L5 Fertility Case Studies
advertisement

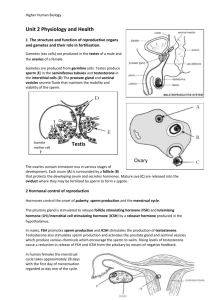
Match Up the Statements Fertile Period Infertile Period Thick mucus Thin Watery Mucus Increase Body Temp. Normal Body Temp. Match Up the Statements Fertile Period Infertile Period Thick mucus Thin Watery Mucus Increase Body Temp. Normal Body Temp. Learning Outcomes •Review topic understanding •Complete activities to ensure comprehensive notes •Revise for checktest Using last lesson information – summarise it in here (take full A4 sheet landscape) ...... Stimulating Artificial Ovulation Insemination Problem Solution Side Effects In-Vitro Fertilisation (IVF/PGS and PGD) Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) Treatments for infertility 4 main ones we will examine; Stimulating ovulation Hormone treatment for ovulation Artificial insemination Low sperm count treated by introducing several samples into reproductive tract. In vitro fertilisation (IVF) + PGS/PGD Counteracts oviduct blockage by fusion of gametes outside body, then once into 8 cells+ reinsert into womb Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) If sperm inactive directly fuse in IVF Stimulating ovulation Problem •Women fail to ovulate, problem with FSH/LH or pituitary gland. Solution •Thus take a drug – mimicking LH/FSH •Or take drugs that prevent negative feedback of oestrogen on FSH in luteal period. Side Effect •Can cause “super-ovulation” where multiple births occur. •Also used in IVF for releasing of eggs Artificial insemination Problem •Low sperm count Solution •Several samples of semen, frozen and then defrosted and released together into cervical region when she is most likely to be fertile. Side Effect •If male sterile, a donor can use same method. In vitro fertilisation (IVF) + PGS/PGD Problem • Blockage of oviducts Solution • Fertilisation occurs outside of body in several stages (see next slide) Side Effect • Examination for genetic abnormalities via pre-implantation genetic screening (PGS) for single gene or common chromosomal abnormalities • Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) specific approach check for known chromosomal/gene defect (eg CF gene) In vitro fertilisation (IVF) + PGS/PGD • Women hormone treatment to stimulate multiple ovulation (egg collection) • Surgery to remove egg from ovary • Eggs mixed with sperm in medium for fertilisation (ICSI alternative – see next) • Fertilised eggs incubated in nutrient media for 2-3 days allowing for cell division to form embryo of 8 or more cells • 2 or 3 embryos choosen, inserted into mothers uterus (ready for implantation) • Remaining embryos frozen in case second attempt needed for implantation Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) Problem •Sperm inactive, so either low count and mature sperm defective Solution •Using a syringe remove healthy sperm and inject directly into an egg for fertilisation. •Egg needs to be held in place by holding tool Using last lesson information – summarise it in here (take full A4 sheet landscape) and add complications from case studies p137-138...... How it works Barrier method (condoms/ diaphragm / cervical cap) Intra-uterine devices (IUD) Sterilisation; • Vasectomy •Tube ligation Pill - combined Morning after pill Mini pill/ implant Complications Physical Methods Complications Not as effective as chemical methods Intra-uterine devices (IUD) How it works Physically blocks sperm reaching ovum T structure into uterus to prevent implantation of embryo, stimulate WBC /substances hostile to sperm / mobility. Sterilisation; • Vasectomy •Tube ligation Cutting/tying sperm ducts / oviducts Irreversible normally but highly effective Barrier method (condoms/ diaphragm / cervical cap) ?Not prevent conception? Ethics! Inflammation/ irritation of uterus allows failure to implant embryo Ectopic pregnancy issue Chemical Methods Pill combined Morning after pill How it works Synthetic oestrogen and progesterone so inhibit FSH and LH (feedback). Thus no mature egg or ovulation. Dummy/placebo on 4th week for menstruation to occur Complications 99% effective – however if vomiting or diarrhoea / antibiotics not protected. Increase risk in breast /cervical and liver cancer, however lowers risk of endometrium/ovarian and colon cancer Oestrogen may cause blood to clot High dose of progesterone and oestrogen- prevent implantation ?Not prevent conception? Ethics! Chemical Methods Mini pill / implant How it works Progesterone only – can be high or low dosage. Complications 50% inhibits ovulation (low dose), dependent on cervical mucus thickening preventing sperm reaching egg. Used while breast feeding/ reduce cramp / heavy bleeding– taken by breast cancer risk or high blood pressure Taken same time every day / mood swings/ irregular menstruation / weight gain Revise & review •Complete testing your knowledge pages 130 and 139 •Make a flow chart/bullet in sequence of 2 phases in menstruation •Use checklist to identify areas for reivison •Then use the keywords (and add other key words) from this topic – write definition/explanation underneath in small writing •Add an arrow linking to another area – along arrow write the connection The Menstrual Cycle Flow Chart 1. 2. Follicular phase (1st half of cycle) before ovulation Development of Graafian follicle from stimulation of FSH and production of oestrogen Repair of endometrium High levels of oestrogen lead to a surge in LH and FSH production at around day 14 OVULATION Luteal phase (2nd half of cycle) after ovulation LH stimulates Graafian follicles to become the corpus luteum which secretes progesterone (vascularisation) No more FSH or LH is released (due to negative feedback) meaning no new follicles are produced Lack of LH degeneration of the corpus luteum (at day 22) no progesterone released to maintain endometrium MENSTRUATION (day 28) Mind Map Review Negative Feedback ICSI FSH Testosterone Ovulation Endometrium Sperm Menstrual Cycle ICSH Vascularisation Chemical methods In vitro fertilisation Luteal Phase Puberty Artificial Insemination Cyclic fertility LH Ovarian hormones Physical methods FSH Negative Feedback ICSI Ovulation Testosterone Endometrium Menstrual Cycle Sperm Vascularisation ICSH Chemical methods Puberty Artificial Insemination In vitro fertilisation Luteal Phase Cyclic fertility LH Ovarian hormones Physical methods