Bio EOCE Study Guide 2
advertisement

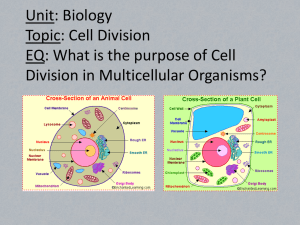
Final Exam Study Guide I. 1. a. b. c. d. 2. a. b. c. d. 3. b. c. d. e. Nature of Science – Ch 1 Write the definitions for these terms: Hypothesis - _______________________________________________________________________________ Independent Variable - ______________________________________________________________________ Dependent Variable - ________________________________________________________________________ Constant - _________________________________________________________________________________ Tom and Jerry were testing to see if soil pH had an effect on plant growth. Tom took three plants of the same species and placed them in 3 different sized pots. Jerry added the different soils to each pot. Each plant got the same amount of sunlight, water, and temperature. They took measurements every day for 4 weeks and measured/recorded the plant growth in a chart. Soil pH Plant Growth (cm) 3.5 150 4.5 100 5.5 50 Were there any flaws in this experiment? If so, explain. _____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Write a possible hypothesis for this experiment. ____________________________________________________ What does Tom and Jerry need to do in order to make this a controlled experiment? ______________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ List each of the different components for this experiment: Independent variable - _____________________________________ Dependent variable - _______________________________________ Constants - __________________________________________________________________________________ a. What is the biosphere? ______________________________________________________________________ Circle the portion of the earth that is the biosphere. Define biodiversity: __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ Where on Earth is the most biodiversity? ________________________ What is a species? ___________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 4. All living organisms share these characteristics: a. All living things are made up of __________, which are the building blocks of life. b. All living things need _____________ so that they can metabolize, or carry out chemical functions. c. All living things ______________ to their environment, due to a stimulus. d. All living things _____________ to pass on their genetic material. 5. What is homeostasis? _____________________________________________________________________ Give an example of homeostasis: ____________________________________________________________ 6. What is the difference between a theory and a law? Theory Law 7. a. Label the parts of the microscope: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. b. What kind of microscope is this? _______________________________________ 8. What is difference between a scanning and a transmission electron microscope? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Write the steps of the scientific method in the correct order: a. State a hypothesis 1._______________________________ b. Analyze data 2._______________________________ c. Make observations 3._______________________________ d. Do research 4._______________________________ e. Plan and conduct experiment 5._______________________________ f. Ask a question 6._______________________________ g. Draw conclusion 7._______________________________ 10. Put the data below into a bar graph from greatest to least amount of sightings. II. Number of Sightings 23 Type of Birds 15 Blue Jays 37 Chickadees 4 Bluebirds 20 Cardinals Crows Macromolecules/Biochemistry – Ch 2 11. Define these terms: a. Atom - _________________________________________________________________________________ b. Element - _______________________________________________________________________________ c. Compound - _____________________________________________________________________________ d. Molecule - ______________________________________________________________________________ e. Ion - ____________________________________________________________________________________ 12. a. Label the protons, neutrons, and electrons in the carbon atom below. b. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms?_________ c. Carbon-based molecules have 3 fundamental structures: ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ 13. Identify the correct type of bond: ___________________ - sharing of electrons between atoms ___________________ - slightly positive hydrogen is attracted to a slightly negative atom ___________________ - oppositely charged ions are attracted to one another 14. Water is a ______________ molecule because the ___________ atom has a slight negative charge and the ________________ atom has a slight positive charge. 15. Water ________________ when it freezes. Fish can survive a cold winter because the ice acts as a(n) _______________________ that allows the water underneath to remain liquid. Ice is _________ dense than water. 16. What type of bond is formed between water molecules? ____________________________ 17. Although hydrogen bonds are 20 times weaker than covalent bonds, they give water some very special properties. Identify the properties of water due to hydrogen bonding: ___________________________ - allows insects to float on water due to surface tension ___________________________ - makes the water inside the cells of your body resistant to changes in temperature ___________________________ - allows water to travel up from the roots to the leaves in plants 18. a. The ________________ is the substance that dissolves. b. The ________________ is the substance that is present in the greatest amount and is the substance that dissolves the solutes. c. Label the solvent, solute, and solution. 19. An __________ releases H+ ions in water so therefore substances like stomach acid has a ________ H+ concentration and a _______ pH. 20. A __________ removes H+ ions when dissolved in water, therefore has a ________ H+ concentration and a _________ pH. 21. Water has a _______________ pH. 22. A small molecule called a__________________ is a subunit that can be bonded together to form a large molecule called a ________________. 23. Fill in the blank boxes in the chart below: The Four Biological Macromolecules Monomer Polymer Carbohydrates Polysaccarides Amino Acids Nucleic Acids Fatty Acids Lipids (triglycerides) 24. Identify this structure. Identify this structure. Identify this structure. Identify this structure. ___________________ ___________________ __________________ ______________________ 25. For each of the four major biological macromolecules, list examples and the primary function for each in the chart below. Biomacromolecules Proteins Nucleic Acids Lipids Carbohydrates Examples Primary Function(s) 26. Define these terms: Catalyst - ___________________________________________________________________________________ Enzyme - ___________________________________________________________________________________ 27. Most enzymes are _______________ which carry out functions and form important structures in the body. 28. Things like ________ and ____________________ can change the shape and function, or activity, of an enzyme. 29. Why is a very high fever so dangerous to a person? ________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 30. Enzyme structure is important because its shape allows only certain ______________ to bind to the enzyme. The specific reactants that an enzyme acts on are called _________________. 31. In the lock and key model, substrates temporarily bind to substrates at specific places called ____________ ___________. III. Cell Structure and Function – Ch 3, 5 32. What are the three major principles of the cell theory? 1. ____________________________________________________________ 2. ____________________________________________________________ 3. ____________________________________________________________ 33. Identify the scientists that made these important discoveries that contributed to the cell theory. _______________ Said that all plants were made up of cells _______________ Looked at cork cells and thought they looked like tiny rooms _______________ Stated all living things were made up of cells _______________ Proposed all cells come from preexisting cells _______________ Looked at pond water and saw tiny animalcules 34. The discovery of cells would not be possible without the invention of the ___________________. 35. Write in each of these descriptions into the correct box: No nucleus Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Has membrane-bound organelles No membrane-bound organelles Has a nucleus Single-cellular Mostly multi-cellular Bacteria Plants and Animals 36. a. Is the cell below prokaryotic or eukaryotic? __________________________ b. Label the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, plasmid, ribosomes, and flagella. 37. a. Label the organelles of the plant cell. b. What 3 structures are only found in plant cells? _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ 38. a. Label the organelles of the animal cell. b. What 2 structure are only found in animal cells? ________________________ ________________________ 39. Both plant an animal cells are _______________________ cells. 40. Identify the function of these important cell organelles: Organelle Name Organelle Function Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Nuclear Envelope Nucleolus Chromatin Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Microtubules Microfilaments Vacuoles Mitochondria Golgi apparatus Chloroplasts Lysosomes Cilia Flagella 41. Another name for the cell membrane is _____________ membrane. 42. Why is the cell membrane referred to as a highly selective barrier? _____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ 43. The cell membrane is made up of two_____________________ layers that are embedded with other molecules, such as _______________, ____________________, and _______________________. 44. Scientist call this phospholipid bilayer a ___________ _____________ ____________ because the cell membrane is flexible and is made up of many parts. 45. Identify these important terms related to movement across the cell membrane: a. _________________________ - does not require energy to move molecules across the cell membrane. b. _________________________ - requires energy to move molecules across the cell membrane. c. _________________________ - movement of molecules from a high to low concentration d. _________________________ - movement of water across the cell membrane 46. a. A hypotonic solution has ___________ solutes than the inside of a cell, causing the cell to _____________. b. A hypertonic solution has ____________ solutes than the inside of a cell, causing the cell to _____________. c. An isotonic solution has an ____________ amount of solute as inside the cell so its size stays the___________. 47. For each of the three solutions above, draw an arrow showing which way water is moving into and/or out of the cell. 48. Fill in the chart below with the correct information: Type of Transport Transport protein With or against used? concentration gradient? Simple diffusion Facilitated diffusion Active transport Requires energy from the cell? Active or passive transport? 49. Label the two processes are depicted below? Do these processes require energy? ______________ __________________________________ __________________________________ 50. What are the 3 main phases of the cell cycle? ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ 51. a. In which phase of the cell is DNA replicated? ____________________________ b. Does this occur before or after mitosis/meiosis? _________________ 52. Write the major events of each phase of mitosis. Phases of Mitosis Picture of phase Major events Prophase 1.Chromosomes ___________________ _________________________________ 2. Nuclear envelope ________________ 3.Centrioles _______________________ _________________________________ 4.Spindle fibers ____________________ Metaphase 1.Chromosomes ____________________ _________________________________ 2. Spindle fibers attach to _________________________________ Anaphase 1. Sister Chromatids ________________ _________________________________ Telophase 1.Nuclear membrane _______________ _________________________________ 2. Chromosomes ___________________ _________________________________ 3.Spindle fibers ____________________ _________________________________ 53. Mitosis results in the formation of ________ daughter cells the are genetically ___________________. 54. Mitosis occurs in _____________, or body cells. 55. Mutations in genes can sometimes lead to ___________________, which is uncontrolled cell division. 56. Cancer can by caused by mutagens, or __________________. 57. List some example of things that can cause cancer. ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 58. What is asexual reproduction? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ IV. Bio EOC Exam Study Guide – Honors/Pre-IB Biology Plants and Cell Energy – Ch 21, 22.2, 4 Part 2 59. Label the structure and write the function for each of the plant parts. a. Flower - ______________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ b. Stem - _______________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ c. Root - ________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ d. Leaf - ________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 60. What materials do the xylem and phloem carry? a. Xylem - _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ b. Phloem - ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 61. In what structures does photosynthesis occur in the plant? ________________________________________________________________ 62. What is transpiration? ________________________________________________________________ 63. How do plants move water from the roots to the leaves using transpiration and the special properties of water? ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 64. a. Label all the parts of a flower. b.Color the female parts pink. c. Color the male parts green. 65. Define these terms: a. Photosynthesis - ________________________________________________________________________ b. Cellular Respiration - _____________________________________________________________________ 66. Look at the equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Identify which equation is photosynthesis and which is cellular respiration and label the reactants and products for each. 67. Compare the equations of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. How are the two processes related? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 68. Fill in the chart below for photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Photosynthesis Cellular Respirtation Organelle for process? Reactants? What does it need? Products? What does it make? Who uses this process? 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. V. What does ATP stand for? __________________________________________ What is ATP used for? _________________________________________________________________________ Cellular respiration is an __________________ process because it uses oxygen to produce ATP. Fermentation is an __________________ process because it does not use oxygen to produce ATP. The two types of fermentation are _____________________ and _____________________. Genetics and Meiosis – Ch 6, 7 74. Mendel’s Law of Segregation states that: Organisms inherit ________ copies of each gene; ________ from each parent Organisms donate only ________ copy of each gene in their gametes. Thus, the two copies of each gene ________________ during gamete formation 75. Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment states that: Allele pairs separate ______________________ of each other during gamete formation, or meiosis. So, different traits appear to be inherited ____________________. 76. Fill in the chart below comparing mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis Meiosis Produces genetically ___________________ cells. Results in __________________ cells which have 2 copies of each chromosome. Cell division of ________________ cells, or body cells. Takes place _________________ an organism’s life. Involved in ________________ reproduction. Produces genetically ___________________ cells. Results in ____________________ cells which have only 1 copy of each chromosome. Cell division producing _______________, or sex cells Takes place only at ____________________ in an organism’s life. Involved in __________________ reproduction. 77. Homologous chromosomes are two chromosomes, one inherited from the ______________, one from the ________________, that have the same _______________ and same general ______________________. 78. Look at the pair of homologous chromosomes to the right. What process is occuring in this diagram? ________________________________________ 79. Due to gene linkage, which genes are more likely to be inherited together, A&B, A&D, or B&D? ____________________ Explain? _______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 80. Answer the questions below using a Punnett square. Show your work and calculate probablities and show phenotypic ratios (Homozygous Dominant:Heterozygous:Homozygous Recessive) for each cross. a. A homozygous dominant gray oompa loompa marries a homozygous recessive orange oompa. Will any of their children be orange?____________Show your work! Phenotypic Ratio: ____________________ % Gray_______________ % Orange ____________________ b. If Roxy oompa and Ronnie oompa have 4 oompa children and 1/4th are orange, what must be their genotypes. Show your work in a Punnett square. ________ X _________ 81. Define the different modes of Inheritance: a. Autosomal recessive - _____________________________________________________________________ b. Autosomal dominant - _____________________________________________________________________ c. Codominant - ____________________________________________________________________________ d. Incomplete dominance - ___________________________________________________________________ e. Sex-linked - ______________________________________________________________________________ f. Polygenic - _______________________________________________________________________________ g. Multiple alleles - __________________________________________________________________________ 82. Identify the different modes of inheritance in the example questions below. a. A cross between a purebred animal with red hairs and a purebred animal with white hairs produces an animal that has both red hairs and white hairs. What type of inheritance pattern is involved? ______________________________ b. In a cross between individuals of a species of tropical fish, all of the male offspring have long tail fins, and none of the females possess the trait. Mating two of the resulting offspring fails to produce females with the trait. Explain the inheritance pattern of the trait. _______________________________________________ c. A red-flowered sweet pea plant is crossed with a white-flowered sweet pea plant. All of the offspring are pink. What is the inheritance pattern being expressed? __________________________________________ d. An ecologist observes that a population of plants in a meadow has flowers that may be red, yellow, white, pink, or purple. Hypothesize what the inheritance pattern might be. ________________________________ e. In cats, the allele for fur color is sex linked. The allele for black fur is XC, and the allele for orange fur is Xc . From this information, explain why calico cats, XCXc, are always female. ______________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ f. Suppose you mate a black rooster with a white hen. The feathers of all the offspring are “blue,” a color that is intermediate between black and white. Explain the inheritance pattern in these chickens. _______________________________ g. Julia purchased a puppy from a breeder. The breeder explained that the puppy should never be bred with another dog because it was a carrier. What did the breeder mean by this statement? __________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ h. Inheritance of the palomino coat color in horses is a result of incomplete dominance. White horse is DD, a chestnut horse is dd, and a palomino horse is Dd. What is the expected ratio of coat colors in the offspring of two palomino horses? _____________________________________________________________________ VI. Molecular Genetics – Ch 8,9 83. a. In the DNA structure to the right, label a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. b.Circle a nucleotide. 84. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are _________________, __________________, ___________________ and ___________________. 85. In DNA, adenine always binds with ________________ and guanine always binds with ___________________. 86. DNA’s genetic code is called a _________________ code because it is common to all organisms. 87. Describe the basic steps of DNA replication. 1. Unzipping:___________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ 2. Nucleotides added:____________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ 3. Two identical molecules formed:__________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 88. Why does DNA replicate? ______________________________________________________________________ 89. Write the complementary base pair sequence for TAC CGC AAT TGG CAG. ____________________________________________________________ 90. The central dogma states that information flows in one direction, from __________ to _________ to ______________. 91. Describe the basic goal of these two processes: Transcription - _________________________________________________________ Translation - ___________________________________________________________ 92. Write the function of these three types of RNA: mRNA - _______________________________________________________________ rRNA - ________________________________________________________________ tRNA - ________________________________________________________________ 93. In RNA, the base thymine is replaced with __________________. 94. Using the DNA base sequence TAC TTT GGA AAC ATG GCT ACT, transcribe the sequence into mRNA and then translate into an amino acid sequence (Pg 244 in Holt). Transcription: DNA RNA Translation: RNA Protein 95. DNA contains ___________ that code for different traits in an organism. 96. Mutations in DNA can cause proteins to be misshapen and not function properly. How could a mutation in DNA affect the phenotypic expression of genes in an organism?____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 97. A mouse that contains the gene for GFP from a jellyfish which makes the mouse glow green is an example of a ____________________ organism. 98. ___________________ _________ is DNA that contains genes from more than one organism. 99. Why is it that a human gene can be inserted into a plasmid (loop of DNA) in a bacterial cell? _______________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 100. What were the two main goals of the human genome project? 1. ________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________ VII. Evolution – Ch 10, 11, 12 101. Many scientists contributed to the theory of evolution. Name the contributions that these scientists proposed. Charles Darwin - _________________________________________________________________ Lamarck - _______________________________________________________________________ Linnaeus - _______________________________________________________________________ 102. What is the theory of natural selection? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 103. Describe these four principles of natural selection. Principles of Natural Selection Description 1. Variation 2. Overproduction 3. Adaptation 4. Descent with modification 104. The fossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, biogeography, molecular biology, and observed evolutionary change are all types of ________________________ of evolution. 105. a. How does the brain size and jaw size change from early ancestory to modern humans?___________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ b.How do you think this influenced things like language and the manufacture of tools? _________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 106. Explain how the finches on the different islands of the Galapagos had such different traits from one island to the next. _________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 107. How is embryology evidence for evolution? _____________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 108. Define these terms: Homolougous structure - __________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Analogous structure - _____________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 109. Which type of structure suggest evidence of a common ancestor? _____________________________________________ 110. A whale’s hip bone is a vestigial structure. What might this structure suggest about an earlier ancestor? _______________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ VIII. Diversity and Classification of Organisms – Ch 17, 18.4, 19.1, 19.5, 20, 23.1 111. Why do we classify organisms? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 112. Define these terms: Taxonomy - _________________________________________________________________________________ Binomial Nomenclature - ______________________________________________________________________ 113. What is the genus and species (scientific name) for a modern human being? ______________________ 114. Linnaeus classified organisms into a heirarchy of taxa. List the classification system in order from broadest to most specific. _________________, ___________________, __________________, _________________, __________________, __________________, _________________, _________________ 115. The evolutionary history for a group of species is called ______________________. 116. According to this cladogram to the right, which organism is most closely related to dinosaurs and birds? _______________________________ 117. Organisms in this cladogram are hierarchically classified based upon _______________________ relationships. 118. What are the three domains: __________________, _____________________, ____________________ 119. The two original kingdoms in 1753 were plantae and animalia. Due to the contribution of many new findings by many scientists, there are now six kingdoms which are __________________, __________________, ____________________, _____________________, _______________________, and _____________________. 120. Explain reasons that might cause an organism’s classification to change. __________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ IV. Ecology – Ch 13, 14, 15, 16 121. Draw an energy pyramid and add the following organisms at the appropriate trophic level: grass, rabbit, grasshopper, snake hawk. Label each level .. . producer through tertiary consumer. Write the amount of energy in kcals if the producers contain 10,000 kcals of energy. 122. Study the marine food web above. What organisms not shown in this food web arfe importan to the stability of the ecosystem? 123. If the fish were contaminated by toxins, how would this event affect the entire ecosystem. Why would the humans be most vunerable? 124. Use a concept map to display the differences between exponential growth and logistic growth. Lable which is known as a “J-curve” and which is know as an “S-curve”. Population Growth 125. Use a main idea chart to explain and give example of density –independent and density- dependent limiting factors. Density Independent Density dependent Ex. 126. Ex. Use a concept map to summarize what you know about climate zones. 127. Use a diagram to summarize what you know about biomes. Earth has six major biomes 128. How do you think the organisms above the high-tide zone are able to obtain the water they need to survive? What adaptations are necessary for the species in the spray zone compared with the species in the low-tide zone? Why wouldn’t fish be a major part of the intertidal zone? 129. What are the limiting factors in the freshwater Which abiotic factor affects the freshwater producers? toxin was introduced which organism would be most How would a severe drought over several years affect this What type of succession is this? 130. ecosystem below? If a water-soluble affected and why? ecosystem? CO2 is important in our atmosphere because it is required for photosynthesis and it traps some Heat, keeping Earth warm. However, human –produced CO2 is a problem. Explain why and what could be done to counter these consequences.