Earth Science
advertisement

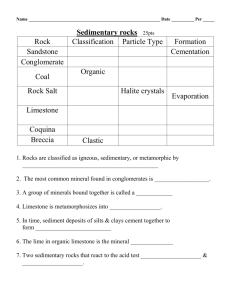
Earth Science Chapter 4 Rocks! Make a chapter cover in your notebook • ROCKS! • ON THE FIRST PAGE LABEL: BELLWORK • ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTION: • WHAT DO YOU THINKS ROCKS AND MINERALS HAVE IN COMMON? Rocks and Minerals • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-f9wrB5yEY Classifying Rocks • Rocks are classified using • 1. mineral composition • 2. color • 3. texture Mineral Content • Rocks can be made of one, or a combination of several minerals • There are about 20 main rockbuilding minerals One mineral Several minerals Color • Can help identify rocks • Granite is usually light • Basalt is usually dark Granite/Basalt Texture Texture Grain size Grain shape Grain pattern Grain size • Fine-some only seen with microscope • Coarse-easily seen without microscope • No visible grain-none seen even with microscope Grain pattern • Bands • Swirls • Colored bands • Random Banded Swirl Colored bands Random Bellwork • What did you find most interesting about the crystal presentations? Igneous Formation •Igneous: forms from the cooling of magma or lava Igneous formation Sedimentary formation • Sedimentary rocks form when particles of other rocks or plant/animal remains are presses and cemented together Sedimentary formation Metamorphic formation • Metamorphic formation: forms when an existing rock is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions. Metamorphic formation You do it! • Read section 2 about igneous rocks. • Create a classification chart describing how igneous rocks are classified • Your chart should include information on origin, texture, and mineral composition of igneous rocks • Charts should also include illustrations, all vocabulary words, and examples of igneous rocks Bellwork • What type of rock is created when lava is cooled quickly? Igneous Rock Classification Origin On or beneath Earth’s surface Texture Depends on the size and shape of mineral crystals Mineral composition Dependent upon the amount of silica in the lava or magma Origin • Extrusive Rock: igneous rock formed from lava that erupted onto Earth’s surface • Most common type is basalt • Makes up most of the ocean’s floors Basalt Origin • Intrusive Rock: igneous rock that formed when magma hardened beneath the Earth’s surface • Most abundant intrusive rock is granite Texture • Rapid cooling=small crystals, fine grain • Slow cooling=large crystals, coarse grain • Extrusive=smooth, fine grain • Intrusive=coarse, large grain Texture Extrusive Intrusive Mineral Composition • Lava is low in silica and dark colored • Magma is high in silica and generally light colored • Geologists look at rocks under a microscope to determine the mineral makeup BELLWORK •WHAT DID YOU FIND MOST INTERESTING ABOUT IGNEOUS ROCK FORMATION? SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • READ SECTION 3 WITH A PARTNER • MAKE A FLOW CHART DESCRIBING THE FORMATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • YOUR CHART SHOULD INCLUDE: – DEFINITION OF SEDIMENT – 4 STEPS OF THE PROCESS INCLUDING EXPLANATION – ILLUSTRATIONS Sedimentary process Erosion Deposition Compaction Cementation Erosion •Natural forces break down and carry small pieces of rock Erosion Deposition •The natural processes eventually drop the eroded rock/sediment and they form layers Bellwork •Discuss a scientific observation you made recently Compaction • This presses the visible layers of sediment together Cementation • During compaction, minerals dissolve in water, fill in gaps in the sediment, and act as a glue holding the newborn rock together Cementation CLASSIFY TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • MAKE A CLASSIFICATION CHART DESCRIBING THE THREE MAIN TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • CHARTS SHOULD INCLUDE DESCRIPTION OF ALL THREE TYPES • HOW THEY FORM • EXAMPLES • ILLUSTRATIONS Classifying Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks Clastic Organic Chemical Clastic • Formed from rock fragments being squeezed together • They can be small or large rock fragments –Clay/pebbles Bellwork •Name three examples of clastic sedimentary rocks Clastic • Most common are shale, sandstone, conglomerate, and breccia • Most form from sand on beaches, ocean floor, riverbeds, and sand dunes Shale Sandstone Conglomerate Breccia Organic Rocks • Remains of plants and animals are deposited in thick layers • Coal and limestone are major examples Coal •Coal forms from swamp plants buried in water •Over millions of years they turn into coal Bellwork •What are the three main types of sedimentary rocks? Limestone • Animals with hard shells made of calcite die and fall to the bottom of the ocean • Over millions of years these make limestone Limestone Chemical Rocks • Form when dissolved minerals crystalize • Examples include ancient sea beds –Could be from salt or dissolved limestone Chemical Rocks Section 4 • Read Section 4: • How do coral animals live? • How do coral reefs form? – Illustrate this as well as writing your answer. • What evidence do limestone deposits from coral reefs provide about Earth’s history? On your Own • Read Section 5: • 1. How are metamorphic rocks formed? • 2. How do geologists classify metamorphic rocks? • What are the different types of metamorphic rocks? Explain each. • What are the uses of metamorphic rocks? Bellwork: fill in the blanks in this chart Magma Rock Cycle • http://PHSchool.com/webcodes10/index.cfm? wcprefix=cfp&wcsuffix=1056&area=view&x=1 4&y=16 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SRaInMD NyE8 If you complete the worksheet.. • Read section 6: The Rock Cycle 1. Make an illustration of the Rock cycle and describe the steps/changes that occur 2. Answer the questions from all three section assessments 3. You may work with a partner, but every student must have their own work to turn in When you complete the questions • Answer the questions from all three section assessments • You may work with a partner, but every student must have their own work to turn in • Due Tomorrow!