course outline dsm 2315
advertisement

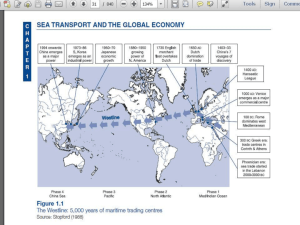
COURSE OUTLINE DSM 2315 Shipping and Transport Logistics Management 1. Name of subject: Shipping and Transport Logistics Management 2. Subject Code: DSM 2315 3. Introduction: • To ensure the student encompasses the cognitive process which is remembering and explaining the types of ships for specific cargo transportation requirements by applying basic concepts of ship design and classification, includes they learn to distinguish the role played by the various parties include in shipping and transportation industry. • To understand the packaging process of cargo to be carry on board of the ship. • To learn the elements of vessel and port operation in shipping industry. 4. Credit Value: 3 Credits. 5. Prerequisite (If any): None. 6. Objective: 7. Learning Outcome: • At the successful competitions of thus subject, students are expected to: Define the suitability of different types of ships for specific cargo transportation requirements of ship design and classification • Identify the roles played by the various parties in shipping and transportation industry • Describe the packaging process of cargo to be carried on board the ship • Discuss the vessel and port operation elements in context of shipping management 8. Assessment Method and Types • Quiz 10% - written • Test 15% - written • Assignment 25% - written (15%) & oral (10%) • Final Examination 50% - written 9. Contact Hours Lectures Tutorial SDL Total 28 Hours 14 Hours 78 Hours 120 hours 10. Course Outline Topic A. Introduction to Basic Ship Design, Layout and Terminologies 1.1 Elementary ship design and layout. 1.2 An overview of different ship types (Bulk / Container carriers, tankers, specialist ships, passenger vessels). 1.3 Measurement of ships and maritime terminologies. B. Parties involved in Shipping and Transportation 2.1 Roles of Non-Vessel Operating Common Carrier (NVOCC) 2.2 Freight Forwarder 2.3 Third Party Logistics (3PL) 2.4 Fourth Party Logistics (4PL) 2.5 Ship Brokers 2.6 Shipping Agents C. Type of Cargo to be Carry Onboard Ship. 3.1 Types and characteristic of cargo 3.2 Dangerous goods 3.3 Deck cargoes 3.4 Individual abnormal load (AIL) 3.5 IMDG Labels D. Packaging of Cargo. 4.1 Functions of packaging 4.2 Types of packing 4.3 Unitized, palletized and container cargo 4.4 Packaging of dangerous 4.5 Marking of goods E. Introduction to Vessel Operation 5.1 Introduction to rules of the roads 5.2 Navigation aids 5.3 Berthing, anchoring and mooring arrangements. 5.4 Watch keeping arrangement 5.5 Crew composition and functions F. 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Introduction to Ports Operations Ports and terminals Terminal design Port equipment and characteristics Harbor configurations L T SDL 4 2 13 5 3 13 4 2 13 4 2 13 5 2 13 6 3 13 6.5 Pilotage 6.6 Port controls 6.7 Tugs 6.8 Fresh water supply 6.9 Bunkering 6.10 Shipchandling Sub Total Total Grand Total 28 14 42 120 78 References • Branch, Alan Edward. (2007). Elements of Shipping. Routledge, New York • Lun, Lai & Cheng. (2006). Shipping and Transport Logistics. McGraw Hill, Singapore • Lloyd’s Practical Shipping Guides: Port Management and Operations (2008), Informa, London • The Admiralty Manual of Navigation Volume I (2008), The Nautical Institute, London Additional references supporting the course • Shipping Law. Institute of Chartered Shipbrokers. Witherby. 2011 • Reeds sea transport: operation and economics (Reeds professional). Patrick M. Alderton. A & C Black Publishers Ltd. 2011 11. Transferable Skill Domain 11.1 Problem solving The three components of this skill are the stage involved in tackling issues and problem in personal, social, and work content. There are often used in sequence and repeatedly. Each component can also be a focus of activity in its own right. 11.1.1 Critical Thinking Critical thinking is about using analysis and reasoning to make decision and to created or suggests ideas, course of actions and strategies. 11.1.2 Planning and Organizations. Planning and organizations is the ability to plan task, taking account of available resource and to manage the task to completely. 11.1.3 Reviewing and Evaluations. Reviewing and Evaluations is the ability to reflect on and review the process of tackling issues and problem, to evaluate the outcome and to identify the alternative strategic might have been use. 11.2 Communication Communication skill underpins almost all personal, social, learning and working activity. They are essential in clarify your though, in interacting and conversing effectively with other also conveying information, feeling and opinions. 11.2.1 Oral communications Oral communications mean being able to take part in discussions and make presentations also interact with your audience. 11.2.2 Written Communications Written communications is the ability to write and respond to writing. 11.3 Numeracy To cope with the demand of everyday life including life and study, people need to be comfortable with number and graft, symbol also calculator. The skill needed for this involved interpretation, process, Transferable Skill communications, qualifications and spatial information. 11.3.1 Using Graphical Information This is the ability to interpreted communications quantifiable information that is given in writing, diagram or picture. 11.3.2 Using Number This ability to apply numerical and other relevant mathematical and statistical skill 11.4 Information and Communication Technology Information and communications technology is concern with the electronic collection, organizations, presentations and communication of information. IT encompasses all media typed and formats as well relevant tools. The skill focuses on the ability to use information and communications technology to process information in a variety of way which will useful work and at home. It is about developing IT specialized who will act as first line support for other or install specialist system. 11.4.1 Accessing Information This is the ability to use information and communication technology to support a range of information-accessing activities. 11.4.2 Providing/Creating Information This is the ability to used information and communications to provide, create and process information. 11.5 Working With other The fact that working with others is a skill emphasizes the important of co-operations and teamwork on social, learning and work situations. Working with other has two components: i. Working Co-operatively with other. ii. Review Co-operative Contribution. Mean while achieving a shared goal is the focus, co-operations with other should be development through all stage of any collaboration. Reviewing your own contribution and learning through reflections also has a wider applications to personal development. 11.5.1 Working Co-operative with other This is about to use interpersonal skill appropriated, to recognize and value the roles of other people ,taking responsibility for your own contributions and support co-operative working in appropriate way 11.5.2 Reviewing Co-operative Contribution This is the ability to discuss the process of working cooperatively with other people, reflecting on and renewing the collaborations. This might include resolving issues and handling other people behaviors. Learner should evaluate the outcome ,identify the value of their contributions, also reflect on any personal learning and development that may need to enhance their contributions to future collaborations work.