass and low growing shrubs. Well Watered Coast Lands • Along the Mediterranean coast and across most of Turkey, hot summers and rainy winters create a good climate for growing fruits, olives and vegetables. Human Environmental Interaction Dams in Turkey • Turkey is building dams and a man-made lake on the upper Euphrates River. • The dams will provide water and hydroelectric power. • *Countries downstream ( ex..Iraq) will lose the use of water for irrigation or hydroelectric power. The National Water Carrier Project • Carries water from northern Israel to sites in the center and south. • Water is used for irrigation in the Negev Desert, and some drinking water. • Because the water sources flow through several countries and access to the water is restricted the project is a source of conflict. Drip irrigation • This is used by several of the countries in the region. This is a practice of using small pipes that slowly drip water just above the ground. The water drips just at the root zone. Evaporation is reduced and water is conserved. *Desalinization • Is the process of removing salt from ocean water. This water cannot be used for irrigation because it is still too salty. • *This process allows countries to be able to survive extreme droughts ex..Israel. • The water is used in sewage systems. Fossil Water • This is the water pumped from aquifers. Since it has been in the aquifers for a long period of time. Fossil water has little chance on being replaced. The region receives too little rainfall to fill the aquifers. Water in the aquifers will only last 25-30 years. Crude Oil • The oil fields of Southwest Asia contain two thirds of the world’s petroleum reserves. Petroleum that has not been processed is called crude oil. Refinery • Crude oil pumped from the ground must be moved to a refinery. A refinery converts the crude oil into useful products. North Africa The Suez Canal •*The Suez Canal is an artificial waterway in Egypt extending from Port Said to Suez and connecting the Mediterranean Sea with the Red Sea. It is one of the world's most important waterways •The geographical position of the Suez Canal makes it the shortest route between East and West Golan Heights • There is a small plateau in southwest Syria called the Golan Heights. It overlooks the Jordan River and the Sea of Galilee. This has been the site of conflict between the Arabs and Israelis. Elevation • *The valleys, mountains, and upland plateaus are a result of tectonic forces. *Water resources are the most important reason for settlement patterns in the Middle East and North Africa. • At 4,184 miles long it is the longest river in the world •*The Nile river is responsible for Egypt's population living in 3% of the land area. *Water, climate, oil resources, and transportation routes are all responsible for the location of cities. •*Oil has helped to modernize the major oil producing countries and has given them political clout. •*The Aswan High Dam was built in Egypt to help regulate flooding on the Nile River. This has led to many positives like flood control and some negatives like loss of fertility in the soil. Positive effects of Dam • • • • Prevents flooding Controls irrigation Can plant 3 crops instead of only 1 a year Creates Hydroelectric power- supplies Egypt with 40% of its electricity • Amount of farmland has increased by 2.9 million acres Negative Effects of Dam • New layer of fertile soil no longer deposited by annual flood, must use fertilizers –Very expensive –Run off pollutes river, pollution kills fish • New soil not added to Delta, which causes erosion *Turkey has built a network of dams and irrigation ditches on the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers which has led to resentment from Iraq. Why? Two of the common characteristics that make the Middle East and North Africa a formal region are religion and the Arab language. Lebanon was once covered by forest but because of shipbuilding, over farming, and herding the land is almost completely deforested. •*Most of the land in the region is used for the activity of subsistence agriculture. •*Libya is a country that relies heavily on oil wealth for its economy. •*One of the ways that countries try to survive water scarcity is by using desalinization plants. These plants remove salt from water. •*In North Africa most people live along the coast in the areas that have a Mediterranean climate (due to expansion of Sahara Desert). This area is more productive for farming. •*People that live in the arid and semiarid areas mainly live a nomadic herding lifestyle. Population Pyramids







