The Effect of Cognition on Physiology
advertisement

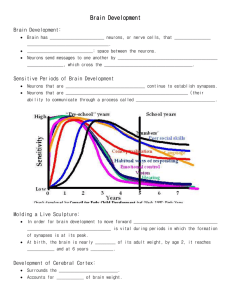
The Use of Technology in Brain Research RIANE B, DAISHA L, PETA G, ASIA G, XENA N, BRITTNY T Technology and Neuropsychology Modern technology is now extensively used in neuropsychology Provides an opportunity to study the active brain Allows researchers to see where specific brain processes take place Enables the study of localization of functions in the brain Experiments with animals is still widely used Allows the study of specific biology that correlates to behavior using invasive techniques: removing(ablation) or scarring(lesioning) brain tissue in order to study behavioral changes Rats and Psychology Hetherington and Ranson (1942) lesioned the ventromedial hypothalamus in rats Rats increased their food intake dramatically, almost doubling their weight. Led researchers to believe the hypothalamus acted as a brake on eating The full purpose of the hypothalamus is still not yet understood. Is it ethical? Ethical concerns arise with using animals with cases that involve lesioning and ablation, potential irreversible harm Brain Scanners EEG(electroencephalogram) When neurons transport information an electrical change occurs EEG picks up voltage change but cannot reveal what is going on the deeper regions Provide a better understanding of behaviors of the brain: sleep, emotions, epilepsy PET(positron emission topography Scan monitors glucose metabolism in the brain Patient injected with radioactive glucose and the radioactive particles emitted are detected by the PET scanner Scans produce colored maps of brain activity Has been used to diagnose abnormalities, to compare brain differences between normal people and ones with psychological disorders and to compare sex differentiation Greatest advantage: It can record ongoing activity in the brain Brain Scanners: Continued fMRI Provides 3D pictures of the brain structure using magnetic fields and radio waves. Shows actual brain activity Higher resolution than PET scans and is easier to carry out. Most frequently used in research today Evaluating Brain Scanning Techniques Although you can learn a lot through brain scanning there are limitations The MRI scanner is not good for cognition(There’s a question of ecological validity) The colors of the different activities of the brain could be exaggerated Areas of the brain activate for many reasons (just because it does not light up does not mean its not working) TOK Ethics PET-fMRI scans help psychologists to identify brain patters for dysfunctional behaviors. Similar to fingerprints(scanning images) Specific patters exists for individuals with schizophrenia, alcoholism, depression and other disorders Even if a person does not show symptoms of disorder, patterns are still present. Brain Plasticity JESSIE HUGHES SARAH KERMAN SANA KHATRI DANIELLE LAFLUER CJ JASINSKI BRIANNA JONES CRISTINA DERESPINES Brain Plasticity Prior to 1960, it was thought that the brain could only be influenced by genetics. In 1965, researchers Hubel and Wiesel introduced that the environment also influences the brain. A higher cognitive functioning area of the brain, the cerebral cortex, could be influenced or modified by the environment. Rats were used as lab experiments. Dendritic branching is when we learn something new Brain Plasticity The changes that occur in the structure of the brain as a result of learning or experience are called brain plasticity. Plasticity can change functional qualities of various brain structures. High levels of stimulation lead to an increase in density of neural connections The brain of a musician should have a thicker area of the cortex related to mastery of music. Studies of brain plasticity were conducted by Rosenweig and Bennet in 1972. Placed rats into on of two environments with the goal of measuring the impact of enrichment or deprivation on development of neurons in the cerebral cortex. Enriched environment involved stimulation play toys Deprived environment involved no toys. Post-mortem studies showed those rats in the stimulation environment had increased thickness in the cortex. The rates also have a heavier frontal lobe which is linked to greater decision making, thinking and planning. Interaction with other rats further increased the cortex thickness. Mozart Effect One of the most well-known claims of brain plasticity is the Mozart Effect. Listening to the music of Mozart with temporarily increase spatial reasoning ability. Exposure to musical compositions that are structurally complex excites the brain the same as when physically completing tasks. The brain develops a more sophisticated ability to solve spatial problems. Experiments on brain plasticity cannot be done in humans due to our genetic makeup and environmental inputs differ. Learning results in an increased of dendrite branching. The Effect of Cognition on Physiology RACHELLE BLASH, MADISON CARR, ADINA BESLAGIC, GLORIA MENSAH, EBONY HARGRO, RASHAAN WILLIAMS The Experiment Conducted in 2004 by Richard Davidson Involved 8 Buddhist monks who were highly experienced in meditation and 10 volunteers who had been trained in meditation for a week Both groups were told to focus on love and compassion while meditating Experimenting Using a PET scan, it was concluded that two of the volunteers and all of the monks had an increase in the number of gamma waves in their brain during meditation Gamma waves are linked to higher reasoning faculties When volunteers stopped meditating their number of gamma waves returned to normal The monks’ number of gamma waves did not decrease; they remained at a high level Monks train for more than 10,000 hours to become adept at meditation Findings The area in the brain creating gamma waves was found to be bigger in the monks rather than the volunteers Davidson concluded that meditation could have significant long term effects on the brain and how it processes emotions Indicates that the brain adapts to stimulation from either the environment or our own thinking Mirror Neurons “Mirror neurons on the wall, reflect behavior of them all.” BAILEY, ALEX, CHASE, TREA, JUSTIN What are mirror neurons? Fires when an animal/ person performs an action or when the animal observes somebody else perform an action. “Mirrors” the behaviors of others. How was it discovered? Discovered by accident in 1996, at the university Parma in Italy, as they carried out an experiment with motor neurons. They found that neural messages send electrical signals in nature. The scientists were able to hear the crackle of the electrical signals when a motor neuron was activated. The Monkey and Peanut Whenever a monkey reached for the peanut, the crackling noise was heard. When the scientists tried to reach for the peanut, they heard the noise of the electrical signal from the electrodes in the monkey’s brain. Humans In 2004, Marco Lacoboni asked participants to look at faces while undergoing an FMRI. The same signals which were activated in the monkeys were activated in the humans. The limbic system was stimulated. A happy face= pleasure! Understanding Mirror Neurons Mirror neurons help us understand why we immediately/ instinctively understand people’s thoughts, feelings, and intentions (empathy) This plays a role in how people react to sports, theatre, and video games. Example http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1tBkPxrQ9dQ The Endocrine System WYATT ANDRESEN EUGENE KYERE ELIJAH DAVILA TRÉ SAUNDERS Hormone Chart Hormone Gland Function Adrenaline Adrenals Fight or Flight, Arousal Cortisol Adrenals Arousal, Stress hormone, Memory Melatonin Pineal Regulation of Sleep Oxytocin Pituitary and Hypothalamus Mother-Child Attraction Testosterone and Estrogen Gonads Development, Emotion Hormones Enter directly into the bloodstream Take longer to produce changes than neurotransmitters Chemicals serve as hormones and neurochemicals Oxytocin Plays a role in inducing labor contractions and lactation Released when hugs are given Induces bonding between mother and child, as well as between lovers Appears to change the brain signals related to social recognition via facial expression This may be done by changing the firing neurons of the amygdala The amygdala has an important role in processing emotional stimuli Oxytocin Continued It is known as the ‘love hormone’ It is an effective mediator of human social behavior Oxytocin given to healthy individual seems to effect circuits involved in fear regulation Trust increases in general Research is being done to see if Oxytocin helps people suffering from social anxiety Melatonin It is produced by the Pineal gland It is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by light Melatonin levels peak near midnight and gradually decrease towards morning As days get shorter during winter there is more darkness, meaning that you are more tired Artificial lighting has certainly affect ‘awake time’ dramatically Melatonin Continued Melatonin correlates with the Circadian Rhythm Circadian Rhythm – any biological process that oscillates over about twenty four hours Taking a melatonin pill in the early evening can help with sleep There is evidence that higher levels of melatonin contribute to Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) SAD is a subcategory of depression characterized by sleepiness, lethargy, and a graving for carbs Reduced levels in autumn and winter are believed to mess up the Circadian Rhythm in certain people