Answers to IGCSE WS
advertisement

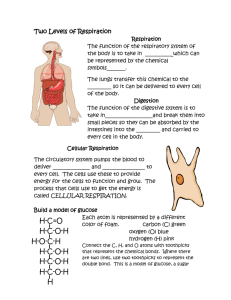
Answers to IGCSE Worksheets Cells, Tissues and Organs a. Cell, tissue, epidermis, organ, systems, excretory system. b. specialised, red blood cell, division of labour, nervous and endocrine c. palisade cell, chloroplasts, leaf, epidermis, xylem Biological Molecules and Food Tests Across 2 water 4 starch 6 biuret 8 blood 9 orange 10 glucose 11 cholesterol 14 DNA 15 condensation 16 emulsion 18 blue-black 20 lipids 21 22 haemoglobin Down 1 purple 3 amino acid 5 hydrolysis 7 protein 12 sucrose 13 benedicts 17 milky 19 urine Movement of molecules in and out of cells a. osmosis b. partially permeable membrane c. water has entered by osmosis making the cell turgid d. solution c has a lower water potential and water has left the cell leaving it flaccid. 2. Experiment a. Graph 4 marks = Axis (x = Concentration of sugar solution 0.0-10.0 and y = % change in mass of potato cylinders +10 - -20), Scale, Plotting, Line b. 0.24 Moles c. When the solution and the cytoplasm inside the cell are in equilibrium (no net movement of water molecules = 0 in the change in mass). Then the concentration inside the cytoplasm must equal the concentration of the sugar solution. d. To repeat the test for reliability. e. To remove any water that would give a incorrect mass reading. f. Extrapolate the graph and read 3. a. i. Turgid cells, photosynthesis, metabolic reactions, movement of nutrients ii. The water potential gradient is lower outside the plant than inside the cells – hence water will leave the cells (flaccid) and the plant will wilt. b. i. Active process ii. Energy is required for active process, which would deprive the plant of the energy needed for growth. iii. Magnesium for chlorophyll and nitrogen for proteins Fill in the missing word Cytoplasm, partially permeable membrane, explode, lower, wall, Amino acids, diffusion, concentration gradient, active process, energy, against Carbon dioxide, diffusion, respiration. Food and Diet in Humans 4. a. Quorn has little fat and 0 cholesterol – reduces risk of obesity and heart attacks, high in fibre (improves digestion) and low in energy content so not fattening. b. (355x 2.5) + (3600/10) + 575 = 1822.5 kJ 5. a. Black b. Biuret c. Sample D d. Control and to see the negative colour for the tests e. Dissovle the food in ethanol, add water and a milky solution is a positive test for fat. f. Obesity that can lead to CHD or diabetes Crossword Across 1 scurvy 3 salt 4 calcium 7 carbohydrate 9 steroid 10 protein 11 fat 13 respiration 14 balanced 15 iron 16 membrane Down 2 ricketts 3 sucrose 5 cholesterol 6 baked beans 8 malnutrition 12 fibre Digestion and Absorption pg 45 1. . a. A= Jaw b. The jaw chews the food and the salivary gland adds saliva to make a bolus that is easy to swallow. c. C is the epiglottis that cuts off the trachea. d. D is the oesophagus and food moves by peristalsis where the circular and longitudinal muscles alternately squeeze the food down the channel. e. Small intestines are very long (7m) and have villi with micro-villi to increase the surface area. f. . i. Glycogen ii. Hepatic portal vein iii. Hepatic vein iv. Bile emulsifies fats - this increases the surface area of the lipids so that digestion can occur easier. Lipids are hydrophobic and do not dissolve in water and therefore form large clumps called micelles. g. i. Pancreatic duct ii. Proteases works on proteins etc. h. E= Re-absorb water, breakdown fibre F = gets rid of solid waste (egestion) 2. . a. Inside A = Black B = Red Brown b. Starch was broken down in tube B by the amylase but remained in tube A because the amylase was boiled and the enzyme was denatured. c. Test tube B for a reducing sugar as maltose or glucose should be present as starch was broken down. d. . i. X= Epithelial cells Y = Blood capillaries Z = Lacteal ii. Small intestines specifically the ileum. iii. X iv. To absorb the fatty acids 3. . a. . i. X = Molar Y = Canine Z = Incisor ii. X = grinding food and Z for cutting food b. Calcium and Vitamin C c. . i. Sugar sticks to the enamel, bacteria feed on the sugar and produce an acid that eats a hole through to the dentine. The bacteria can enter into the dentine to continue the decay. ii. Brush teeth twice a day, use mouthwash, go to dentist regularly, avoid sugary foods, floss etc. 4. . a. Lipase b. Acid c. . i. 8.7 – 8.1 = 0.6 8.1 – 7.7 = 0.4 ii. 0.6 + 0.4 = 1 / 4 = 0.25 pH per min Bile is an emulsifier and increases the surface area of the fat in the milk. 5. . a. . i. Protease ii. Amino acids b. The effect of pH on the activity of Protease c. Stomach d. So the small products of digestion can be absorbed into the blood supply and assimulated in our body cells. 6. . A – 12 B – 22 C – 21 D – 17 E–3 F – 13 G – 19 H–1 I – 20 J – 18 K–2 L – 14 M–9 N – 16 O–6 P–8 Q–7 R–5 S–4 T – 15 U – 11 V - 10 Useful Microbes Crossword Across 1 biogas 4 sewage 8 chymosin 9 GMO 10 acid 13 bacteria 15 mycoprotein 16 vector 17 restriction 19 penecillin 20 lipase 22 acetic acid 23 alkanes 24 lactobacillus Down 1 Brewing 2 plasmid 3 whey 5 protease 6 dioxide 7 lactic 11 carbon 12 fermentation 14 amylase 15 methane 18 21 yeast Matching Terms Distillation Fermentation Bioreactor Chymosin Carbon dioxide Whey Hops Yeast Alcohol Pasteurisation Lactobacillus Acetobacter Sterilisation Mycoprotein Bacterium Photosynthesis Match the terms A-4 B-10 C-15 D-1 E-13 F-8 G-5 H-14 I-12 J-6 K-2 L-9 M-11 N-7 O-3 Plant Transport - Fill in the missing words Osmosis Hairs Surface area Ions Nitrate Diffusion Active transport Support Solvent Photosynthesis Xylem PhloemVascular 1a i The plants absorb nitrate so removed the ions from the soil. Usually when organisms decay the nitrogen would be put back in the soil but the plants were removed. ii. Add synthetic fertilisers or natural manure b. These are leguminous plants and they have nitrogen fixing bacteria in their root nodules that take atmospheric nitrogen and make it available to the plant as ammonia. Transport in Animals 6. a. i glucose and oxygen ii. carbon dioxide b. i. Cardiac muscle ii. it will contract iii. the blood in the left ventricle will be forced to leave through the semi lunar valves and into the aorta to be pumped around the body. c i there is a build up of cholesterol in the arteries due to a fatty diet or smoking. Ii Below point B d. Veins have a large lumen to allow the blood to flow back to the heart and they have valves to stop the blood flowing backwards. Crossword Across 1 cholesterol 3 pacemaker 4 muscle 7 blood pressure 9 arteries 10 coronary 12 semilunar 15 tendon 16 ventricle 18 left 19 pulmonary 21 atrium 22 veins Down 1 capillaries 2 valve 5 smoking 6 vena cava 8 exercise 11 diastole 13 systole 14 aorta 17 bypass 19 pulse 20 right Defence Against Disease Excretion and Osmosis pg 83 4. a. It is killed or only a part of it is used. b. The vaccine has antigens on it that bring about an immune response from the host. This means antibodies that are specific to that antigen are produced by lymphocytes to help destroy the antigen. At the same time the lymphocytes produced are stored so the next time the antigen enters the body the immune response will be quicker. 1. a. Water gain = 1000 + 1300 = 2300cm 3 - Water loss = 450 + 500 + 150 = 1050 cm 3 Loss in urine = 1200 cm 3 b. The hypothalamus registers a decrease or increase in the water in blood. It either releases more or less ADH. If the water content is low in blood more ADH is released and more water is reabsorbed from the kidney tubule (loop of Henle) into the capillaries surrounding the nephron. This is a negative feedback as the opposite effect occurs from the stimulus. 5. a. i. Section of DNA (gene) that codes for the surface antigen ii. surface antigen b. Even though it was stopped from reproducing it was still a live vaccine that contained the Hepatitis B virus, which could be passed on. Fill in the missing words Blood loss Pathogens Disease Platelets Proteins Fibrinogen Fibrin Red blood cells Haemophilia Breathing and Gas Exchange Fill in the missing words Pulmonary Respiration Energy Carbon dioxide Hydrogencarbonate Capillaries Thin Surface area Alveoli Carbon dioxide Oxygen Pulmonary Left atrium Respiration and the Release of Energy 5. a. false b. true c. false d. true e. true f. true g. false h. true i. true j. true k. true Fill in the missing words Living cells Glucose Oxygen Energy Aerobic Movement Growth Heat c. i. Advantages of a dialysis machine over kidney transplant are; There may be rejection of the kidney The person has to take immune-depressant drugs that can lead to illness The person is under constant medical supervision with dialysis ii. Disadvantages are; Constant stay in hospital for the dialysis that interferes with lifestyle Kidneys are more efficient at removing waste from blood There is a risk the urea level will reach lethal high levels. 2. a. i. They are too large to go through the membrane ii. Glucose is small enough to be in the filtrate but is reabsorbed in the tubule as it is an important nutrient. The capillaries around the nephron take the glucose back to the body to be used for storage or respiration. b. ADH controls the re-absorption of water in the kidney. On a hot day whilst exercising more water is lost through sweat thus more water needs to be replaced in the body. The increased ADH increases the re-absorption of water in the loop of Henle. 3. a. Excretion is the removal of waste products from the body ii. Egestion is the removal of undigested material from the body i. b. i. ii. Liver Proteins (amino acids). c. Q = Renal artery R = Renal vein S = Ureter T = Urethra d. Component of Blood Glucose RBCs Salts Urea Water WBCs glucose in the blood more than if a person is sedentary. Present in Urine X X v v v x b. ‘Hypo’ means there is too little glucose and the person will require glucose immediately. Sugar will provide it. Starch contains glucose but takes time to break it down. c. The hormone glucagon is produced by the pancreas to convert glycogen in the liver to glucose. 4. a. The kidneys are not working so urea is not removed b. They have more room to increase their urea concentration before the next dialysis treatment = more time between treatments c. The patient is given immune-suppressant drugs to help prevent the patient from rejecting the kidney. They will have to be given antibiotics to help fight any infections because they are immune-suppressed. d. Negative feedback is when the reaction is opposite to the situation e.g. when blood sugar is high insulin is released to convert glucose to glycogen, which lowers the blood sugar. Fill in the Gaps Hormones Endocrine organ Bloodstream Target organ Adrenaline Trachea 5. ACROSS 2 urine 3 urea 4 henle 5 bladdar 8 filtration 9 renal artery 10 sphincter 13 excretion 14 plasma 15 glucose 16 bowmans 18 liver 19 kidney 20 dialysis 1. a. b. c. d. e. f. 2. a. b. c. d. DOWN 1 nephron 2 urethra 3 ureter 6 renal vein 7 diuretic 11 hormone 12 amino acids 14 protein 17 anti Hormones and the Endocrine System a. i. Diabetics cannot produce enough or any insulin themselves from the pancreas or it doesn’t result in the uptake of glucose. ii. as insulin converts glucose to glycogen too much insulin will remove all the glucose from blood. iii. Exercise requires movement of the muscles, which requires energy. This energy is from aerobic respiration that requires glucose. This reduces the e. The Nervous System and Co-ordination pg 92 . A D A E C B . 4 4 3 x 3 + 1.6 = 10.6 units = 210 – 80 = 30 mg per 100 cm3 over the limit Co-ordination impaired, reaction time increased, feeling of invincibility etc 10 hours and 10 minutes f. Cirrhosis 3. i. ii. iii. iv. Road traffic accidents 5/20 = 1/5 Damage central nervous system – cerebral All nerves end in the spinal column so she has damaged nerves that affect her lower body but not her upper body. 4. . a. A= Sensory neurone B = Spinal column C = Relay neurone D = Motor neurone E = Synapse b. The electric signal reaches the end of the neurone and stimulates the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. If enough chemicals are released that cross the gap (synapse) then the electrical signal is stimulated on the next neurone. c. Stimulants = caffeine chemical persists, heroin and nicotine copies chemical, cocaine prevents removal thus stimulating an electrical signal. Sedative = marijuana which blocks the chemical and stops the electrical signal. 5. . a. . i. ii. iii. iv. No of Heart rate (beats per min) Mean coffees drunk 0 74, 76, 72, 72, 78, 68 74 1 78, 78, 82, 72, 72,70 75 2 78, 78,79, 87, 80, 72 79 3 80, 82, 78, 81, 78, 76 79 4 76, 78, 88, 90, 88, 86, 78 83 5 80, 90, 88, 88, 94, 92 89 X-axis = coffees drunk , y axis = mean heart rate (beats per min), scale 70-90 Yes as increasing cups of coffee increased heat rate. Precautions; Each person should have been tested for each cup of coffee number otherwise different people may have different heart rates. Age and sex should be consistent in the study group. Timings exact for drinking coffee and heart rate measured after. Coffee concentration and volume kept the same. b. This trial cannot be done in real life thus data collected from women who are heroin addicts and get pregnant can be used to support this investigation. 6. . a. A = Relay neurone – takes the signal from the sensory neurone to the motor neurone so the effector is stimulated. b. Synapse c. . i. Electrical ii. chemical d. .Unnecessary e. i. The limb would not sense the hot surface ii. The effector would not react f. No as the message would not be received g. C = Neurone D = Myelin sheath E = Cell body F = Node of Ranvier G = Dendrites Match the words A–5 B–9 C–1 D – 10 E–2 F–3 G–6 H–4 I–7 J–8 Human Reproduction and Growth pg 107 1. . a. A = Vas deferens B = Urethra C = Testis D = Scrotum E = Penis b. C c. F (prostate gland) d. C e. B f. A 2. e, a, d, b, f, c 3. . a. A = Oviduct B = Ovary C = Uterus D = Endometrium E = Cervix F = Vagina b. X = Oviduct Y = Uterus wall = endometrium c. . i. The diaphragm is inserted before the cervix so sperm cannot enter the uterus and oviduct ii. The pill thickens the lining of the uterus so the body thinks it is pregnant. Also the pill prevents ovulation from occurring. 4. . a. . i. Urea, carbon dioxide ii. Mothers’ capillaries and foetuses’ capillaries come in close contact together in the placenta. There is a large surface area in the placenta to allow maximum contact. iii. Kidneys to remove urea, Liver to deaminate proteins, stomach to digest proteins, small intestines to digest food and absorb nutrients etc b. . i. Amniotic fluid is to protect the baby in the watery environment. ii. Down’s Syndrome c. . i. bar graph ii. % increase 30-34 = 4.9 - 0.5 = 4.4 / 0.5 = 8.8 % increase 45-49 = 27.2 – 0.5 = 26.7 / 0.5 = 53.4 iii. HRT benefit reduces the onset of menopause and its symptoms e.g. hot flushes, tiredness, mood swings. HRT disadvantages can lead to breast cancer. 5. . a. . i. A hormone is a chemical substance, produced by a gland, which alters the activity of one or more specific target organs and is then destroyed by the liver. ii. Carried by the blood b. Safe to have sex without a contraceptive c. Oestrogen stimulates ovulation and maintains the lining of the uterus. LH triggers ovulation and matures the corpus luteum to produce progesterone to maintain the endometrium. d. Benefits 99% effective if used correctly, reduce period pain. Disadvantages – can put on weight, increase risk of cervical cancer 6. . a. Head develops e.g. face and ears, Foot gets toes b. . i. 7mm at 6 weeks and 95mm at 6 months ii. 95/7 = 13.6 times 7. . a. P = Ovary Q = Cervix R = Vagina b. The oviducts are closed so the ovum cannot be fertilised and travel to the uterus. c. i. Endometrium in uterus ii. To replicate the journey down the oviduct where the zygote is dividing and forming a ball of cells. d. Implantation after day 14 when the uterus is fully thickened and progesterone is starting to increase to maintain the wall of the uterus. Matching Pairs A – 13 B–9 C–8 D–1 E–3 F – 18 G – 15 H–2 I – 10 J – 20 K–5 L–6 M–7 N–4 O – 17 P – 11 Q – 14 R – 12 S – 16 T – 19 Cell Division and Human Life Cycle 5. a. i. Meiosis ii. haploid nucleus iii. zygote iv. if a boy he will have an X and a Y chromosome and a girl has two X chromosomes b. i. Ovary ii. oviduct iii. uterus Matching Pairs on Cell Division A–7 B–5 C–8 D–6 E– F–9 G–2 H – 10 I–3 J–4 Sensitivity and Movement in Plants Match the Terms A–5 B–7 C–6 D–9 E–3 F – 10 G–4 H–1 I–2 J–2 c. i. Shoot up root down ii. root response is positive geptropism where the auxin gathered on the underside and reduced the growth of the cells so the root grows down. shoot response is a negative geotropism and the auxin has stimulated the growth of cells causing them to elongate so the shoot bends upwards. iii. Gravity was felt on all sides equally. Reproduction in Plants Across 4 stigma 7 fruit 9 hermaphrodite 10 wind 12 seed 13 anther 15 nectary 17 ovary 18 dispersal 19 pollination 20 insect 22 variation 23 filament 24 tuber Down 1 egg 2 competition 3 sepal 5 asexual 6 fertilisation 8 runner 11 petal 14 germination 16 pollen 21 style Enzymes pg 35 ii. iii. iv. Bar Chart Sample A for Liver (8 cm 3) is about twice the volume of oxygen collected than for potato (4.5 cm3). The larger surface area of the chopped pieces of liver provided more catalase and therefore there was more oxygen produced as more hydrogen peroxide was broken down. b. C and D are controls as the enzyme was denatured when the potato and liver were boiled and therefore proves that the enzyme has to be present to breakdown hydrogen peroxide. 1. i. Proteins ii. Pathways iii. Catalysts iv. Specific v. Denatured 2. . a. Temperature b. Amount of catalase (potato pieces)= same sizes use a cork borer, volume of hydrogen peroxide = burette c. Amount of oxygen produced = movement of the manometer (mm) d. Boiled potato to denature enzymes e. Identify anomalies and reduce errors when collecting gas. 3. . a. Slow increase to 25o C as temperature is low and the KE of the particles is low. Then steep increase to 35o C (optimum temperature). Steep decrease to zero oxygen consumption at 65 o C as enzymes have denatured. b. Input = temperature Outcome = oxygen consumption mm per s Fixed = number and size of maggots, availability of oxygen, removal of carbon dioxide. 4. a. Enzyme is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst. b. . i. Carbohydrases to breakdown carbohydrates, proteases to breakdown proteins and lipases to breakdown lipids can all be present in Biological washing powders that turn large coloured molecules into small colourless molecules so the stains are removed. ii. If temperature is too high then the enzymes will be denatured and no longer breakdown the large molecules. iii. 40o C as this is the optimum temperature at which many enzymes work. c. Enzymes can be made mass produced in fermenters. Bacteria can cultured by providing the optimum conditions e.g. food, water, temperature, oxygen so that they can grow and then the enzymes can be extracted. 5. a. i. Tissue Vol of Oxygen collected / cm 3 A B C D Potato 4.5 6.5 0 0 Liver 8 10 0 0 c. Oxygen relights a glowing splint. 6. a. Immobilised means that it cannot move and stays on the plastic. b. The oxygen concentration will decrease as it is used during the reaction with glucose in the presence of glucose oxidase. c. The Transducer converts the oxygen concentration into an electrical signal. Across 1 Denaturation 5 Metabolism 8 Hydrogen 9 10 Substrate 13 Inhibitor 15 Protease 16 Catalyst 17 And 18 Lock 19 Pepsin 20 Optimum Down 2 Temperature 3 Lipase 4 Amylase 6 Active 7 Key 10 Site 11 Activator 12 Catalase 14 Product Germination and Plant Growth Across 3 fertilisation 4 amylase 5 embryo 7 testa 8 radicle 9 ovule 10 cotyledon 13 flower 15 plumule 16 enzymes 17 water Down 1 germination 2 gamete 6 oxygen 11 dormant 12 fruit 14 lipase 15 pollen DNA Genes and Proteins Across 2 amylase 4 protein 5 genotype 7 mutagen 10 chromasome 13 messenger 14 bases 15 aminoacid 16 replication 18 phenotype 19 haemoglobin 20 gene Down 1 bacterium 3 mutation 6 nucleus 8 transcription 9 ribosomes 11 radiation 12 double helix 17 allele Variation and Selection pg 133 1. 1 – A 2–A 3–A 4–N 5–N 6–N 7–A 8–A 2. a. 120 b. Histogram B as the number of limpets measured was much higher giving a more reliable result. c. Area 2 as the bases of the shells was larger so they can cling on better. d. Continuous e. Height 3. . a. Statement 1 – 3, 4 2–2 3–1 b. . i. The paint spot was small ii. The snails with more faded paint had spent longer in the sun as the paint was light sensitive. iii. So that there is an equal chance that the light will reach that part of the snail. iv. They are camouflaged with the dark surroundings 4. . a. Desert as it has adaptions suited to a dry climate b. It has reduced leaves to needles, a large stem to store water and deep roots to reach water. c. A – 4 B–2 C–6 D–1 E–5 F–3 Fill in the Gaps Discontinuous Blood Grouping Continuous Body mass Discontinuous Genotype Continuous Environmental Genotype Phenotype Evolution Mutation Effects of Environment Genes Crossing over Independent assortment Fertilisation Natural selection Evolution Genes Patterns of Inheritance b. they don’t get enough oxygen to their cells for respiration and the production of energy c. sickle-cell anaemia d. mutation e. UV radiation, 5. i recessive otherwise the parents and the first child would have the disease. ii. Parents Phenotype Carriers Parents Genotype Ff Ff Gametes F f Offspring F f F FF Ff f Ff ff Phenotypes 1 normal : 2 carriers : 1 cystic fibrosis 1 in 4 chance 3:1 ratio c. i. Identify and cut gene for normal DNA – Insert into virus RNA – multiply virus ii. danger using viruses as may change other genes, interfering too much with nature, allergies may arise Fill in the Gaps Mendel Garden pea Stamens Stigma Insects Tall Height Homozygous Tall Dominant 1:1 Mendel DNA Genes Chromosomes Nucleus Ecology and Ecosystems Across 3 kiolojoule 5 ecosystem 6 quadrat 9 consumer 10 heterotroph 12 community 14 food chain 17 herbivore 18 habitat 19 omnivore Down 1 autotroph 2 producer 4 population 7 transect 8 carnivore 11 sunlight 13 carbon 14 food web 15 biomass 16 sample Recycling of Nutrients Across 1 denitrification 3 photosynthesis 4 carbon dioxide 5 nitrification 8 fixation 9 nodules 12 respiration 14 fungi 15 bacteria 16 17 excretion 18 active 19 amino acid Down 2 eutrophication 6 enzymes 7 leaching 10 protein 11 combustion 13 nitrate Human Impacts on the Environment Fill in the Gaps Infra red Methane Carbon dioxide Pests Photosynthesis CFCs Ultra violet Cancer Mutation Acid rain Mesophyll Nitrate Pesticides Acid rain Batteries Motor oil CFCs Conservation Across 1 recreation 4 panda 6 food web 8 restoration 9 CITES 13 14 habitats 16 breeding 17 tiger 18 resources 19 zoo 20 elephant Down 2 captive 3 5 agriculture 7 10 rhinoceros 11 12 turtles 15 DDT Farming and Food Production Match the Term with the Definition A–E B–I C–J D–G E–A F–C G–D H–B I–H J–F