BSc (Hons) Fire Safety and Risk Management (Sept 2013)
advertisement
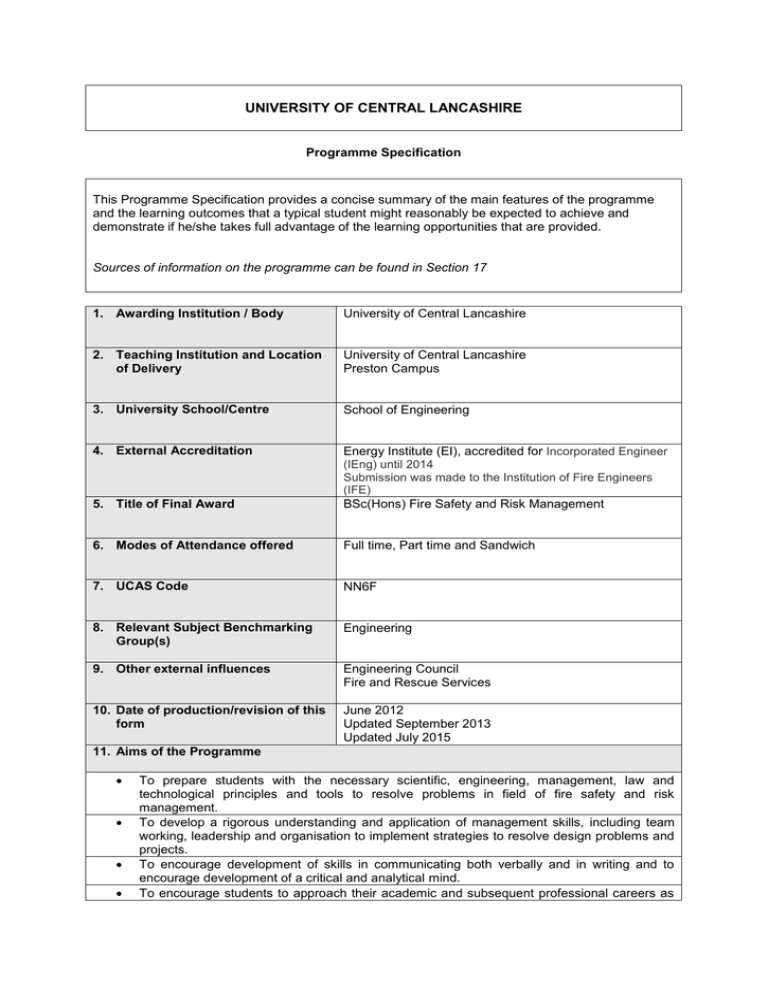
UNIVERSITY OF CENTRAL LANCASHIRE Programme Specification This Programme Specification provides a concise summary of the main features of the programme and the learning outcomes that a typical student might reasonably be expected to achieve and demonstrate if he/she takes full advantage of the learning opportunities that are provided. Sources of information on the programme can be found in Section 17 1. Awarding Institution / Body University of Central Lancashire 2. Teaching Institution and Location of Delivery University of Central Lancashire Preston Campus 3. University School/Centre School of Engineering 4. External Accreditation 5. Title of Final Award Energy Institute (EI), accredited for Incorporated Engineer (IEng) until 2014 Submission was made to the Institution of Fire Engineers (IFE) BSc(Hons) Fire Safety and Risk Management 6. Modes of Attendance offered Full time, Part time and Sandwich 7. UCAS Code NN6F 8. Relevant Subject Benchmarking Group(s) Engineering 9. Other external influences Engineering Council Fire and Rescue Services 10. Date of production/revision of this form June 2012 Updated September 2013 Updated July 2015 11. Aims of the Programme To prepare students with the necessary scientific, engineering, management, law and technological principles and tools to resolve problems in field of fire safety and risk management. To develop a rigorous understanding and application of management skills, including team working, leadership and organisation to implement strategies to resolve design problems and projects. To encourage development of skills in communicating both verbally and in writing and to encourage development of a critical and analytical mind. To encourage students to approach their academic and subsequent professional careers as creative and innovative individuals. To provide students with detailed contextual knowledge of subjects underpinning fire safety and risk management in the broad areas of combustion, law, economics, management, risk assessment and fire dynamics. To develop the use of appropriate technical methods in the study of fires and risks; and the resolution of fire safety and risk management problems for the built environment and related infrastructure. To develop an expertise in the application of health and safety management systems to resolve problems, implement safe solutions and to ensure safe working environments. To provide students with the skills necessary to enable them to adapt and contribute to changes and advances in the subject matter and direction of the discipline of fire safety and risk management. 12. Learning Outcomes, Teaching, Learning and Assessment Methods A. Knowledge and Understanding A1. Demonstrate an understanding of the underpinning science, risk management principles and law applicable to fire safety. A2. Demonstrate a systematic understanding of key principles of all relevant technical and engineering aspects relating to fires, combustion and risk management as they relate to the study of fire safety for the built environment and related infrastructure. A3. Demonstrate an understanding of the design, operation and performance of design solutions to achieve fire safety in built structures. A4. Demonstrate an understanding of the interrelationships between the professional inputs into fire engineering and fire project solutions with respect to all applicable managerial, legal, environmental and social parameters. A5. Critically evaluate appropriate strategies for the application and implementation of fire safety and risk management within built environment and related infrastructure. Teaching and Learning Methods Lectures, seminars, tutorials, laboratory classes, directed reading, problem-solving, case studies, discussions. The method is dependent on individual modules. Assessment methods Varying methods of assessments are utilised appropriate to learning outcomes of individual modules. Examples include Workbooks, seminar presentations, essays, reports, group and individual presentations and end of module seen and unseen examinations. Detail dependent on module choice. B. Subject-specific skills B1. Critically evaluate ideas, proposals and solutions or arguments independently and/or collaboratively in response to set scenarios and/or self initiated activity. B2. Critically evaluate designs to make judgements whether they integrate social, legal, environmental and technical requirements. B3. Identify appropriate design and governance problems and formulate clear objectives using data and ICT software as appropriate. B4. Develop design briefs with clarity graphically and/or in written specifications. B5. Apply specialist fire safety and risk assessment knowledge to design problems and to ensure safe working environments. B6. Demonstrate the ability to identify areas of research and conduct independent research on appropriate fire safety project. Teaching and Learning Methods Varying teaching methods are adopted across different course modules. For example, laboratory classes with workbook (testing of materials). Preparation of laboratory reports and interpretation of other data. Projects where students input their own practical solution to real problems. Case study materials used in seminar environment. Detail dependent on individual module. Assessment methods Subject specific skills are assessed from laboratory reports, individual and group projects. A range of research and industry-relevant examples and designs are used for context, for example, the completion of the design problem in the module FV3003 and risk assessment problems in FV3103 assignments will enable achievement of such skills and also attention is given to personal development planning. Detail dependent on individual module. C. Thinking Skills C1. Select, analyse, synthesise and interpret information from a range of sources. C2. Demonstrate ability to plan and carry out independent learning. C3. Critically evaluate the concepts, values and debates which inform study and practice in fire safety and risk management. C4. Identify and analyse broadly defined problems, evaluate possible optional strategies and propose appropriate solutions. Teaching and Learning Methods Skills developed through lectures, seminars, case studies, dissertation / research project, presentations, group and project work will enable students to acquire and develop problem solving skills. Detail dependent on individual module. Assessment methods Through directed seminar presentation, reports, problem solving / case studies, end of module seen and unseen examinations and dissertation work. Case studies and / or project based scenarios emphasis is placed upon justification and consideration of practical implementation of solutions. Detail dependent on individual module. D. Other skills relevant to employability and personal development D1. Communicate effectively in a variety of formats. D2. Demonstrate literacy and information sourcing and retrieval skills from a range of sources, such as books, scientific reports, journals, case studies, CD-ROMs, the internet. D3. Use ICT effectively including computer simulations/predictions. D4. Demonstrate self reliance, time management skills and ability to work effectively with others in the context of a team. D5. Demonstrate skills in negotiation, listening and evaluation of opinions and values of others. Teaching and Learning Methods Discussions and seminar presentations; IT through coursework; team-working skills practiced and developed through group based activities and project work in specific modules at level 2 and 3, class work in tutorials/case studies/problem solving. Details dependent on individual module. Assessment methods Written reports, oral presentations, word processed documents, PowerPoint presentations, data analysis and presentation, group projects and presentations; individual presentations. Detail dependent on individual module. 14. Awards and Credits* 13. Programme Structures* Level Level 6 Module Code FV3900 FV3001 FV3002 FV3103 FV3004 FV3101 Module Title Credit rating Engineering Dissertation Enclosure Fire Dynamics Fire Protection Engineering Hazards and Risk Management Fire Investigation Strategic Risk Decision Making 20 20 20 20 20 20 Bachelor Honours Degree in Fire Safety and Risk Management Requires 360 credits including a minimum of 100 at level 6, 120 at level 5. Bachelor Degree in Fire Safety and Risk Management Requires 320 credits Including a minimum of 180 credits at level 5 or above and 60 credits at level 6. Level 5 FV2001 FV2003 FV2004 FV2101 FV2102 FV2103 FV2207 FV2800 Level 4 FV1001 FV1101 FV1201 Fluid Dynamics of Fires Fire and the Built Environment Fire Safety Management and Legislation Accidents and Catastrophes Safety, Health and Environment Project Management Structures, Materials and Fire Industrial Experience Introduction to Combustion and Fire Safety and Fire Law Energy Transfer and Thermodynamics FV1202 Engineering Design Practice FV1502 Skills for Science and Engineering FV1207 Buildings, Materials and Fire FV1302 Engineering Analysis 1 15. Personal Development Planning 20 20 20 10 20 10 20 120 (O) 20 10 20 20 10 20 20 Bachelor Honours Degree with Sandwich Requires 360 credits including a minimum of 220 at level 5 or above with a minimum of 100 at level 6. Sandwich element requires successful completion of module FV2800 which has a notional credit rating of 120 credits. Diploma HE in Fire Safety and Risk Management Requires 240 credits of which 100 must be at level 5 and 120 at level 4 or above Certificate HE in Fire Science Requires 120 credits of which 100 must be at level 4 or above. PDP is developed across the degree it is an integral part of the Fire Safety and Risk Management course, it is delivered and monitored through the personal tutor system. The personal tutor will monitor progression at regular intervals throughout level 1. In specific modules the student will be encouraged to review and reflect upon progression and develop an awareness of the personal and professional needs, to reflect and develop skills relevant to the role of fire safety professional. Students are provided with a PDP handbook and an introductory lecture on it during induction week. Academic skills alone are clearly insufficient to meet the demands of the fire professionals. The development of additional interpersonal qualities is essential to enable students to initiate, direct and control events effectively. To help students develop these skills, many of the tutorial activities and assignment work will provide them with the opportunity for practical project work, the development of problem solving skills and discussion and critical appraisal. Students are required to make oral presentations at intervals throughout their course. Presentations may be solo or joint events, by two or more students and group discussion on contentious points will be encouraged. 16. Admissions criteria Programme Specifications include minimum entry requirements, including academic qualifications, together with appropriate experience and skills required for entry to study. These criteria may be expressed as a range rather than a specific grade. Amendments to entry requirements may have been made after these documents were published and you should consult the University’s website for the most up to date information. Students will be informed of their personal minimum entry criteria in their offer letter. Applicants will normally be required to have, one of: CCC at A2, ND with MMM, IB- 24P. Pass Access Course with Merits in 30 Level 3 Credits. In addition applicants will be required to have Maths and English GCSE at Grade C or equivalent. Applicants will be required to have a minimum level of proficiency in English Language equivalent to IELTS grade 6 with no subscore lower than 5.5 Applications from individuals with non-standard qualifications, relevant work or life experience and who can demonstrate the ability to cope with and benefit from degree-level studies are welcome. If candidates have not studied recently they may be required to undertake an Access programme. APL/APEL will be assessed through standard University procedures. Please consult the UCLAN admissions department for the most up to date requirements. 17. Key sources of information about the programme University web site (www.uclan.ac.uk) UCAS web site (www.ucas.ac.uk) School website (www.uclan.ac.uk/forensic) Course Leader Admissions tutor 18. Curriculum Skills Map LEVEL 6 Please tick in the relevant boxes where individual Programme Learning Outcomes are being assessed Level Module Module Title Core (C), Programme Learning Outcomes Code Compulsory Knowledge and Subject-specific Skills Thinking Skills (COMP) or understanding Option (O) LEVEL 5 A3 FV3001 Enclosure Fire Dynamics COMP Fire Protection Engineering COMP FV3004 COMP FV3900 Fire Investigation Strategic Risk Decision Marking Hazards and Risk Management Engineering Dissertation FV2001 Fluid Dynamics of Fire COMP FV2003 COMP COMP COMP COMP FV2103 Fire in the Built Environment Fire Safety Management and Legislation Accidents and Catastrophes Safety, Health and Environment Project Management FV2207 Structures, Materials and Fire FV2800 COMP COMP COMP FV1202 Industrial Experience Introduction to Combustion and Fire Safety and Fire Law Energy Transfer and Thermodynamics Engineering Design Practice COMP O COMP FV1207 Buildings, Materials and Fire COMP FV1302 Engineering Analysis 1 Skills for Science and COMP FV3101 FV2004 FV2101 FV2102 FV1001 LEVEL 4 A2 FV3002 FV3103 FV1101 FV1201 FV1502 Note: A1 Engineering A4 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 COMP COMP D4 D5 D3 D2 D1 C4 C3 COMP C2 C1 C COMP A5 Other skills relevant to employability and personal development Mapping to other external frameworks, e.g. professional/statutory bodies, will be included within Student Course Handbooks.