genetic code - e-CTLT
advertisement

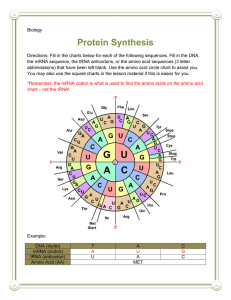
FEATURES OF GENETIC CODE AND NON SENSE CODONS by mrs. Anita jain Pgt biology k.v. no.1 hindan ghaziabad GENETIC CODE The relationship between the sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chain and nucleotide sequence of mRNA or DNA is called genetic code. Or The genetic representation of codon by which the information in RNA is decoded in a polypeptide is called genetic code. Or The order in which bases (nucleotides) are arranged in RNA deciding the order in which amino acids are arranged in proteins. (i.e. it is the relationship between nucleotide bases and the amino acids). It was hypothesised by George Gamow that triplet code is operative as DNA contains only four bases while the no. of Amino acids are 20. So it generates (4)=64 triplet codons. Har Gobind Khurana synthesised homopolymers &copolymers i.e. RNA molecules with specific combinations of bases. Marshal Nirenberg helped in deciphering the code by making a cell free system for protein synthesis. For this work , Har Gobind khurana shared Nobel prize in 1968 with Nirenberg & Holley. CODON Sequence of 3 nitrogenous bases (triplet) on MRNA coding for a particular amino acid is known as codon. Or A triplet of bases present on MRNA coding for one amoinoacid is called codon. E.g. If MRNA has a triplet code AUG, for which corresponding aminoacid in the protein would be methionine. Similarly UUU code for phenylalanine . Thus codons for all 20 aminoacids of proteins were found. Many amino acid have more than one codon. Anti-codon A triplet of bases present on ERNA & that corresponds with codon of MRNA is called anti-codon. e.g. UAC (ERNA anticodon) THE SALEINT FEATURES OF GENETIC CODE 1) The genetic code are triplet . Thus 4 bases (AUGC) when arranged in the form of triplet code can generate 43 or 64 codons. Of these codons do not code for aminoacid but function as Stop/ terminator codons/ Non-sense codons. (UAA, UAG & UGA), so there are 61 codons which code for 20 aminoacids. 2) One codon codes for only one aminoacid hence it is ‘unambiguous’ & ‘specific’. 3) Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon hence the code is ‘degenerate’ E.G. methionine is the amino acid that is coded by only one codon i.e. AUG. 4) AUG have dual functions as it codes for methionine & also acts as initiation/ starf codon. It is the first amino acid in the polypeptide chain. 5) The codons are real in a continuous fashion in 5’ direction i.e. without punctuation. 3’ 6) The code is non-overlapping i.e. same letter cannot for 2 different codons. 7) The code is nearly universal i.e. the codon codes for same amino acid in any organism from bacteria to human beings./ (i.e. in all organism). e.g. UUU would code for phenylalanine , in all organisms. Comma less Non sense codon Non ambiguous (UAA, UAG, UGA) universal Initiation Codon (AUG) Genetic code Degenerate Linear Non Overlapping Triplet First position U C A G third position Second position U C A G UUU UUC UUA UUG phe phe leu leu UCU UCC UCA UCG ser ser ser ser UAU UAC UAA UAG tyr tyr stop stop UGU UGC UGA UGG cys cys stop trp CUU CUC CUA CUG leu leu leu leu CCU CCC CCA CCG pro pro pro pro CAU CAC CAA CAG his his gin gin CGU CGC CGA CGG arg arg arg arg AUU AUC AUA AUG ile ile ile met ACU ACC ACA ACG thr thr thr thr AAU AAC AAA AAG asn asn lys lys AGU AGC AGA AGG ser ser arg arg GUU GUC GUA GUG val val val val GCU GCC GCA GCG ala ala ala ala GAU GAC GAA GAG asp asp glu glu GGU GGC GGA GGG gly gly gly gly U C A G U C A G U C A G U C A G RECAPITULATION 1.Define genetic code , codon , & anti-codon. 2.What are initiating codons? 3.Mention the features of genetic code. 4.What are terminating codons? 5.Why are terminating codons also called as non sense codons? 6.Following is the DNA sequence representing a part of the gene TAC CCC CAC CAG TTA TAT ATA CGG GGG CAT CAT ATG From it derive (i) The RNA transcript. (ii)The spliced MRNA (assuming that all codons containing ac represent the intron. 5. Complete the following table using alphabets (a to k) DNA triplet 3’ 5’ MRNA codon 5’ Anticodon Aminoacid 3’ UAC UGG tryptoplan AAG GAC 6. Read the sequence of the nuleotides in the given segment of MRNA and the respective amino acid sequence in the polypeptide chain met phe met pro val ser X AUG UUU AUG CCU GUU UCU UAA MRNA (i) (ii) (iii) Provide the triplet of bases (codon) for (a) valine (b) proline Write the nucleotide sequence of the DNA strand from which this MRNA was transcribed. What does the last codon of this RNA stand for? 7. AUG GUC GGG UUU CUU AUC UAA Given above is a sketch MRNA in 5’ – 3’ direction. Answer the following: a) Make the DNA strand on which this RNA got synthesised. b) How many amino acid will be coded on this MRNA? c) What are their anticodons for different amino acids? d) What happens if last ‘A’ is replaced by ‘C’? Will the chain terminate or not? Why? 8. A MRNA strand has a series of codons of which 3 are given (i)AUG (ii)UUU (iii)UAG a) What will be the DNA codes for above codons? b) Which amino acid will be coded? c) What will be their anti codon? 9. If one nucleotide (encircled) gets missed in the given series then how many amino acid will be changed? AUG U AU CAA AAG UAG 10. The sequence of the nucleotide on template strand of DNA is GTG CAT TCA GCA TGA ATG TAC. a) Write the nucleotide sequence on coding strand. b) Write the MRNA sequence formed on basis of template strand. c) Give the anticodons of all amino acid. Which will be coded? 11. Given below is strand of MRNA: AUG GAC CCC CUG AUA UUU UCA UGA a) Write the base sequence of one DNA strand from which it has been transcribed. b) Upon translation how many amino acids will be present in resulting peptide? Thank you