Section 17.1 Summary – pages 443-449
advertisement

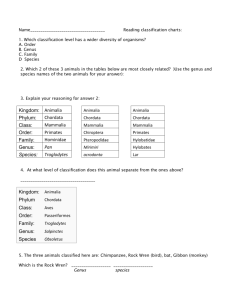
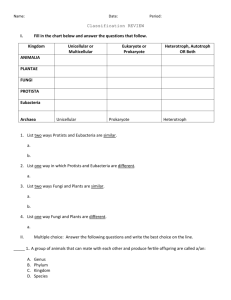
• Taxonomy is the study of how living things are classified into groups. • The groups that organisms are classified into are called taxa. (Taxon if singular) Organisms are physical similarities classified based genetic similarities on: When a taxonomist discovers a new organism they start classifying it based on certain characteristics…..first, they look at what kind of cell structure it possesses. Types of Cells prokaryotic eukaryotic Once they know this, they can place the organism in the correct Domain. Domain is the most broad taxon. There are three domains…. Types of Cells prokaryotic Domains Archaea Bacteria eukaryotic Eukaryota Organisms in this Domain are prokaryotic, small, and survive in extreme “unlivable” conditions Organisms in this Domain are prokaryotic, larger than Archaea, and live in hospitable conditions Organisms in this Domain are made of eukaryotic cells, more complex than bacteria In which Domain would they classify a human? Next, they would need to decide which Kingdom it belonged in… Types of Cells Domains Kingdoms prokaryotic Archaea Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Protista eukaryotic Fungi Organisms are grouped into kingdoms based on: 1.Type of cell 2.How they obtain energy 3.How many cells they are made of, and 4.How complex their body structure is Plantae Animalia 8 Classification Groups “Taxa” Domain- Most broad, only three domains: Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya Example: Humans at this level are grouped with all other organisms made of eukaryotic cells– (Algae, Fungus, Plants, and Animals) Kingdom- More specific, based on cell type, method of obtaining energy, and # of cells, and complexity: Example: Humans at this level are grouped with all other animals- (Sponge, Insects, Birds, Mammals) Phylum- Based on even more specific characteristics. For plants This is called “Divisions” Example: Humans are grouped with other animals that have backbones at this level. Class - Based on even more specific characteristics. Example: Humans are grouped with other animals with backbones that feed milk to their young. Order - Based on even more specific characteristics. Example: Humans are grouped with other animals with backbones that feed milk to their young and have opposable thumbs. Family - Based on even more specific characteristics. Example: Humans are grouped with other great apes that have opposable thumbs and have very close DNA strand sequence. Genus - Even more specific Example: Humans at this level are grouped with other humanlike ancestors based on the use of language and tool use. Species - Exact organism Example: “Modern” humans with our brain size, learning capacity, and longevity. • Organisms classified Solar System from most broad group, domain, Earth down to most specific, species North America U. S. TX DFW Denton County Justin Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778), a Swedish botanist “binomial nomenclature” Was created by Linnaeus. It is a two-word naming system for living things. SCIENTIFIC NAMING! • The “Binomial nomenclature” or scientific name for each species, is a combination of the genus name and species name. Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Homo = Genus, Homo sapiens sapiens = species Why not use common names? • Misleading – starfish – Dragonfly • Confusing – blue jay, blue coat, corn thief – dog, perro, chien They all have ONE scientific name. Pisaster ochraceus Pyrrhosoma nymphula Cyanocitta cristata The common name of many animals can be misleading. Ceylon frogmouth (Batrachostomus moniliger) is a bird…. Killer whales (Orcinus orca )are the largest member of the dolphin family. Flying fish (Parezocoetus mesogaster) do not fly, but glide. Seahorse (Hippocampus zosterae) is not a horse, but a fish. What language is used for the scientific naming? LATIN 1. Latin is no longer used in conversation. 2. It’s tradition. 3. Universal. What is the correct way to write the scientific name? * Always capitalize the Genus and not the species. •If handwriting, underline the name: Felis concolor •If typing, put the name in italics: Felis concolor •You can also abbreviate the Genus: F. concolor Question 1 According to the table, at what level does the domestic cat diverge from the ferret? Classification of Representative Mammals Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordata Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Order Cetacea Carnivora Carnivora Family Mysticeti Mustelidae Felidae Genus Balenopora Mustela Felis Species B. physalus M. furo F. catus Ferret Domestic Cat Common Name Blue Whale The domestic cat belongs to the family Felidae and the ferret belongs to the family Mustelidae. Classification of Representative Mammals Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordata Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Order Cetacea Carnivora Carnivora Family Mysticeti Mustelidae Felidae Genus Balenopora Mustela Felis Species B. physalus M. furo F. catus Common Name Blue Whale Ferret Domestic Cat Question 2 How many levels of classification do all three animals share? Classification of Representative Mammals Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordata Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Order Cetacea Carnivora Carnivora Family Mysticeti Mustelidae Felidae Genus Balenopora Mustela Felis Species B. physalus M. furo F. catus Common Name Blue Whale Ferret Domestic Cat All three animals belong to the same kingdom, phylum, and class.