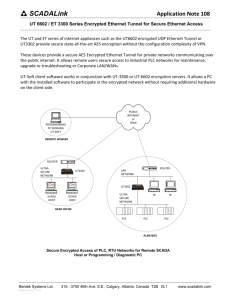
PLC,SCADA AND AUTOMATION Automation

PLC,SCADA AND AUTOMATION
Automation
the act of implementing the control of equipment with advanced technology; usually involving electronic
Hardware. "automation replaces human workers by machines"
•Increasing Productivity
• Increasing Quality
• Reducing Cost
• Increasing Safety in working conditions
Automation History
Manual
Control
Pneumatic
Control
Electronic
Control using
Logic Gates
Programmable Logic
Controller
Programmable Logic Controller
PLC is an electronics device which interface between input and output module using software logics such as on-off
, timing , counting , logical operations etc .
The PLC (i.e. Programmable Logic Controller) is a device that was invented to replace the necessary sequential relay circuits for machine control.
Examples:1. Allen Bradley
2. Siemens
Advantages of PLCs
Reduced space
Energy saving
Ease of maintenance
Economical
Greater life & reliability
Shorter project time
Easier storage, archiving and documentation
10
Major Components of a Common PLC
POWER
SUPPLY
From
SENSORS
Pushbuttons, contacts, limit switches, etc.
I M
N O
P D
U U
T L
E
PROCESSOR
O M
U O
T D
P U
U L
T E
To
OUTPUT
Solenoids, contactors, alarms etc.
PROGRAMMING
DEVICE
8
Major Components of a Common PLC
POWER SUPPLY
Provides the voltage needed to run the primary PLC components
I/O MODULES
Provides signal conversion and isolation between the internal logic- level signals inside the PLC and the field’s high level signal .
9
Central Processing Unit
Made of a microprocessor & a memory system
Reads the input, executes logic, performs calculations & controls the outputs accordingly
10
INPUTS
PUSHBUTTONS
PLC
OUTPUTS
CONTACTOR
MOTOR
LAMP
Ladder Logic
• Represents how electrical current flows through the devices to complete an electrical circuit
• Each electrical circuit in the diagram is considered a rung having two components
L2
Rung
L1
PB1 Stop
Power
Bus
PB2
Start
M1
Auxiliary
Holding Contact
Motor
M1
Power
Bus
12
Normally Open
(NO)
Normally Closed
(NC)
NO is true when the input or output status bit controlling the contact is 1.
NC is true when the input or output status bit controlling the contact is 0.
Coils
When a coil is energized it causes a corresponding output to turn on by changing the state of the status bit controlling the output to 1.
14
Rung
AND OPERATION
A B C both inputs A and B must be true (1) in order for the output
C to be true (1).
15
Rung
A
OR OPERATION
C
B
In the rung above, it can be seen that either input A or B is be true (1), or both are true, then the output C is true (1).
Rung
NOT OPERATION
A
C
In the rung above, it can be seen that if input A is be true (1), then the output C is true (0) or when A is (0), output C is 1.
AB PLC – Addressing I/O
FILE
LETTER
SLOT
NO
:
WORD
NO
. /
BIT
NO
I
I
:
:
1
1
O : 2 .
O : 2 .
.
.
1
0 / 0
(0 to 15)
/ 0 ,,
0 / 0 ,,
0 / 0 ,,
15
Addressing BINARY (Flag)
File
Letter
B3
B3
.
.
.
B3
File
Number
BIT
Number
: 0 / 0 (0 to 15)
: 1 / 0 ,,
.
.
.
.
.
.
: 15 / 15
16
Types Of Timers
three types of timer is available :
1. TON
2. TOF
3. RTO
22
Types Of Counters
• two types of counter is available:
1.CTU
2.CTD
23
Compare Blocks
• Equal(EQU)
• Not Equal(NEQ)
• Greater
Than(GEQ)
• Less Than(LEQ)
22
LADDER LOGIC EXAMPLE
SEQUENTIALLY OPERATING THREE
MOTORS WITH DELAY BY USING
TIMER
COADING OF
PROGRAM
Program using COUNTER
An Introduction to
S
CADA
Fundamentals and
Implementation
• Supervisory Control And
Data Acquisition
WHAT IS SCADA?
• SCADA stands for supervisory control and data acquisition. As the name indicates it is not a full control system, but rather focuses on the supervisory level
• A SCADA program normally runs on a PC and communicates with external instrumentation and control devices.
• It’s an optional device used in automation for continuous monitoring.
27
Common System Components
Sensors and control relays
Remote
Telemetry Units
SCADA
SCADA Master
Units
Communication
Network
28
Traditional Control
SC ADA ?
SCADA ?
S upervisory
C ontrol
Graphics and Batch processing
A nd
D ata
A cquisition
Archiving, Logging,
Access Control, Alarms
Data Server
9 - 12 Oct. 2000
Distributed database
Data Server PLC’s
PCaPAC'2000 - DESY
Field Bus
Control Programs
30
Features
Dynamic Process Graphics
Real Time & Historical Trends
Alarms
Recipe Management
Security
Device Connectivity
Scripts
31