China and US: Situation and Problems in Economy & Trade
advertisement

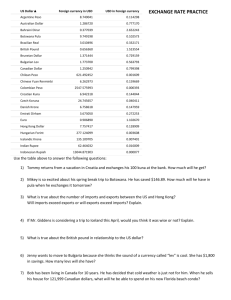
China and US: Situation and Problems in Economy & Trade Dr. Haixin Yao Professor of Economics, Liaoning University, China Visiting Scholar, California State University, Northridge (CSUN) April 15, 2008 Outline I. II. III. IV. Introduction Status Quo Problems Prospect and Suggestion I. Introduction 1. 2. A brief review The comparison of some index: China vs. US 1. A Brief Review (1) Feb.21,1972 , President Richard M. Nixon of USA visited China. This was the milestone for the normalization of ChinaUS relationship --cont’ (2)In Dec.1975, President Ford of USA visited China. (3)On Dec. 16,1978, China –US published the joint communique. (4)At the end of 1978, China started to make economic reform and open up to the world ! (5)0n Jan. 1, 1979,China and US established their formal diplomatic relationship. Before establishing formal diplomatic relationship in 1978. The total trade between China and US was only $0.99 billion. In 1979,this volume of trade increased rapidly to $2.45 billion! --cont’ (6)On Jan. 28, 1979, China leader Deng Xiao-ping visited USA. -- cont’ (7)On Feb.1, 1980, The trade agreement of China-US validated formally. (8)During May 5-9,1982, Vice president George Bush visited China. (older Bush) (9)On Aug.17, 1982, Two government published the China-US joint communique. (10)During Apr. 25- May. 1,1984,president Ronald Reagan visited China. China and U.S. signed four agreements. -cont’ (11) On Nov.19,1993, President Jiang Ze-min of China met President Bill Clinton in Seattle -cont’ --In 1993, the volume of China-US trade increased rapidly to $27.65 billion. --China became US’s the fourth largest import trade partner and 13th largest export trade partner of US. --US also became the second largest export trade partner and third largest import trade partner of China. -cont’ (12)During Oct. 26- Nov. 3, 1997, President Jiang Zemin of China visited U.S. Two countries published the joint communique. -cont’ (13)During Jun.25- Jul.3,1998, President Bill Clinton visited China. (14)On Apr. 6-14, 1999, Premier Zhu Rong-ji of China visited U.S. (15)On Nov.15, 1999, China and US signed formally the bilateral agreement about China joining WTO. This bilateral negotiation had lasted for 13 years! -- cont’ (16)On May 25, 2000, US gave formally the permanence normal trade position to China. (17)On Oct. 19,2001, President Jiang Ze-min talked with President George W. Bush in Shanghai (18)On Dec.11, 2001, China joined formally WTO! (19)On Feb. 21-22, 2002, President George W. Bush visited China. (20)On Oct. 19, 2003, China’s current President Hu Jin-tao met with President George W. Bush in Bangkok -- cont’ (21) On Dec. 7-10, 2003, China’s current premier Wen Jia-bao made a formal visit to US. (22)On Nov. 19-21,2005,President George W. Bush made a formal visit to China. (23)In Sep. 2006, China-US started strategic dialogue mechanism -- cont’ (24)On Dec.15,2006,the First economic strategic dialogue. The two parties reached a series of substantial agreements on security, finance, energy and aviation. (25)On May 22-23, 2007, the Second economic strategic dialogue. --cont’ (26)On Dec. 11, 2007, the Third economic strategic dialogue . 14 cooperation files about economy & trade. (27)The Fourth economic strategic dialogue of ChinaUS will be held in Washington in June, 2008. 2. The comparison of main social and economic index : China vs. US Table 1 International Comparison(1)(2005) Country acreage (million sq.km) Population by the end of year (billion) Density of pop. (person/ sq.km) Country /area World Developed countries Developing countries 134.279 56.433 77.891 6.4378 1.0113 5.4264 47.9 17.9 69.7 G7 North America Southeast Asia union 21.445 21.572 4.48 0.7176 0.4319 0.5514 33.5 20.0 123.1 China USA Russia 9.600 9.629 17.098 1.3076 0.2965 0.1432 136.2 30.8 8.4 Source: national bureau of statistics, P.R.C. Table 2 International Comparison (2)(2005) GDP Country /area Per capita GDP (billion u.s. (u.s .dollar) dollars) GDP growth GDP composing(%) (%) Primary Secondary Tertiary World 44384.87 6987 4.9 3.5 28.0 68.5 Developed countries 34466.20 35131 2.6 1.6 26.2 72.2 Developing countries 9926.40 1746 7.4 11.7 36.0 52.3 2228.9 1740 10.2 12.6 47.5 39.9 12455.07 43740 3.5 1.2 22.3 76.5 763.72 4460 6.4 5.6 38.0 56.4 China USA Russia Table 3 International Comparison(3)(2005) Trade balanc e (billion (billion (billion (billio (2003, u.s. u.s. u.s. n u.s. (2003,million million dollar) dollar) dollar) dollar) Standard Standard unit) unit) 10672.01 1054371.0 21146.0 10393.0 10753.0 -360.0 energy productions Country /area World Developed countries Developing countries G7 Europe union China USA Russia Energy consume Goods import Goods export Total trade 4351.54 537772.7 15141.5 7351.0 7790.4 -439.4 6369.97 520347.8 5903.7 3041.6 2862.1 179.5 2645.58 445.24 122127.5 8753.8 6076.0 4034.2 3085.6 4719.6 2990.4 -685.4 95.2 1380.79 1631.38 110692.4 140937.7 228079.1 63971.7 1421.9 26376.0 370.4 761.95 904.29 245.26 659.95 102.0 1732.71 -828.42 125.1 120.13 Table 4 China’s some index ranks in world (1978-2005) index 1978 1980 1990 2000 2003 2004 2005 Country acreage 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 population 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Expected life 75 77 83 88 86 87 GDP(U.S. dollar) Per capital GDP(U.S. dollar) Total trade amounts(U.S.dollar) 10 11 11 6 7 7 4 175 177 178 141 134 132 128 27 25 16 8 4 3 3 export 28 28 14 7 4 3 3 import 27 22 17 9 3 3 3 60 12 9 2 2 3 37 7 2 2 2 2 FDI(U.S. dollar) Foreign exchange reserve(U.S. dollar) 40 Table 5 International Comparison of Per capita national income units:U.S. Dollar Country /area Total in world Low income countries Middling income countries Modlling-low income countries High income countries non-OECD members OECD members Area of European dollar China USA 1990 4075 356 2000 5244 383 2002 5158 394 2003 5559 439 2004 6338 507 2005 6987 580 1170 1723 1770 1938 2265 2640 848 1158 1183 1295 1507 1746 19617 26528 26130 28195 32132 35131 9150 20394 17747 14368 27564 22034 14109 27184 20524 14740 29389 23118 16341 33547 27921 17656 36715 31914 320 930 1100 1270 1500 1740 23330 34400 35230 37780 41440 43740 Table 6 International Comparison of GDP Units: billion U.S. dollar Country /area 1990 2000 2002 2003 2004 2005 Total in world Low income countries Middling income countries Modlling-low income countries High income countries non-OECD members OECD non-members Area of European dollar 21748 597 3258 31776 837 5215 32821 926 5402 36875 1055 6104 41366 1216 7227 44385 1391 8535 386 6052 6327 7158 8443 9926 17894 596 17293 5583 25725 1163 24564 6130 26496 1138 2536 6753 29719 1218 28493 8316 32928 1358 31562 9501 34466 1528 32952 9813 China Germany Japan U.K. USA 355 1707 3040 990 5757 1199 1900 4746 1438 9765 1454 2022 3971 1565 10435 1641 2443 4291 1798 10951 1932 2741 4623 2124 11712 2229 2782 4506 2193 12455 II. China-US economy & trade relationship: Status quo 1. 2. 3. 4. Trade Investment Exchange rate Finance field and capital market 1. Trade From 1979 to 2006,the total trade between China and US has increased 106 –fold ,its growth rate has averaged 18.9% per annum! In 2006, US was the second largest trade partner of China , the first largest export market, the sixth import origin place, and the third tech. import origin place. In 2007 US was still the second largest trade partner of China, it had 13.9% shares of total foreign trade in China. But, US has become the second largest export market of China ! Table 7 term year The data of China-US trade in recent 3 years unit:billion Total trade amount Export to US Growth rate amount Growth rate Import from US amount Growth rate 2005 211.63 24.78% 162.90 30.4% 48.73 9.1% 2006 262.68 24.12% 203.47 24.9% 59.21 21.8% 2007 302.08 15% 232.70 14.4% 69.38 17.2% Source: China customs - customs statistics Table 8 the trade between China and main trade partner (2005-2007) unit:billion Total trade year 2007 2006 2005 country EU USA Japan HK Southeast union EU USA Japan HK Southeast union EU USA Japan HK Southeast union export amount growth amount import growth amount growth balance 356.15 302.08 236.02 197.2 27% 15% 13.9% 18.7 245.19 232.70 102.07 184.4 29.2% 14.4% 11.4% 18.8 110.96 69.38 133.95 12.8 22.4% 17.2% 15.8% 18.9 134.23 163.32 -31.88 171.6 202.6 26 94.2 32.1 108.4 21.0 -14.2 272.3 262.7 207.3 166.2 25.3 24.1 12.4 21.6 182.0 203.5 91.6 155.4 26.6 24.9 9.1 24.8 90.3 59.2 115.7 10.8 22.7 21.8 15.2 -11.8 91.7 144.3 -24.1 144.6 160.8 23.3 71.3 28.8 89.5 19.4 -12.8 217.3 211.6 184.5 136.7 22.6 24.8 9.9 21.3 143.7 162.9 84.0 124.5 34.1 30.4 14.3 23.4 73.6 48.7 100.5 12.2 5.0 9.1 6.5 3.6 70.1 114.2 -16.5 112.3 130.4 23.1 55.4 29.1 75.0 19.1 -19.6 2. Investment (1)U.S. Enterprise invest in China U.S. started to invest directly in 1980. At the beginning of 1990s, the investment of U.S. Enterprise had less than $0.4 billion per annum . In 1990, there were only 45 U.S. Enterprises. Table 9 U.S. enterprise invest in China:1986-2007 project year Actual investment proportion amount(billion % U.S. dollar) 0.3262 14.54 number proportion% 1986 102 6.81 1987 104 4.66 0.2628 11.36 1988 269 4.52 0.2360 7.39 1989 276 4.78 0.2843 8.38 1990 357 4.91 0.4560 13.08 1991 694 5.35 0.3232 7.4 1992 3265 6.7 0.5111 4.64 1993 6750 8.09 2.0631 7.5 1994 4223 8.88 2.4908 7.38 1995 3474 9.39 3.0830 8.22 1996 2517 10.25 3.4433 8.25 --cont’ project year Actual investment number proportion% amount(billion U.S. dollar) proportion % 1998 2238 11.3 3.8984 8.58 1999 2028 11.99 4.2159 10.46 2000 2609 11.67 4.3839 10.77 2001 2606 9.97 4.4332 9.46 2002 3363 9.84 5.4239 10.28 2003 4060 9.88 4.1985 7.85 2004 3925 8.99 3.9410 6.50 2005 3741 8.50 3.0612 5.07 2006 3208 7.73 3.0000 4.56 2007 2627 6.94 2.6262 3.50 --cont’ --cont’ --cont’ in recent five years, the number of projects invested and actual investment of U.S. enterprise has decreased gradually. By the end of 2006, 52,211 U.S. Investment enterprises actual accumulated investment reached $54 billion 8.78% and 7.87% share of total FDI In 2007,those two proportions had decreased to 6.94 % and 3.5% respectively. By the end of July, 2007, accumulated project 53,754, actual accumulated investment $55.42 billion Table 10 industry distribution of U.S. investment in China (2004-2006) New set up corporate industry year number Actual investment prop(%) amount(million prop(%) U.S. dollar) 2004 agricultur e Manufactur e , mining and extraction service 2005 79 2.11 40 1.31 2006 62 1.93 27 0.95 2004 2669 68 2773 70.4 2005 2403 64.23 2287 74.70 1926 59.87 1965 58.58 2004 1150 29.3 1057 26.8 2005 1259 33.65 734 23.98 2006 1217 37.97 873 30.47 2006 ---cont’ The basic aim is to produce in China and sell in China globalization strategy In 2002 and 2003, the U.S. enterprise’s investment in commerce, finance, insurance and real estate in China has increased obviously The characteristics of U.S. investment in China ――multinational companies are main participants. ――purchasing from international market. ――production base in China, sold in China market. ――pay attention to localization business. ――business performance is all right. The performance of U.S. enterprise investment in China 2004: Investment Return rate :19.2% (the IRR of its whole world was only 10.1% ) 2005: U.S. enterprises in China earned profit about $3.0 billion 81% U.S. enterprise in China earned profit. --cont’ (2)China’s invest to U.S. China’s outward FDI is relatively small! Table 11 China’s non-finance FDI to North America (20032006) unit:million U.S. dollar. year flow stock 2003 65.05 502.32 2004 119.93 665.20 2005 231.82 822.68 2006 198.34 1237.87 Source: www.fdi.gov.cn By the end of Jun. 2007,China’s FDI to U.S. had only $1.036 billion! 3. Exchange rate Before exchange rate reform, i.e. July. 21, 2005, $1 = 8.2765yuan Table 12 Chinese currency exchange rate (average value, exchange U.S. dollar) year 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 yuan/us dollar 1.5549 1.4984 1.7050 1.8925 1.9757 2.3270 2.9366 3.4528 3.7221 3.7221 3.7651 4.7832 5.3233 5.5146 year 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 yuan/us dollar 5.7620 8.6187 8.3510 8.3142 8.2898 8.2791 8.2783 8.2784 8.2770 8.2772 8.2770 8.2765 8.0759 7.8238 --cont’ Fig. 3 The reform of Chinese currency exchange rate On July. 21,2005, China decided to reform its exchange rate ――give up pegging US dollar and set consult a basket of currencies. ――Chinese currency revalue 2%, from 8.2765 yuan/us dollar to 8.11yuan /us dollar . ――Chinese currency exchange rate was decided by the central rate set by a basket of currencies(fluctuation 0.3%) Table 13 Chinese currency exchange rate change since reform (2005.07.21 — 2008.04.14, selected date) date 2005/7/21 Exchange rate(yuan /us dollar) 8.1100 2005/12/30 8.0702 2006/6/30 7.9956 2006/12/29 7.8087 2007/6/29 7.6155 2007/9/28 7.5108 2007/12/28 7.3046 2008/2/1 7.1903 2008/3/3 7.1058 2008/3/28 2008/04/14 7.0137 6.9996 --cont’ Fig.4 --Cont’ Since exchange rate reform, Chinese currency is appreciating continually with a faster speed. In theory, Chinese currency appreciate would decrease adverse balance of US’ trade to China. But in fact, this effect is very limited. From Jul. 21, 2005 to Mar. 28, 2008, 8.11yuan/us dollar → 7.01yuan/us. Dollar, appreciated accumulatively by 15.7%. But, during this period , US’ adverse balance to China has not decreased! 4. Finance field and capital market China is gradually opening Finance field and capital market. More and more US’s finance institution go into China’s capital market directly or indirectly by all ways. More and more US’s enterprise are holding or controlling the shares of listed companies in China through capital market, or by making M&A. -- 17 US’s finance and investment institutions obtained the QFII. -- 6 US’s investment companies held the shares of fund management companies. -- 25 US’s enterprise are holding or controlling the shares of China’s enterprises. Table 14 List of US’s QFII Companies in China No. Name of QFII (USA) Date approved Rations approved (100 millions) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Morgan Stanley &Co. International Limited Citigroup Global Markets Limited Goldman, Sachs & Co. J.P. MORGAN Chase Bank Merrill Lynch International Lehman Brothers International Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation INVESCO Asset Management Limited Templeton Asset Management Ltd Goldman Sachs Asset Management Intl. JF Asset Management Limited AIG Global Investment Corp. AMP Capital Investors Limited 2003.06.05 2003.06.05 2003.07.04 2003.09.30 2004.04.30 2004.07.06 2004.07.19 2004.8.4 2004.9.14 2005.05.09 2005.12.28 2005.11.04 4.0 5.5 3.0 1.5 3.0 2.0 1.0 2.5 2006.4.10 2 14. 15 Yale University 2006.04.14 Morgan Stanley Investment Management 2006.07.07 Intl. 0.5 2.0 16 17 Stanford University GE Asset Management Incorporated 0.5 2.0 2006.08.05 2006.08.05 2.0 1.5 0.5 Table 15 US’s enterprise are holding or controlling the shares of China’s enterprises US’s enterprise The Blackstone Group Synnex Group Carlyle Asia Partners II Prudential Ins. Co. Anheuser-Busch Limited Best Buy China’s enterprises 中国蓝星集团 中国万网 扬州诚德钢管 深圳怡景中心城 唐山啤酒厂 江苏五星电器 Goldman Sachs Group Pacific Alliance Group 中国工商银行 好孩子集团 2005 FedEx Carlyle Group 大田快递 徐工机械 2004 Bank of America Corp Monster Morgan Stanley 中国建设银行 中华英才网 永乐家电 Amazon.com Cendant Travel Group Anheuser-Busch Limited P&G 卓越有限公司 中青旅电子商务 哈尔滨啤酒集团 宝洁(中国)有限公司 Kodak New Bridge Capital Ltd Anheuser-Busch Limited General Motors Emerson Electric 乐凯胶片 深圳发展银行 青岛啤酒 上汽五菱汽车 安圣电气有限公司 20% 15% 20% 34% 100% IDT 新涛科技有限公司 Ford Motor PPG 江铃汽车 南昌市化工原料厂 100% CMOS 、 semiconductor 20% auto 100% Charcoal year 2007 2006 2003 2002 2001 2000 Share(%) 20% >50% 49% 50% 100% 51% 4.93% 67.5% 50% 45% Industry chemistry network Steel tube Real estate beer Home electronic 银行业 Child’s goods express Expert equip. 8.19% bank 45% network 20% Home electronic 100% EC 40% Tour service 29.6% beer 100% consumable chemistry bank beer auto communication --cont’ In recent 5 years, more and more China’s enterprises go to overseas for listing and financing. By the end of 2007, 77 China’s enterprises had been listed in America , -- 19 companies listed in NYSE -- 30 companies listed in NASDQ -- Other 28 listed in OTC --cont’ China has also held the second largest US’s treasury bill. By the end of 2007, China held $346.6 billion US’s treasury bill(government bond). It had 8.1% share of total US’s treasury bill III. Relationship of China-US Economy & Trade: Problems 1. Basic features Larger complementary Processing trade is main part of China-US trade The volume of U.S. invested in China is more than that of China invested in U.S. China has become the center of world assembling, “made in China” is also “made in world ”. The degree of trade imbalances remains large. In goods trade, China has trade surplus to US In services and capital investment trade, China has adverse trade balance to US. Trade surplus is in China, while profits is in US. For example: The report published by three researchers in UC showed Apple Company sold iPod at $299 each one. Its cost and profit were as following: Sell price: $299 Cost: purchased main parts $73 (from Japan ) purchased other parts $60 (from other country) assemble $3 (in China !) Profit: $163 (in US) Apple Company gained $80 Other $83 2. The problems of China-US Economy & Trade larger balance of trade, i.e. trade imbalances! Chinese currency exchange rate: marketization China’s intellectual property rights (IPR) China’s safety of product China’s capital market: further opening US: trade problem is being politicized US’s export controlling over China US’s protectionist policy on trade 四、Prospect and Suggestions 1. Prospect a. Complex and uncertainty b. Chinese currency (Renminbi) will continue to appreciate c. Trade friction and disputed will still increase. d. Energy resources and environment protection will become new topics e. Trade balance (trade imbalances) of China-US will reduce gradually f. China’s finance ,service and infrastructure industry will open further to world. g. China’s reform and opening has its irreversibility! h. China and US economy will be face up long-term structural challenges. 2. Suggestions China is the world’s third largest trading nation. With the largest population with over 1.3 billion people and one of the world’s fastest growing economies China has the largest potential and realistic market U.S. is the second largest trade partner of China and the second largest export market of China . China is the fourth largest trade partner of U.S. --cont’ The relationship of China-US economy and trade is and should be mutual beneficial and reciprocal relation in nature! From the view of Game theory, If cooperate , then both will obtain the benefits; If not cooperate, then both will lose! U.S. should a. Adjust and control excess import. b. Implement export free, cancel export restrict ions to China. c. Adjust trade policy and system, improve outdated national trade act. Further liberalize trade . d. Enlarge opening of industry and tech. market to other countries e. Not politicize the trade problems China should Continue to adjust economic structure. Continue to deepen reform Reform and adjust national policy and system about distribution Change the relationship of consumption, investment and saving. Decrease saving rate. Further Enlarge import. Control export,adjust and change export policy. Make Renminbi exchange rate more marketable Further reform the financial system. Enhance protecting for IPR. Cancel some government subsidy for export enterprise Any Questions? Thank You ! Contact Me e-mail: hxyao5807@sina.com hxyao@lnu.edu.cn Tele: (0) 818-677-2446