Dry Ice and Phase Diagrams

Dry Ice and Phase Diagrams
Warm Up – WKSHT #2 AND
PROGRESS REPORTS OUT!
1. How much energy is required to boil 15g water?
2. How much energy is required to heat a block of ice from -20C to -5C?
EQ: How do we interpret a phase diagram?
HOT Q1: What is dry ice?
HOT Q2: Where is the
“triple point”?
HOT Q3: What happens when we cross a line on a phase diagram?
Warm Up – WKSHT #3 AND
PROGRESS REPORTS OUT!
1. How much energy is required to completely boil 15g water that is initially
40C?
EQ: How do we interpret a phase diagram?
HOT Q1: What is dry ice?
HOT Q2: Where is the
“triple point”?
HOT Q3: What happens when we cross a line on a phase diagram?
2. How much energy is required to heat a block of ice from -20C to -5C?
Agenda
• Warm-Up
• Agenda
• Quiz Return
• Lab: Dry Ice
• Consensus: Phase Diagrams
• Exit Ticket
HOMEWORK: FINISH WS #3, ONLY PROBLEMS 1-3 and WORKSHEET #4! Study in preparation for
TEST TUESDAY
Agenda
• Warm-Up
• Agenda
• Quiz Return
• Lab: Dry Ice
• Consensus: Phase Diagrams
• Exit Ticket
HOMEWORK: WORKSHEET 4. Study in preparation for TEST TUESDAY
Mini Lab: Dry Ice Date
• We will only have a Background Info and Data
Analysis section of this lab.
Background Info
• Dry Ice - solid form of carbon dioxide gas.
• Sublimation – The transition of a substance from the solid phase to the gas phase without going through the liquid phase.
Mini Lab: Dry Ice
Rules:
• must keep goggles on at all times.
– No goggles = book work and/or burned eyes
• Do not touch the dry ice with your hands or put it on anybody – it is too dangerous and I will write you a referral for intent to commit bodily harm (10 days)
Mini Lab: Dry Ice Date
Data / Analysis:
Read and follow the procedure at lab station.
Write down answers to questions in lab notebook.
You do not have to copy the question!!!
Take out Worksheet #4!
Discussion
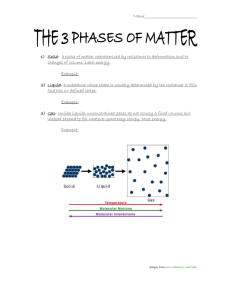
Intro to Phase Diagrams:
• What state of matter would you expect at a very high temperature?
• What state of matter would you expect at a very low temperature?
• What state of matter would you expect at a very high pressure?
• What state of matter would you expect at a very low pressure?
Conclusion
• Looking at your answers, what state of matter would you expect if temperature was somewhere in the middle?
• Looking at your answers, what state of matter would you expect if pressure was somewhere in the middle?
Using your answers from above, please label A, B and C as solid, liquid or gas.
Consensus
• The triple point is where solid liquid and gas all exist at the same time. Where do you think that is on this graph?
• What do all of the lines represent on the graph?
For example if I cross the line from A to B (solid to a gas) what happened?
Phase Diagrams
• Partner Challenge-
– Put your answers to the problems on your whiteboard
– Flip them up so I can check them when I tell you to
Phase Diagram Worksheet
1) If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 1.25 atm and a temperature of
300 o C and lowered the pressure to 0.25 atm, what phase transition(s) would occur?
Practice
• 2) If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 0.75 atm and a temperature of -
100 0 C, what phase change(s) would occur if I increased the temperature to 600 0 C? At what temperature(s) would they occur?
13)
Solving for Different Variables
You Try!
Tricky Units!
12) While you were “sweating” your chemistry test, water vapor evaporates from your body, absorbing 135 kJ of energy. (assume no temperature change). What mass of water evaporates?
1. Region S represents which phase?
Exit Ticket
2. At Point H, a substance would be: a. Melting/Freezing b. Evaporating/Condensing c.
A Critical Point d. A Normal Point
3) To completely freeze 12g of liquid water at 45C, how much energy is required?
Two-Step!
• Trickier quantitative energy problems…
• Like your dollar bill, with hard work, you too will be on FIRE!!!
Two-Step
10) A 50.0 g sample of liquid water at 0.0˚C ends up as ice at – 20.0 ˚C. How much energy is involved in this change?
• You begin with a 75g glass of 50 ° C water.
You cool it to 0 ° C and then completely freeze it. How much energy was lost?
• Daniel has 25g of water at 80 ° C and boils it
completely into gas. How much energy was lost?