Personality: refers
to an individual’s
unique
constellation of
consistent
behavioral traits
Used to explain
1)consistency in
behavior and
2)distinctiveness of
behavior
Personality trait: a
durable disposition
to behave in a
particular way in a
variety of situations
Cattell concluded
that personality can
be described
completely by
measuring just 16
traits
McRae and Costa
1) Openness to
experience
2)
Conscientiousness
3) Extraversion
4) Agreeableness
5) Neuroticism
Def: include all the
diverse theories
descended from the
work of Sigmund
Freud, which focus
on unconscious
mental forces
Attempts to explain
personality,
motivation, and
psychological
disorders by focusing
on childhood
experiences, on
unconscious motives,
and methods used to
cope w/sexual and
aggressive urges
3 parts:
1) Id: primitive, instinctive component;
operates according to pleasure principle
2) Ego: decision-making component;
operates according to the reality principle
3) Superego: moral component; incorporates
social standards about what represents right
and wrong
Conscious: whatever one is aware of at a
particular point in time
Preconscious: material just beneath the
surface of awareness that can be easily
retrieved
Unconscious: thoughts, memories, and
desires that are well beneath the surface of
conscious awareness but that nonetheless
exert great influence on behavior
Freud: people’s
lives are dominated
by conflicts that
center on sexual
and aggressive
impulses
Sexual and
aggressive desires
are thwarted more
often
Lingering conflicts
can produce anxiety
Worry about: 1) id
going out of control
and creating negative
consequences or
2)superego out of
control creating guilt
about a real or
imagined
transgression
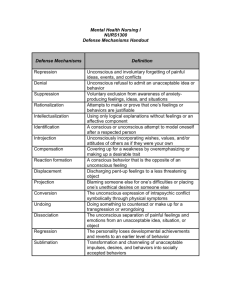
Def: largely
unconscious
reactions that
protect a person
from unpleasant
emotions such as
anxiety or guilt
Rationalization: creating false but plausible causes to
justify unacceptable behavior
Repression: keeping distressing thoughts and
feelings buried in the unconscious
Projection: attributing one’s own thoughts, feelings,
or motives to another
Displacement: diverting emotional feelings (anger)
from original source to a substitute
Reaction Formation: behaving opposite of what you
feel
Regression: reverting to immature behavior
Identification: bolstering self-esteem by forming an
imaginary or real alliance with some person or group
Def: developmental
periods w/a
characteristic
sexual focus that
leave their mark on
adult personality
Fixation: failure to
move forward from
one stage to
another as
expected
Oral stage: 1st year;
erotic focus is the
mouth
Anal stage: 2nd
year; erotic
pleasure from
bowel movements
Phallic stage: c. age
4; erotic focus on
the genital; selfstimulation
Latency stage:
expanding social
contacts beyond
the immediate
family
Genital stage:
refocus on genitals,
channeled toward
peers
Unconscious has 2
layers
1) Personal
unconscious:
repressed or
forgotten material
2) Collective
unconscious: a
storehouse of latent
memory traces
inherited from
people’s ancestral
past
People share an
unconscious
Archetypes:
emotionally
charged images
and thought forms
that have universal
meaning
1st to describe
Introverts:
preoccupied w/the
internal world of
their own thoughts,
feelings, and
experiences
Extraverts:
interested in
external world of
people and things
Striving for
superiority: a
universal drive to
adapt, improve
oneself, and master
life’s challenges
Compensation:
involves efforts to
overcome imagined
or real inferiorities by
developing one’s
abilities
Excessive feelings
of inferiority leads
to an inferiority
complex
People
overcompensate
and pursue status
and power over
others
Unconscious forces can influence behavior
Internal conflict often plays a key role in
generating psychological distress
Early childhood experiences can have
powerful influences on adult personality
People do use defense mechanisms to reduce
unpleasant emotions
Criticisms:
Poor testability—ideas too vague to test
Inadequate evidence
Sexism—a bias against women exists