Power Point
advertisement

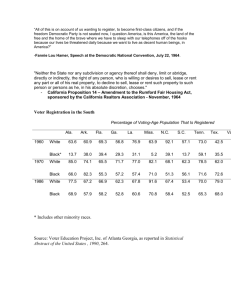
Chapter 8 LOCATE AND SET UP YOUR BUSINESS LESSONS 8.1 Choose a Retail Business Location 8.2 Choose a Location for a Non-Retail Business 8.3 Obtain Space and Design the Physical Layout 8.4 Purchase Equipment, Supplies, and Inventory ENTREPRENEURSHIP: Ideas in Action © SOUTH-WESTERN PUBLISHING Lesson 8.1 CHOOSE A RETAIL BUSINESS LOCATION GOALS Research retail location possibilities. Begin to select your location. LOCATION POSSIBILITIES Downtown areas Neighborhood shopping centers Community shopping centers Regional shopping centers Super-regional shopping centers Stand-alone stores Warehouses DOWNTOWN AREAS Advantages Central Likely to attract business shoppers Disadvantages Parking problems Distance from suburbs Crime Lack of evening shoppers NEIGHBORHOOD SHOPPING CENTERS Advantages Supermarkets and other businesses bring in customers Low rent Disadvantages Attracts only customers who live in area COMMUNITY SHOPPING CENTERS 1 or 2 Anchor Stores and 10 or more smaller stores Advantages Anchor stores bring in customers Moderate rent Disadvantages Distance is too great when convenience is important ANCHOR STORE Larger stores that advertise a lot and attract customers from the community EXAMPLES JC Penney Macy’s Wal-Mart K-Mart Kroger Walgreens REGIONAL SHOPPING CENTERS 3 or 4 Anchor Stores and 40 or more other stores Advantages Anchor stores bring in customers Walk-in traffic Attracts customers from a large area Disadvantages Distance is too great when convenience is important High rent SUPER-REGIONAL SHOPPING CENTERS Very large and have hundreds of stores. Advantages Huge number of customers Services a large area Disadvantages Very high rent Competition from many companies Distance is too great when convenience is important STAND-ALONE STORES Advantages Rent can be lower No competition next door Disadvantages No anchor store to attract customers Extra expense of advertising WAREHOUSES Advantages Low rent Can charge lower prices than competition Disadvantages No anchor store to attract customers Requires heavy advertising Customers may not be aware of your business BEGIN SELECTION OF YOUR SITE The trade area is the area from which you expect to attract customers. Location type and availability QUESTIONS TO ASK Is the location safe? Is it attractive? Does it seem to attract the kind of customers your business will be targeting? Is it easy to reach? Is parking adequate? Do businesses in the vicinity seem to be thriving? Lesson 8.2 CHOOSE A LOCATION FOR A NON-RETAIL BUSINESS GOALS Examine a location for a service business. Select a location for an industrial business. Operate your business from your home. LOCATION FOR A SERVICE BUSINESS For some service businesses, location is as important as it is for a retail business. Is location always important? LOCATION FOR AN INDUSTRIAL BUSINESS Industrial parks are sections of land that can be used for industrial business locations. Enterprise zones are areas that suffer from lack of employment opportunities. OPERATE YOUR BUSINESS FROM HOME Zoning laws Office space considerations Advantages and disadvantages Can write off percentage of home costs No travel expenses Work when convenient for you Distractions Lesson 8.3 OBTAIN SPACE AND DESIGN THE PHYSICAL LAYOUT GOALS Evaluate leasing versus buying space. Consider the costs and kinds of leases. Design the layout for different types of businesses. LEASE OR BUY SPACE Kinds of commercial leases Gross lease—Tenant pays rent, landlord pays everything else. Net lease—Tenant pays rent plus all other expenses except landlord pays insurance. Percentage lease—Tenant pays rent plus pays a percentage of sales. Compare different locations Calculating rent per customer Rent per Month ÷ Estimated Customers per Month Why Lease/Rent? Not enough money to buy Easier to get out of lease than sell Landlord generally handles building maintenance DESIGN THE LAYOUT OF YOUR BUSINESS Your layout must include enough space for: Employees Customers Merchandise Equipment Restrooms Stockrooms Storage Offices CREATE THE FLOOR PLAN Supplies and Inventory Clothing tables Clothing Sample Floor Plan Clothing Clothing racks Clothing Window display Counter Cash registers Clothing Window display Dressing rooms LAYOUT OF A RETAIL BUSINESS Choose appropriate lighting Think carefully about window displays Make the entrance inviting Use common sense when organizing the merchandise in your store Leave at least four feet of aisle space Create attractive in-store displays Use wall space wisely Place the cash register in a central location LAYOUT OF A SERVICE BUSINESS Layout is influenced by where services take place: At the business location—Just like a retail business At the customer’s location (on-site)— Organization is the only concern LAYOUT OF A WHOLESALE BUSINESS Locate in a one-story warehouse Keep merchandise close to the shipping dock Store popular items in accessible locations Be sure there are areas that accommodate merchandise of all sizes Keep walkways free of merchandise Store items safely LAYOUT OF A MANUFACTURING BUSINESS Work teams should be situated close together Supervisors should be able to easily observe the people they supervise Exits should be clearly marked and easily accessible Any hazardous materials should be stored safely Equipment and machinery should be positioned in a way that reduces the chance of an accident Lesson 8.4 PURCHASE EQUIPMENT, SUPPLIES, AND INVENTORY GOALS Acquire equipment and supplies by evaluating different vendors. Determine the level of inventory needed for your business. OBTAIN EQUIPMENT AND SUPPLIES Identify suppliers Evaluate proposals STANDARD EQUIPMENT AND SUPPLY NEEDS FOR MOST BUSINESSES TYPE Furniture ITEMS Desks, chairs, bookcases, filing cabinets, tables, computer stands Fixtures Lamps, overhead lights Office Equipment Computers, modems, fax machines, telephones, photocopiers Office Supplies Stationery, pens and pencils, scissors, tape, staplers, paper clips, file folders, calendars Maintenance Supplies Toilet paper, paper towels, cleaning supplies Kitchen Supplies Coffee maker, small refrigerator, coffee, tea PURCHASE INVENTORY Inventory is the quantity of goods and materials on hand Purchase inventory for Start-up business Ongoing business The reorder point is a predetermined level of inventory when new stock must be purchased.