Cell Membrane - Solon City Schools
advertisement
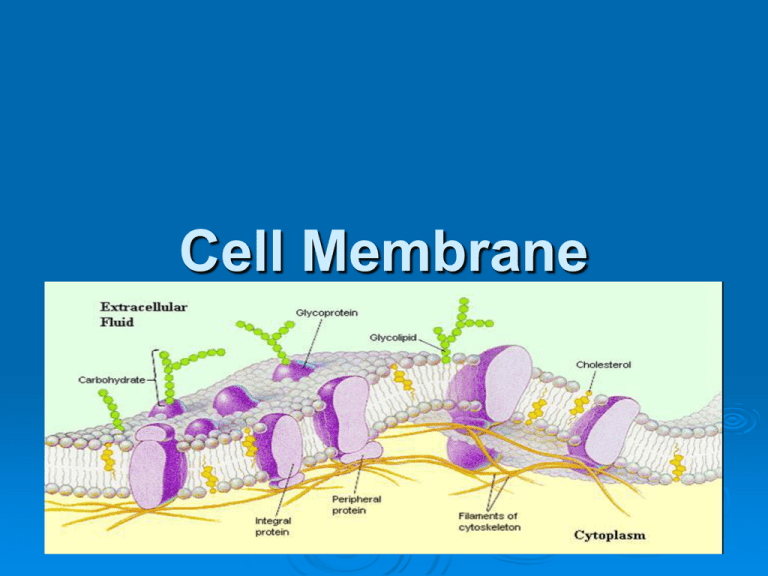
Cell Membrane Function of Cell Membrane Separates the cell’s contents from materials outside the cell Regulates what moves in and out of a cell *without the cell membrane to contain the substances the cell needs for life, the cell would die. Structure of Cell Membrane -composed of groups of organic compounds (glycolipids, glycoproteins, proteins, cholesterol, and phospholipids) Phospholipid – shaped like a head with 2 tails -made from a phosphate group connected to 2 fatty acid tails (forms a double layer called a lipid bilayer) Structure of Phospholipid Why are the phospholipids arranged tail to tail? -b/c water is inside and outside the cell phosphate group is hydrophilic (polar) end -attracts water fatty acid tail end is hydrophobic (nonpolar) -repels water Arrangement of phospholipids “tail to tail” Polar vs. Nonpolar Polar- positive and negative ends (b/c electrons are not shared equally) Ex. Water Nonpolar- does not have oppositely charged ends (atoms share electrons equally) Arrangement of phospholipids “tail to tail” due to water inside & outside the cell Fluid Mosaic Model of Cell Membrane -lipid bilayer is not strong & firm like a hard shell, but it is fluid like a soap bubble (often called a fluid mosaic model) -individual phospholipids, arranged side by side, float within the bilayer (cholesterol prevents phospholipids from sticking together) Structure of Cell Membrane -nonpolar interior zone- true barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings many polar particles like sugars, proteins, ions, & most cell wastes cannot cross this zone b/c they are repelled by the nonpolar region What’s in the cell membrane? Solution? -passageways through the barrier that enable the cell to regulate what substances go in and out. Cell Surface Proteins- proteins embedded within the plasma membrane of cells Proteins- 50% to 70% of cell membrane Types of Cell Surface Proteins Proteins- act as “gates” to the cell interior, transporting food & other molecules (sugar, proteins, ions) in & wastes out Channel Types of Cell Surface Proteins Receptor proteins- information receivers they are the informers of the cell, gathering information about the cell’s surroundings *many hormones act by binding to specific receptor proteins Ex. Glycoproteins- combination of protein and carbohydrates Ex. Integral proteins- span entire range of cell membrane Types of Cell Surface Proteins proteins- “name tags of the cell” identifies what kind of cell it is (ex. Liver cell, heart cell, or brain cell) marker proteins have long exterior arms that often have carbohydrates attached to them Ex. Glycoproteins or glycolipids Marker Arrangement of cell surface proteins Cell Membrane Structure






