10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection
advertisement

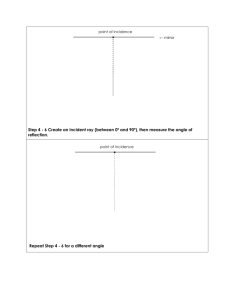
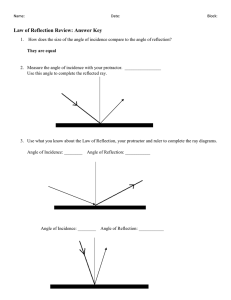
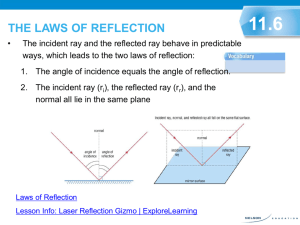
10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Reflection When light (electromagnetic waves) hits a surface its direction is changed This change in direction is referred to as reflection. Reflection can be seen best on surfaces that are mirrors or have mirror like properties. Rays of Light Light travels along a medium. A medium is a term that refers to a substance through which light is traveling through (e.g. water, air) Light will travel in a straight line as long as its moving through the same medium Therefore, if light is travel through air, it will travel in a straight line However, if light travels through air then through water, it may no longer travel in a straight line. Predicting the Path of Light By understanding the properties of light and mediums we can predict the path of light and also the formation of shadows A ray is used to predict the path of light A ray is a straight line with an arrowhead that shows the direction in which light waves are travelling. Rays are commonly used in a process call ray tracing. Ray Tracing Ray tracing is the process of drawing rays from a light source to one or more objects. Shadows can be detecting using this strategy Fermat’s Principle Fermat’s principle predicts the path light will take after reflecting from a surface or passing through more than one medium (e.g. air to water) Light will follow the shortest path possible Leads to the laws of reflection The Laws of Reflection A ray of light moving towards a surface is known as the incident ray. The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and a perpendicular (Normal) line at the point where the ray touches the surface The Laws of Reflection The reflected ray begins at the point of contact and is at a right angle to the incident ray. The angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the perpendicular (Normal) line. The angle of incidence/ray is equal to the angle of reflection/ray Laws of reflection Drawing Ray Diagrams Follow figure 10.14 and draw a ray diagram for: An incident ray at 5 cm from the normal at a 30o angle An incident ray at 10cm from the normal at a 20o angle Homework Questions Answer questions 2-3 on page 414 Images in Plane Mirrors When light is applied to an object in a plane mirror, the image of that object is formed on the other side. Using the laws of reflection, one can predict the characteristics of the image and where the eye sees the image. Image Four Characteristics of an Image In general an image has four characteristics: 1. Its location (i.e. closer than, farther than, same distance) 2. Orientation (upright or inverted) 3. Size (same, smaller, or larger) 4. Type (real or virtual) E.g. Location (farther than) E.g. Orientation (inverted) Size (larger) Type (real image) Homework Questions Answer questions on page 418` #1,2,4, 6,7