Corporate Template Sample One - American Statistical Association
advertisement

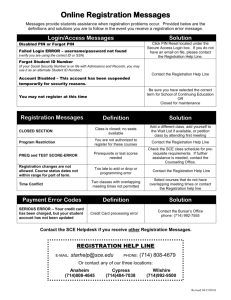
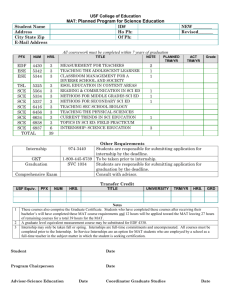
Implementation of a Validated Statistical Computing Environment Presented by Jeff Schumack, Associate Director – Drug Development Information September 16, 2005 Statistical Computing Environment (SCE) • • • • Data Repository of source code, input data & output Version controlled programs and output Reusable programming ability Links to Clinical Data Management System (CDMS) & Documentum 2 Prototype • Determined requirements • Performed market search • Worked collaboratively to achieve our vision • Conducted extensive pilot 3 SCE: Where Does it Fit in? Clinical Data Management Capture and Organize Data Clintrial/CRO Clinical Biostatistics Regulatory Affairs Analyze Data, Generate and Deliver Reports Submission of Reports to the FDA Documentum/Publishing SAS, Files Statistical Computing Environment Analysis, Programming and Reporting under 21 CFR Part 11 compliance 4 Interfaces Clinical Data Management Core SCE Documentum 5 Clinical Data Management Connector 6 Extraction Process Query CDMS • SAS or XML • Execute data extraction – Extraction in context – Record data and output under correct study 7 Audit Trails • • • • Who What When Comment if any 8 Core SCE Functionality 9 Database Connectivity Oracle Role Based Security • Require username / password • Secure – only authorized personnel allowed to connect • Level of access based on user privilege 10 External Applications • SAS system version 8.12 (or higher) • R (Splus) version 1.9.1 or higher • UltraEdit version 10 or higher 11 Repository • Secure Oracle Database • Easily retrievable • Hierarchical Structure – Indication -> Study -> Programs (etc.) 12 Traceable Pathway SCE provides • • • • • Clear pathway from “field” to report Mechanism for data extraction of analyses Dependency map of input-to-programs-to-output “Push” analyses into Documentum Audit Trails 13 Dependency Map Graphically represent “program-to-input-to-output” – Including version numbers 14 Security Manager • Individual user accounts • Password Management: LDAP • Permissions: – Group – User – Project 15 File Management • Folder types / File types / File properties • Check out / Check in • File annotations • Source Code Editor • File Viewers • Execution and display results, logs, graphics • Audit Trails 16 Pack & Go • “Pull” files from SCE onto local disks – Indication – Study – Analysis • Useful for Archival • Collaboration with external contributors – Partners – CROs – Data Monitoring Committees 17 Study Setup - Templates • Nested Hierarchy templates – Indication – Study – Analyses • Replicate Studies using templates • Retire templates no longer in use 18 Job Management • Server based running of jobs • Define jobs / Submit jobs / Run jobs / Run & Record • Input / output dependencies • Table of Content user interface / comment blocks • Relative file pathways – Macro search – Common Code search • Batch execution / job sequencing • Record Outputs • Traceability – Dependency Mapping – Input data / program / macros -> main program -> Output (s) 19 Life Cycle Management • Draft / Quality Controlled / Final • Business rules • Draft from Final 20 Reporting • Audit Trail reports • Output formats – PDF, XML, RTF etc. • Combine Outputs • Interface with external reporting tools 21 Documentum Connector 22 Documentum Authentication • Username / password protected • Documentum user information verification • Documentum permissions verification 23 User Interface • Automatic population of Documentum based on lifecycle state of document in SCE • Manual population based on user triggers • User comments • Version controls 24 Audit Trails • Who • What • When • Version control information 25 Conclusion • New technology • Close to realizing HGS SCE vision • Acknowledgments: – HGS Biostats & IT teams – Waban Software – Alan Hopkins • Contact Information: – Jeff_Schumack@hgsi.com – 240-314-4414 26