Pedagogical Goals - slisonlinelearningguide
advertisement

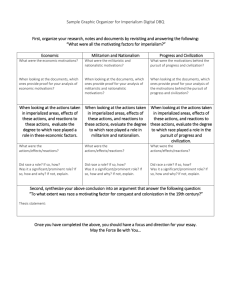
PEDAGOGICAL GOALS: Face to Face and Online Question: If you wanted to understand Keynesian economic theory what would you do? In 1936:? •Read: “The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money” by John Maynard Keynes In 1973:? •Read Keynes •Read books about Keynesian theory •Look it up in an encyclopedia In 2010:? Google it!, search on Amazon and let it suggest other readings, search scholarly research websites, read Wikipedia and encyclopedias, watch various documentaries and movies, even watch YouTube! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d0nERTFo-Sk Question: What is the future of education at SLIS? “It’s time that higher education was held to a higher standard” Kaplan University Question: What are the educational goals of SLIS? To teach students to: Analyze the changing cultural, educational, and social roles and responsibilities of librarians and information professionals, and the place of the library and other information agencies in society; Select, acquire, and process information resources for libraries and other information agencies' Interpret and effectively utilize general and specialized information sources and bibliographic tools; Organize and describe information materials in a manner that will facilitate and enhance utilization of resources; Interpret and apply basic management principles; Describe advances in technology pertinent to the acquiring, organization, and dissemination of information and apply this knowledge to libraries and other information agencies; Identify, analyze, evaluate, and conduct research in the field of library and information science and relate findings to the solution of problems in the profession; Analyze the information needs and use patterns of specific user populations, describe the place of the library in the information transfer process, and the design of information services to meet user needs. What pedagogical strategies will help us reach our educational goals? Discussion: Important Pedagogical Concepts Encourage deep learning Challenge mental models Learn to be a facilitator as well as an teacher Design to encourage personal motivation Understand and let students use the opportunities that technology brings Understand the importance of feedback Encourage creativity Provide active learning opportunities Deep Learning and Mental Models Learning for the sake of understanding meaning Design assignments and assessments that reward those willing to think beyond the obvious answers rather than the surface or strategic learner Challenge mental models Mental Models Developing new mental models Middle Ages Tech Support http://www.youtube.com/profile?user=oculture#p/f/ 98/LRBIVRwvUeE Personal Motivations Creating a Social Presence Autonomy and Competence Membership and Generosity Personal Motivations Creating a Social Presence If you had to make an “instant” connection with someone, how would you do it?” Personal Motivations Autonomy and Competence Intrinsic motivations are those in which the activity itself is the reward. Extrinsic motivations are those in which the reward for doing something is external to the activity, not the activity itself. Deci identified two intrinsic (personal) motivations: 1. The desire to be autonomous (to determine what we do and how we do it). 2. The desire to be competent (to be good at what we do). Personal Motivations Membership and Generosity Why does Wikipedia exist? Learn to be a facilitator as well as a teacher Sage on the Stage vs Guide on the Side Encouraging peer to peer interactions Encouraging active, deep learning rather than rote memorization and surface/strategic learning. Understand the importance of feedback Feedback: Information about how we did in light of some stated goal. Guidance: Instructions for future direction Evaluation: Summary of whether work has been deemed successful. Encourage Creativity The decline of creativity in America Example of encouraging creativity in Akron, Ohio Treffinger: Creative enterprise Mess-finding Data-finding Problem-finding Idea-finding Solution-finding Acceptance-finding Understand and let students use the opportunities that technology brings “Human motivations change little over the years, but opportunity can change a little or a lot, depending on the social environment. In a world where opportunity changes little, behavior will change little, but when opportunity changes a lot, behavior will as well, so long as the opportunities appeal to real human motivations.” Clay Shirky “Cognitive Surplus” Active Learning Students are given an opportunity to take a more interactive relationship with subject matter Students are asked to generate and not just receive knowledge Knowledge is Constructed, not received Designing an online course https://vista8.kent.edu - Planning Online Course Discussion: How do we incorporate our pedagogical goals in the classroom? Look at established processes. Share reference materials http://slisonlinelearninguide.iwiki.kent.edu Establishing a Community of Practice to share ideas.