The Fuel of the Future: Starch Ethanol vs. Cellulosic Ethanol
advertisement

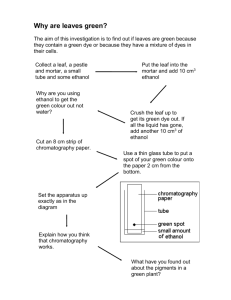
Tommy Underhill Ethanol Made by fermenting sugars into alcohol Flammable Used in thermometers, and alcoholic beverages Commonly referred to as grain alcohol History Ethanol residues have been found on 9,000 year old clay pots in China First recorded production of alcohol from wine was in the 12th century. 1796: Johann Tobias Lowitz obtained pure ethanol by filtering distilled ethanol through charcoal 1826: Samuel Morey developed the first engine that ran on ethanol 1908: Henry Ford’s Model T was designed to run on ethanol or gasoline. 1940’s: First Ethanol Plant was built in Nebraska 1974: The Solar Energy Research, Development, and Demonstration Act was the first legislation action to promote ethanol as fuel. 1992: The Energy Policy Act 2007: Energy Independence and Security Act Ethanol Production Starch Ethanol Wet Milling Dry Milling Fermentation Separation Purification Ethanol Production Cellulosic Ethanol Have to be Pretreated Physical - grinding Chemical – acids Require the use of enzymes to break down cellulose Cellbiohydrolases Endo – β-1,4-glucanases β-glucosidases Fermentation Separation and Purification Funding US government has given out numerous grants, loans, and tax incentives for the production and use of ethanol Government spends $5 billion per year to subsidize ethanol production 2007 : US department of Energy spent $385 million on six large scale ethanol plants and another $200 million on biorefinery plants. Big Oil Contributions: Chevron - $40 Million BP – $500 Million Exxon - $600 million Environmental Conventional ethanol reduces greenhouse-gas emissions 10 to 20 percent Cellulosic range from 80 percent to completely CO2 neutral Cellulosic ethanol requires less care than starch ethanol Political http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j9QQcP_Y1II Other Concerns with Starch Ethanol Rising prices of corn and starch Concerns with Cellulosic Ethanol Price of Enzymes Future Competition with other ethanol sources such as Algae. Competition with electric cars and hydrogen fuel cells Sustainability Resources Biello, D. (2008). Grass Makes Better Ethanol than Corn Does. Scientific American. Retrieved from http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=grass-makes-better-ethanolthan-corn Biofuels. (2011). The New York Times. Retrieved from http://www.nytimes.com/info/biofuels/ Brahic, C. (2006). Humble grasses may be the best source of biofuel. New Scientist. Retrieved from http://www.newscientist.com/article/dn10759-humble-grasses-may-be-the-bestsource-of-biofuel-.html Bothast, R., Schlicher, M. (2005). Biotechnological processes for conversion of corn into ethanol. Appl Microbial Biotechnical, 67, 19-25. Retrieved from http://www.tamu.edu/faculty/tpd8/BICH407/fulltext.pdf CBS News. (2007). UN: Biofuels Could Devastate Environment. Retrieved from http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2007/05/08/tech/main2774983_page2.shtml?tag=co ntentMain;contentBody Dale, Bruce. “Cellulosic Biomass to Ethanol.” Diagram. PowerPoint presentation. 7/16/2007 Doggett, Tom. (2007). Ethanol to take 30Percent of U.S. corn crop in 2012. Retrieved from http://www.reuters.com/article/2007/06/11/us-usa-ethanol-cornidUSN1149215820070611 “Dry Mill Process.” Diagram. Icminc.com 2009. <http://www.icminc.com/ethanol/production_process/> Ethanol Timeline. (2008) Green Plains Renewable Energy, Inc. Retrieved from http://www.gpreinc.com/Ethanol-Timeline “Fuel Ethanol Production in the United States.” Graph. Data360.org 5/20/2008. <http://www.data360.org/dsg.aspx?Data_Set_Group_Id=1344> Fuel Testers. (2009). Ethanol Fuel Timeline. Retrieved from http://www.fueltesters.com/ethanol_fuel_history.html Gecan, R., Johansson, R., FitzGerald, K. (2009). The Impact of Ethanol Use on Food Prices and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Congressional Budget Office. Retrieved from http://www.cbo.gov/ftpdocs/100xx/doc10057/toc.shtml Greer, D. (2005). Creating Cellulosic Ethanol: Spinning Straw into Fuel. Biocycle. Retrieved from http://www.harvestcleanenergy.org/enews/enews_0505/ enews_0505_Cellulosic_Ethanol.htm Gupta, R., Demirbas, A. (2010). Gasoline, Diesel, and Ethanol Biofuels from Grasses and Plants. New York, NY. Cambridge University Press. Jacquot, Jeremy. “Biofuel Comparison Chart.” Diagram. Treehugger.com 05/10/08. <http://www.treehugger.com/files/2008/05/biofuel-comparison-chart.php> Kleiner, K. (2007). The backlash against biofuels. Nature Reports Climate Change. Retrieved from http://www.nature.com/climate/2008/0801/full/climate.2007.71.html Kubiszewski, I. (2007). Energy Timeline. Earth Portal. Retrieved from http://www.earthportal.org/?p=80#1940AD “Maize Price Chart.” Chart. Mongabay.com 2009. <http://www.mongabay.com/images/commodities/charts/maize.html> Murray, Shailagh. (2007). Ethanol Undergoes Evolution as Political Issue. The Washington Post. Retrieved from http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/03/12 /AR2007031201722.html Myth: Corn ethanol is great. You Tube. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j9QQcP_Y1II State Energy Conservation Office. Cellulosic Ethanol. Retrieved from http://www.seco.cpa.state.tx.us/re_ethanol_cellulosic.htm “Sugar, world price chart.” Chart. Mongabay.com 2009. <http://www.mongabay.com/images/commodities/charts/sugar.html> The Economist. (2010). The post-alcohol world. Retrieved from http://www.economist.com/node/17358802?story_id=17358802&CFID=161806477&CF TOKEN=18203629 U.S. Department of Energy. (2011). Federal Incentives and Laws for Tax Incentives. Retrieved from http://www.afdc.energy.gov/afdc/laws/laws/US/incentive/3234 Wang et al. (2007). Diagram. Environmental Research Letters, Vol 2. Diagram Wikipedia. (2011). Ethanol. Retrieved from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethanol