Infection Control in Long Term Care Settings
advertisement

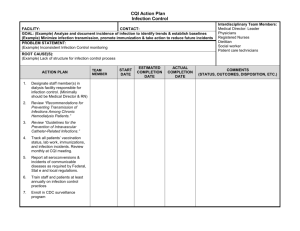
Infection Control in Long Term Care Settings Moderator: Carol Goldman, RN, BScN, CIC Infection Control Consultant IFIC Board member, CHICA-Canada Expert Guest: Allison McGeer, MD, FRCP Director, Infection Prevention and Control Dept. Mount Sinai, Hospital Toronto, Canada Infection Control in Long Term Care Settings Thank you for sponsoring this workshop Infection Control in Long Term Care Settings Format for today’s workshop: • Define and review long term care (LTC) settings • Discuss common infections and outbreaks associated in LTC • Review surveillance in LTC • Work collaboratively in groups to review and present the elements of an IPC programme in LTC Infection Control in Long Term Care Settings • A facility that provides rehabilitative, restorative, and/or ongoing skilled care for those of all ages in need of assistance with activities of daily living – nursing homes – rehabilitation facilities, – Extended care situations – behaviour health, psychiatric, physical and mental challenges – long-term chronic care Infection Control in Long Term Care Settings The differences of Infection Control in a LTC vs. Acute Care • fewer resources • less expertise/increased turnover • multiple duties • diagnostic facilities • residence • medical record • limited research Infection Control in Long Term Care Settings • • • • urinary infections respiratory infections skin and soft tissue infections Outbreaks also occur frequently, and some facilities have a high prevalence of colonization of residents with antimicrobialresistant organisms. Infection Control in Long Term Care Settings • Prevalence of infection documented between 5.4 and 32.7 per 100 residents per month • Infection incidence rates have been documented between 1.5 and 9.4 per 1,000 resident days • An estimated 1.5 million infections occur annually in LTC facilities in the United States • Facility-acquired infections account for 30% of all hospital admissions from nursing homes • Are the most common immediate cause of death in nursing home residents • NURSING HOMES, May, 2006 by Linda L. Spaulding Infection Control in Long Term Care Settings • 3 yr study looking at respiratory infections in Toronto • 0.42 infections per 1000 resident-days • Outbreaks occurred year round, with no seasonal pattern • Pneumonia developed in 72 (15%) • 58 (12%) required transfer to hospital • The case-fatality rate was 8% (37/480) CMAJ, April 2000, McGeer et al Infections in residential long term care for the elderly in Canada, 1994-6 Rate of infection per 1000 resident days 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Respiratory Skin Gastro Urinary Prevalence of infections in Italian long term care facilities 30 25 20 Percent of 15 residents 10 5 0 Lower resp Skin Conjunctivitis Urinary Infection Control in Long Term Care Settings questions you need to ask Who are your patients and what kind of infections are they most at risk of? - slide on NH distribution - but it depends on populations Are these infections sporadic, or do they occur as outbreaks? What opportunities are there to prevent disease?