Session 2 TCE

Welcome
Strategies of Network Companies
Jonathan D. Wareham wareham@acm.org
What we will study…
Transaction Cost Economics
Virtual Companies & formation of firm boundaries
Markets
Networks
Firms
Agents
Economic Theory : Boundary of the firm
A Virtual Firm
Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Sun Microsystems, a leading maker of computer workstations, concentrates on hardware and software design, where it distinguished itself from competitors, and outsources nearly everything else in its value chain
It relies so heavily on external manufacturers and distributors that its own employees never touch one of its top selling products
After a vendor assembles the machine, another contract supplier delivers it to the customer
Virtual Designs
In a Virtual Corporation,...:
"...the majority of the activities of the firm are contracted or outsourced."
This allows the firm to focus on its strategic, core processes ( core competencies )
Strategic alliances.....
Economic Paradox
In 1958 the Harvard Business Revenue predicted that computers would lead to a greater concentration of power in
American business because they would allow bosses to keep better track of information within large firms. Eventually, it predicted that the economy would be dominated by a few giants. In 1967 economist J.K. Galbraith argued that new technology would inevitably lead to increasing dominance by big corporations immune to market forces.
These predictions have turned out wrong: the average size of firms has shrunk and competition has decreased since
1960’s. Recent research suggests that the economy is beginning a transition from large, vertically integrated enterprises to organizational forms that draw on resources of small, independent specialists suppliers. For example, in a study of 549 large firms, increased use of IT has found to be associated with substantial decreases in firm size and diversification.
The Manager’s role
Procure inputs in the least cost manner
Costs
Provide incentives for workers to put forth effort
$100
80
Failure to accomplish this results in a point like A
0
A
B
$10
C(Q)
Output
Methods of Procuring Inputs
Spot Exchange
When the buyer and seller of an input meet, exchange, and then go their separate ways.
Contracts
A legal document that creates an extended relationship between a buyer and a seller.
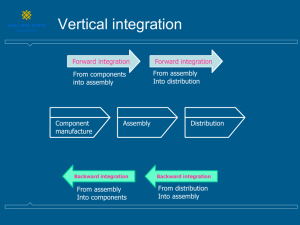
Vertical Integration
When a firm shuns other suppliers and chooses to produce an input internally.
Knight (1921) & Coase (1937)
Coase (1937) Why do we have firms?
Knight (1921) Why don’t we have one big firm?
possibility of monopoly rents motivates continuous and unlimited expansion of firms, But we do not always see it.
There must be offsetting mechanisms.
Ronald Coase (1937)
Why do we have firms?
there must be some cost in using the price mechanism.
• Price discovery/search costs
• Contract negotiation
• Long term stability of supply sources
(uncertainty)
Ergo, operation of the market costs something, and by forming and organization and letting some authority to allocate resources, some costs are saved
Coase’s Argument
Transactions vary in nature and dimension, and will align themselves with the governance mechanisms which manages these transactions most efficiently.
Size of firm increases until additional rent gained by bringing transaction in house is superceded by cost of bringing it in. That is, it has to be more costly on the market
Coase theorem: Efficiency determines organizational structure
Coordination Costs
Price determination
Details of transaction
Disclose existence of buyers and sellers to execute transactions
Search prices or quality control
Compiling and transferring information
Basic attributes of transactions
Specificity
Frequency
Duration
Complexity
Uncertainty
Difficulty of measuring performance
Connectedness
Asset Specificity
Investments made to allow two parties to exchange but has little or no value outside of the exchange relationship
Site specificity
Physical-asset specificity
Dedicated assets
Human capital
Lead to higher transaction costs and the problem of “hold-up”
Rule of thumb
No
Substantial specialized investments relative to contracting costs?
Yes
Spot Exchange
Contract
No
Complex contracting environment relative to costs of integration?
Yes
Vertical
Integration
Coordination Costs
Price determination
Details of transaction
Disclose existence of buyers and sellers to execute transactions
Search prices or quality control
Compiling and transferring information
Basic attributes of transactions
Specificity
Frequency
Duration
Complexity
Uncertainty
Difficulty of measuring performance
Connectedness
Specificity & Frequency
Frequency
Occasional
Standard
Standard Equipment
Machinery, PCs, Automobiles
Markets
Once off negotiated transaction
Frequent
Specificity
Medium
Customized Equipment
Machinery requiring some custom config.
Company to company negotiation
Semi-complex contracts
High
Constructing a plant
Turn-key projects
Company to company negotiation
Very complex contracts/government regulation
Standard Raw Material
Sugar, RAM chips, Steel
Markets
Contracts short to medium term
I year supplier: price based on index
Customized Material
Raw mat. with special process unique to customer
Value adding processes as specific site production processes within one or several factories within same location/proximity
Joint ventures, transfer of equity
Long-term binding contracts with significant investment
Hierarchies
Internal integration/ vertical conglomerate
Your Mission
You are a principal in a high tech start-up with 70m in funding and a rapidly growing customer base. Your business model has been tested in several pilot markets and the board has given the green light to scale up from 2 to 10 markets. This will make significant scalability demands of your IT function that, up to now, you have grown internally. At a management meeting, the chairman asks:
“ What do you recommend?“
Your Task
Use the tools provided by TCE to evaluate the following alternatives:
1.
Full outsourcing
2.
Partial outsourcing (specify what functions)
3.
Internal integration
Consider these factors
1.
Specificity
2.
Frequency
3.
Duration
4.
Complexity
5.
Uncertainty
6.
Performance measurement
7.
Connectedness
8.
Search Costs
9.
Price Determination
10.
Quality Monitoring
IT, Complexity & Specificity
Hierarchy
Market
Asset specificity
IBM
Computer
Associates
Outsourcers: Who?
AT&T
Lotus
Compaq
MCI
Peachtree
Software
Bell
South
Factors Favoring Outsourcing
Managers can and should make use of two kinds of arguments in their case for (or against) outsourcing
(bandwagon reasoning is not a defensible managerial decision!)
Need for organizations to focus on their strategic assets or core competencies
Realization of greater economies (lower costs)
Need for greater flexibility and expertise in workforce
Given a positive financial assessment:
Is the Web system or service being considered.....
No
A Core
Competency/
Strategic Asset?
Yes
Consider Inhouse Bids vs.
Outsourcer Bids
Most Likely to
Outsource
Retain In-house
If Outsource,
Legal
Protections
Critical
Yes No
Does Firm Have Internal Expertise?
Outsourcing & Virtual design
A tale of 2 companies….
Sell 50,000 computers with only 4 days of inventory
Keep few suppliers very close
30 suppliers 75% of materials
When order is made, signal is sent to supplier, 90 minutes later, supplies are delivered to Dell.
“We sell what we have, we don´t sell what we don´t have”
Dell From HBR
Have as few suppliers as possible
In real time, communicate your inventory levels and replenishment needs to them
Order from suppliers only when you receive demand from customers.
By going direct; no Channel Push
VARS
Manufacturers
Wholesalers/Distributors
End Users
Avoiding the Risks…
Assets & Inventory
Accounts receivable
Use technology to bring benefits of vertical coordination to the network
Darling of stock market.
First Virtual company
No inventory, no warehouses
But what happened…..
3,500 modular parts
30+ suppliers
Over 1 million products, many suppliers
Bringing vertical coordination to the network… but how?
IT, Complexity & Specificity
Hierarchy
Market
Asset specificity