Chapter 4: Structure and Function of the Cell…
advertisement

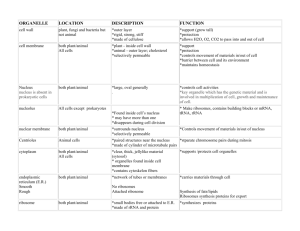
Structure and Function of the Cell Section 7.1 Introduction to the Cell… 1+ cell(s)…. make up EVERY living thing… (unicellular or multicellular) cells contain…. atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids cells… carry out chemical reactions…. enzymes speed these chemical reactions A cell is… - the smallest unit of matter that can carry on LIFE PROCESSES Discovery of the cell was made possible by the development of the MICRO-SCOPE. The study of the cell is…. known as CYTO-LOGY or CELL BIOLOGY. A Brief History… 1500’s - Europe - the first lenses were used 1600’s - telescope and microscope were invented Robert Hooke (1660’s) observed dead (plant) cells from cork • coined the term “cell” • Anton Van Leeuwenhoek (1670’s) observed living (animal) cells o microscope maker o made detailed descriptions and drawings of cells o “father of microbiology” o More Scientists… SCHLEIDEN – Botanist… all plants are made of cells SCHWANN – Zoologist… all animals are made of cells VIRCHOW – Physician… cells come from existing cells These ideas contributed to the Cell Theory….. The Cell Theory (1800’s) 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. All cells come from pre-existing cells. 3.The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. CELLS PROKARYOTIC or EUKARYOTIC PRO-KARYOTIC CELLS simple (primitive) few specialized functions bacteria LACK a nucleus (but still have DNA) LACK membrane-bound organelles known as “prokaryotes” EU-KARYOTIC CELLS complex many specialized functions plants, animals, fungi and protists have a nucleus (DNA enclosed within a membrane) have membrane-bound organelles including … mitochondria, golgi, lysosomes, vacuoles, ER, … known as “eukaryotes” What is the Endo-symbiont Theory? ENDO - “within/inside” SYMBIONT – “living together” explains the origin (development) of eukaryotic cells It is believed that many of the organelles (including mitochondria and chloroplasts) were actually prokaryotic cells that came to live inside larger prokaryotic cells in a beneficial relationship, thus leading to the development of eukaryotic cells. There are two prokaryotic cells One cell "engulfs" the other cell A double membrane can be found inside HYPERLINK – animation: endosymbiosis http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/9834092339/student_view0/chapter4/animation _-_endosymbiosis.html Classification of Cells CELLS EUKARYOTIC PROKARYOTIC Bacterial cells Animal cells Plant cells Fungal cells Protist cells What are the differences between animal and plant cells? ANIMAL PLANT no vacuoles or small no cell wall centrioles ◦ visible during cell division large vacuoles cell wall ◦ outside the cell membrane plastids ◦ chloro-plasts ◦ chromo-plasts ◦ leuco-plasts Review Video 4 Common Features of ALL CELLS… 1) plasma/cell membrane 2) ribosomes 3) cytoplasm 4) genetic material (DNA) Cell Diversity 1. size 2. shape - reflects function 3. internal organization What is an organelle? “a little organ” a cell part that performs a special function *most ORGANELLES…. are surrounded by a membrane (a wrapping) “membrane- bound organelles” mitochondria, golgi bodies, lysosomes, chloroplasts, vacuoles,… *some ORGANELLES …..like RIBOSOMES are not surrounded by a membrane In our study of cells, we will focus primarily on eukaryotic cells…because we are eukaryotes, as well as most living things Main Parts of the Eukaryotic Cell 1.nucleus – contains DNA – control center of cell 2. plasma (cell) membrane – outer boundary of the cell 3. cytoplasm – “jelly-like” material – site of many chemical reactions 4. organelles - “little organs” – perform special functions PLASMA (CELL) MEMBRANE – “fence” thin, flexible, fluid barrier SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE… regulates what enters and leaves the cell water, O2, CO2, glucose, wastes… primary function is HOMEOSTASIS maintains OSMOTIC (water) BALANCE PLASMA (CELL) MEMBRANE – made of…. (PHOSPHO)LIPIDS…. barrier between cell and external environment remember…water (polar) and lipids (nonpolar) don’t like each other 2 layers of lipids – LIPID B-ILAYER PROTEINS…. no specific arrangement some provide structural support = structural proteins some are Transport/Carrier proteins = transport/carrier proteins CARBOHYDRATES…. PLASMA (CELL) MEMBRANE pattern of lipids and proteins is constantly changing CYTOPLASM • • • area between the cell membrane and nucleus includes jelly like material (CYTOSOL) and organelles made of water, proteins + carbohydrates FUNCTIONS… • site of chemical reactions • cytoplasmic streaming (cyclosis) = movement of cytoplasm within the cell CYTOSKELETON - “the cell’s skeleton” SUPPORT, STRUCTURE, SHAPE network of protein fibers (microtubules and microfilaments) involved in…. ◦ cell movement ◦ cell division ◦ cytoplasmic streaming (cyclosis) NUCLEUS “brain” nuclear envelope/membrane: surrounds and protects the nucleus – of lipids + proteins nucleoplasm: jelly like material chromatin: thin strands of DNA + protein nuclear pores: allow for the passage of materials nucleolus: ribosome synthesis NUCLEUS FUNCTIONS…. stores genetic information controls cell division forms chromosomes during cell division RIBOSOME(S) - “factories” UNIQUE!!! – NO MEMBRANE • small, spherical, numerous • PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • made of RNA & protein • RIBOSOMES can be….. 1. free in the cytoplasm 2. attached to Rough ER Membrane-bound Organelles…. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Golgi Vacuole Lysosome Chloroplast Mitochondrion These are surrounded by an ENCLOSING or SEPARATING membrane that acts as a selective barrier (similar to that of the cell membrane) of lipids embedded with proteins ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) “intracellular highway” • movement of materials within the cell • near the nucleus • made of protein Rough ER • has ribosomes • protein synthesis Smooth ER • no ribosomes • breaks down toxins • lipid synthesis GOLGI APPARATUS or GOLGI BODY “post office” flattened stack of membranes made of protein process, package, secrete substances packages = VESICLES works with the ER VACUOLE(S) – “closet” storage site for wastes, food, enzymes, water,… animal cells – if vacuoles are present, they are small plant cells – large vacuoles Contractile Vacuole – special type of vacuole that stores excess water and pumps its out of the cell LYSOSOME(S) “stomach + recycling center” spherical contain digestive enzymes intracellular digestion digests… ◦ food particles ◦ bacteria and foreign particles (think of Lysol) ◦ worn, damaged and old cell parts HYPERLINK – animation: lysosomes http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/9834092339/student_view0/chapter4/lysosomes.html CENTRIOLE(S) small; usually found as a pair of microtubules (protein) function during cell division near the nucleus in ANIMAL cells PLASTIDS Chloro-plasts ◦ green; photosynthesis Chromo-plasts ◦ other colors; photosynthesis Leuco-plasts ◦ clear; food storage CHLORO-PLAST(S) PHOTOSYNTHESIS - captures light energy and convert it into chemical energy (food; usually sugars) green pigment – CHLOROPHYLL found in PLANT cells, some protists and some bacteria UNIQUE !!! have their own DNA + ribosomes Chromo-plasts • contain pigments other than chlorophyll • food production • capture the sun’s energy Leuco-lasts • clear; colorless • food storage – as starch (carbohydrate) MITOCHONDRION “powerhouse” cell’s that need a lot of energy have many mitochondria… like MUSCLE CELLS • • provide energy for the cell’s activities process of CELLULAR RESPIRATION in which the chemical energy stored in food is converted into ATP UNIQUE!!! - have their own DNA + ribosomes CELL WALL • • • • • • plants, fungi, some protists + some bacteria composition varies rigid outside cell membrane protection and support pores - some substances enter and exit CILIA + FLAGELLA - ‘hair-like” extensions from the cell surface - composed of protein microtubules - used in the movement of cells or in stationary cells to move substances along the cell’s surface Flagellum or Flagella • long, tail-like; few Cillium or Cilia • short; numerous • like oars of a boat Cell = City Cell Part ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Mitochondria Nucleus Plasma membrane ER Cilia/Flagella Lysosome Vacuole Analogy?