Data - Open PHACTS
advertisement

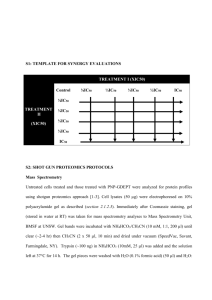
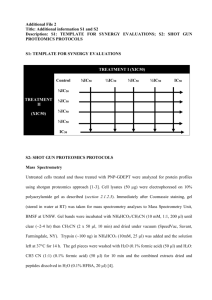
Open PHACTS “Data integration for all” Andrew Leach Task, workflow and results Task: create a focussed set to identify leads against voltagegated potassium channels AUREUS search targets: voltage-gated potassium channels Apply filters (MW, cLogP, Lipinski + remove undesirable target) ⇒ ~1000 molecules Similarity searches Series for lead optimisation (RG, TP, Daylight) Cluster analysis ⇒ ~10000 molecules selected IonWorks© single shot screening 5 full curve actives (in at least one test occasion) 240 single shot hits progressed into full curve assay Stefan Senger, ca. 2004 We (may) know where the data is, but integrating is a pain, bespoke, and often only for experts Q: Identify all oxidoreductase inhibitors with an activity <100nM in both mouse and human Q: The current Factor Xa lead series is characterised by substructure X. Retrieve all bioactivity data in serine protease assays for molecules that contain substructure X. Q: For a given interaction profile, give me compounds similar to it. ChEMBL Gene Ontology DrugBank ChEBI Uniprot Wikipathways UMLS ChemSpider ConceptWiki etc. Internal The Innovative Medicines Initiative Biggest public-private partnership in area of medicine Collaboration between European Commission and European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA) Promotion of medical innovation in Europe Tackle key bottlenecks Recognises “in kind” contributions Focus on key problems – Efficacy, Safety, Education & Training, Knowledge Management Public Domain Drug Discovery Data Pharma are accessing, processing, storing & re-processing GSK Literature Genbank PatentsLiterature PubChemGenbank PatentsLiterature PubChemGenbank PatentsLiterature PubChemGenbank Patents PubChem Databases Databases Databases Databases Downloads Downloads Downloads Downloads AZ Pfizer Merck Data Integration Data Integration Data Integration Data Integration Data Analysis Data Analysis Data Analysis Data Analysis Firewalled Databases Firewalled Databases Firewalled Databases Firewalled Databases Why repeat at each company? Information Tombs – Built for primary use-case – Tailored indexes – Tailored GUIs – Unique language & metadata – Poor interoperability/integration In vivo Portfolio Literature HR Synthesis SAR Docs Safety Etc Project Partners Pfizer Limited – Coordinator Universität Wien – Managing entity Technical University of Denmark University of Hamburg, Center for Bioinformatics BioSolveIT GmBH Consorci Mar Parc de Salut de Barcelona Leiden University Medical Centre Royal Society of Chemistry Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam Spanish National Cancer Research Centre University of Manchester Maastricht University Aqnowledge University of Santiago de Compostela Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn AstraZeneca GlaxoSmithKline Esteve Novartis Merck Serono H. Lundbeck A/S Eli Lilly Netherlands Bioinformatics Centre Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics ConnectedDiscovery EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute Janssen OpenLink A use-case driven approach, focussed on delivery for the real world Main architecture, technical implementation and primary capabilities driven by a set of prioritised research questions Based on the main research questions define prioritised data sources Develop three Exemplars to demonstrate the capabilites of the Open PHACTS System and to define interfaces and input/output standards Work Streams Build: Service layer and resource integration Drive: Development of exemplar work packages & Applications Sustain: Community engagement and long-term sustainability ‘Consumer’ Firewall Target Dossier Pharmacological Networks Compound Dossier OPS Service Layer Assertion & Meta Data Mgmt Transform / Translate Integrator Std Public Vocabularies Business Rules Supplier Firewall Work Stream 2: Exemplar Drug Discovery Informatics tools Develop exemplar services to test OPS Service Layer Target Dossier (Data Integration) Pharmacological Network Navigator (Data Visualisation) Compound Dossier (Data Analysis) Work Stream 1: Open Pharmacological Space (OPS) Service Layer Standardised software layer to allow public DD resource integration − − Db 2 − Db 4 Corpus 1 Db 3 Corpus 5 Define standards and construct OPS service layer Develop interface (API) for data access, integration and analysis Develop secure access models Existing Drug Discovery (DD) Resource Integration Platform Explorer Apps API Standards Prioritised research questions Number sum Nr of 1 Question 15 12 9 All oxido,reductase inhibitors active <100nM in both human and mouse 18 14 8 Given compound X, what is its predicted secondary pharmacology? What are the on and off,target safety concerns for a compound? What is the evidence and how reliable is that evidence (journal impact factor, KOL) for findings associated with a compound? 24 13 8 Given a target find me all actives against that target. Find/predict polypharmacology of actives. Determine ADMET profile of actives. 32 13 8 For a given interaction profile, give me compounds similar to it. 37 13 8 The current Factor Xa lead series is characterised by substructure X. Retrieve all bioactivity data in serine protease assays for molecules that contain substructure X. 38 13 8 41 13 8 44 13 8 46 13 8 59 14 8 Retrieve all experimental and clinical data for a given list of compounds defined by their chemical structure (with options to match stereochemistry or not). A project is considering Protein Kinase C Alpha (PRKCA) as a target. What are all the compounds known to modulate the target directly? What are the compounds that may modulate the target directly? i.e. return all cmpds active in assays where the resolution is at least at the level of the target family (i.e. PKC) both from structured assay databases and the literature. Give me all active compounds on a given target with the relevant assay data Give me the compound(s) which hit most specifically the multiple targets in a given pathway (disease) Identify all known protein-protein interaction inhibitors Kamal Azzaoui et al, DDT in press 2013 Pathways Interactions Proteins Pharmacological Activities Genes Transcripts Clinical Drug Applications ` Biological Processes Diseases Pathological Processes Indications Drugs Chemicals Compounds Open PHACTS will be built upon semantic technologies and standards, providing an opportunity to: • Demonstrate that semantic technologies can perform to the same degree as existing systems • Provide an open platform to address common drug discovery questions; expose pharma’s use-cases and knowledge • Create a pre-competitive infrastructure that can be sustained and expanded into new areas; providing the platform for future collaboration Why Semantic Technologies? • Rapidly developing technology, powerful algorithms for integration and querying of data • “schema free” • Open standards – facilitating sharing public, private, commercial • A community of developers, leverage work going on elsewhere User Interfaces & Applications Linked Data API Linked Data Cache Domain Specific Services Data Identity Mapping Service Identity Resolution Service Key architecture components Open PHACTS Explorer 1st Gen Apps Partner Apps Oct. 2012 Core Platform App Framework Identity Resolution Service (ConceptWiki) “Adenosine receptor 2a” Identifier Management Service (BridgeDb+) P12374 EC2.43.4 CS4532 Linked Data API (RDF/XML, TTL, JSON) Semantic Workflow Engine (LARKC) Chemistry Normalisation & Q/C ChemSpider Data Cache (Triple Store) VoID VoID VoID Nanopub Public Ontologies Db Domain Specific Services Db Public Content VoID Nanopub Db Db Commercial VoID Nanopub User Annotations Data Import Building Quality High quality chemical names and synonyms. Leverage ChemSpider and Concept wiki curation, Q/C and mapping ChemSpider Validation and Standardization Platform (CVSP) for flagging chemical representation issues Basic curation interface for editing concept terms available through Concept Wiki Data quality issues detected in data sources reported back to depositors for their evaluation STANDARD_TYPE Quantitative Data Challenges -----------------IC50 IC50 STANDARD_TYPE UNIT_COUNT ---------------- ------- IC50 AC50 7 IC50 Activity 421 IC50 EC50 39 IC50 IC50 46 IC50 ID50 42 IC50 Ki 23 IC50 IC50 Log IC50 4 IC50 Log Ki 7 Potency 11 IC50 IC50 log IC50 0 IC50 IC50 IC50 >5000 types Implemented using the Quantities, Dimension, Units, Types Ontology (http://www.qudt.org/) STANDARD_UNITS COUNT(*) ------------------ -------nM 829448 ug.mL-1 41000 38521 ug/ml 2038 ug ml-1 509 mg kg-1 295 molar ratio 178 ug 117 % 113 uM well-1 52 p.p.m. 51 ppm 36 uM-1 25 nM kg-1 25 milliequivalent 22 kJ m-2 20 ~ 100 units Chemistry within Open PHACTS The challenges associated with handling chemistry data require the support of a publicly accessible platform to integrate, standardise and host the data. ChemSpider, an online database from the Royal Society of Chemistry hosts the chemical compound collection underpinning Open PHACTS and is responsible for standardising the chemical compounds and providing both regular updates and ongoing data curation. To serve the Open PHACTS platform, a structure validation and standardisation platform (CVSP) has been developed to ensure chemical structures are normalised to rules derived from the FDA structure standardisation guidelines and modified based on input from the EFPIA members. The many challenges of chemistry representation… Identities within Open PHACTS Open PHACTS integrates information from multiple different databases, many of which use unique identifiers. The Identity Mapping Service (IMS) ensures these identifiers are linked and available for use interchangeably throughout the Open PHACTS platform. Synonyms: Aspirin Dispril 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid Acetyl salicylic acid Salicylic acid, acetyl- DrugBank ID: APRD00264 ChEBI ID: CHEBI:15365 ChemSpider ID: 2157 FDA: 16030 IMS To maintain vocabulary heterogeneity and provide interoperability, the ConceptWiki is used. The ConceptWiki is an open access system that accepts essentially unlimited numbers of synonyms, in multiple languages, and then maps all the terms correctly back to one unique concept identifier, alleviating vocabulary problems and identifier differences. Explorer Why Provenance Matters Using a community specification known as “VoID” (Vocabulary of Interlinked Datasets) Record version, author, derivations Builds trust with users – know what you are querying (and why it might have changed) Provides mechanism to provide usage statistics back to providers, help them understand the value Easier to track errors and ensure quality Actively participating in community provenance programme (W3C) What does Open PHACTS do? Currently integrated databases Database ACD Labs / ChemSpider ChEBI ChEMBL_v13 ConceptWiki DrugBank Enzyme Gene Ontology SwissProt WikiPathways TOTAL Number of triples (million) 161.34 0.91 146.08 3.74 0.52 0.07 0.85 156.57 0.14 470.21 Open PHACTS draws together multiple sources of publiclyavailable pharmacological and chemical data, allowing public access to the information via the Open PHACTS Explorer, an intuitive interface. Licensing: 3 “public” databases All are available as “open” RDF you can download right now. But: Drugbank OMIM Comparative Toxicogenomics Database “CUTTING THE GORDIAN KNOT” What are the problems with licensing we had to address? – To make the data and software generated by the project usable and reusable – Multiplicity of unclear or non-standard licenses on original data sources • • • – ‘Public’ can mean use but not redistribute, use in commercial environment, Legal position on use and reuse extremely unclear Different issues than just linking to data What is the legal status of integrated collections of the above, and of derived knowledge from such a collection? – Appropriate software license selection – Legal clarity for EFPIA and end users – Approaches for commercial data integration, EFPIA in-house data AIM: to enable maximum possible dissemination and usability of the integrated data and architecture generated by the project - with approaches that will be applicable in other data integration projects Data Licensing Solution Chose John Wilbanks as consultant A framework built around STANDARD well-understood Creative Commons licences – and how they interoperate Deal with the problems by: Interoperable licences Appropriate terms Declare expectations to users and data publishers One size won‘t fit all requirements Open PHACTS and the scientific community MoU Associated partners Associated partners Support, information Exchange of ideas, data, technology Opportunities to demo at ctions, mostommunity webinars Need MoU +Annexe Development partnerships Development partnerships Influence on API developments Opportunities to demo ideas & use cases to core team Need MoU and annexe Consortium 28 current members Consortium Example applications Advanced analytics ChemBioNavigator Navigating at the interface of chemical and biological data with sorting and plotting options TargetDossier Interconnecting Open PHACTS with multiple target centric services. Exploring target similarity using diverse criteria PharmaTrek Interactive Polypharmacology space of experimental annotations UTOPIA Semantic enrichment of scientific PDFs Predictions GARFIELD Prediction of target pharmacology based on the Similar Ensemble Approach eTOX collector Automatic extraction of data for building predictive toxicology models in eTOX project ChemBioNavigator Matthias Rarey et al PharmaTrek Jordi Mestres et al Call for expressions of interest Open PHACTS ENSO proposal The Open PHACTS Foundation Open PHACTS intends to submit a proposal for IMI ENSO funding. Open PHACTS has a successor organisation, the Open PHACTS Foundation. We are currently drafting our ENSO proposal and invite all EFPIA companies with an interest in Open PHACTS to contact us to discuss opportunities for involvement. Please register your interest with us for further information on membership and other opportunities to get involved within Open PHACTS. For more information and/or to register interest email us at pmu@openphacts.org Acknowledgements Stefan Senger Gerhard Ecker The OpenPHACTS consortium SERVICES Application (Knowledge) Fact Visualisation e.g. Target Dossiers; SAR Visualisation Assertions e.g. Gene-to-Disease; Compound-to-Target; Compound-to-ADR Standards Ontology/taxonomy; Minimum information guide; Dictionaries; Interchange mapping Data Targets; Chemistry; Pharmacology; Literature; Patents After Barnes et al Nature Review Drug Discovery 2009 doi10.1038/nrd2944 Nanopublications – Capturing scientific information in the Triple Store