Ch. 6 Electricity
advertisement

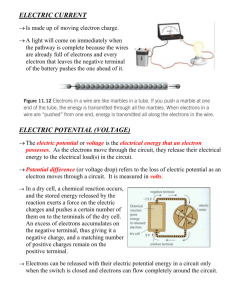
Chapter 6 – Electricity 6.1 Electric Charge Positive and Negative Charges Atoms • Matter is composed of _______ • Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons and electrons • The amount of positive charge on a proton is _____ equal to the amount of negative charge on an electron • Atoms have _______________ no electric charge (electrically neutral) • Amount of electric charge is measured in coulombs ________ (C) 6,250 million billion protons in 1 C of electric charge 6,250 million billion electrons in -1 C of electric charge Coulomb's Law: Like charges _____ repel and opposite attract charges _______. • The difference between the # of protons and the # of electrons determines an object’s electric charge therefore ___________; more electrons. (-) charged obj. have ______ fewer (+) charged obj. have ______electrons. transfer electrons. Obj. are charged by the _______of Transferring Charge • Electrons are bound more tightly to _______________ some atoms and molecules than others • Some atoms can transfer _______electrons more easily than others • Leads to an buildup of electrons on other substances (excess negative charge) Static electricity _____________ STATIC ELECTRICITY Law of Conservation of Charge Charge can be transferred _________ from object to object, destroyed cannot be _______or created _________ but it _______ Charges Exert Force The force between electric charges depends on Distance • ________between charges Amount • ________of charge Mass • _____ Gravitational Forces have similar properties. _______________ On this scale gravity dominates! Comparing Electric Forces and Gravitational Forces weaker than electric • Force of gravity is much ______ force – Electric force between a proton and an electron in a hydrogen atom is about a thousand trillion trillion trillion times larger (1039 X) than the gravitational force between the same particles. • Chemical bonds in molecules are due to electrical forces between atoms _______ gravitational forces – Much larger than the ___________ between the atoms force dominates! On this scale electrical ___________ Electric Fields • Surround every electric charge and exerts the force attracted that causes other electric charges to be _________ repelled or ________. touching to exert force on each • Do not need to be ________ other • Any charge that is placed in an electric field will be pushed or _______ pulled by the field ______ Electric Field Near Negative Charge Electric Field Near Negative Charge Conductors and Insulators Conductor electrons move easily • Material through which ____________________ metals • Best electrical conductors are ________ low resistance? • Conductors have _____ Insulator not able to move easily • Material in which electrons are ____________________ tightly to atoms that make up • Electrons are held ______________ insulators glass , ______ plastic , rubber • Best insulators are _____ ______ and ceramic ________. high resistance • Insulators have a _____ Conductors and Insulators Types of Charging Charging by Contact Charging by Induction The process of transferring charge by _________ touching or ________. rubbing • Also called charging by conduction ___________ rearrangement of The _______________ electrons on a _________ neutral object caused by a _______ nearby object Lightning 6.1 Summary • 2 types of electric charges are (+) & (-). • Like charges repel, unlike charges attract. • On molecular level, electric force is stronger than gravitational force • Electric force acts through electric fields. • Electric fields surround charged objects. Any charged object that enters a region with an electric field experiences an electric force. • Electrons move easily through conductors • Electrons do not move easily through insulators 6.2 Electric Current Current and Voltage Difference Electric current the net movement of electric • ________________: charges in a single direction amperes (A) • Measured in _________ 1 Coulomb of electric charge • 1 ampere = __________________________ • A voltage causes charges to move, which in turn produces a current _______. closed for a current to be produced. • A circuit must be ______ A charged object has electric PE due to its position in an electric field. Potential difference or ________ voltage is the difference in electrical PE per unit charge. – SI unit for pot. diff. (V) = volts = 1Joule/coulomb – Ex. 12V vs. 9V higher voltage to • Electric current is from _____ lower _____voltage • Voltage difference is related to the force that causes electric charges to flow _____________________________ volts (V) • Voltage difference is measured in _____ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Charge Flow _ _ _ _ Current Low Voltage _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ High Voltage Electric circuit a closed path that electric • ___________: current follows Current and Flow Direction direction of the electric current is always The _______ higher voltage to a _____ lower voltage, but … from a _____ • The electrons _______ in a circuit _____actually flow from a lower voltage to a _____ higher voltage _____ Batteries https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CX84l5ZZHVg Dry – Cell Batteries Wet – Cell Batteries • Consist of ___________ 2 electrodes surrounded by a material electrolyte called an ___________ charges • Electrolyte enables ________ to move from one electrode to another Chemical reaction occurs • _________________ when the 2 terminals are circuit connected in a ________. Voltage difference between • ________ these 2 terminals causes a current through a ____________. Closed ciruit battery • Example: Flashlight _______________ • Contains 2 Connected plates made _________________ metals or of different _______ metallic compounds in _________ electrolyte an ___________ • The electrolyte is a conducting liquid solution ____________________ • Example: Car __________ battery Dry - Cell Anode (negative) Cathode (positive ) Wet - Cell Resistance Resistance • ___________: the tendency for a material to resist the flow of electrons and to convert electrical energy into other forms of energy – Measured in ohms ( ) • Caused by _____________ internal friction which slows the through conducting material movement of charges ____________________________ A special type of • Resistor: ______________ conductor used to _______________________ ______________________ control current. Superconductor • Certain metals and compounds that have zero resistance when their temp. falls _____ critical below a certain temp called ______ temperature __________. Semiconductor pure state are insulators • Semiconductors in _________ ________. • However, as atoms/impurities are added, or become compounds, these materials begin conduct electric charge to be able to ___________________. Schematic circuit • Diagram or drawing used to build a _______. • There are two types of circuits. Series one path for electrons, if one bulb – ________: goes out they all do Parallel more than one path for electrons, if – _________: one bulb goes out the rest can still shine Schematic Symbols-Draw symbols on the right side margin of notes Series Circuit Parallel Circuit Open vs Closed Circuit • • Closed ______circuit allows electron to flow, lights on Open circuit does not, lights off ______ Circuit Breakers and Fuses • Too many appliances on at the same time in a home cause the overall resistance of the circuit to be lowered. – Result is a circuit carrying more electrical current than is safe it is ___________ overloaded . Fires can result when this happens. Circuit breakers act as a switch and – _______________ open the circuit. Formulas • SI unit for electric charge Coulomb is the quantity of the electricity transported in – _________ one second by the current of one ampere. Symbol: (C) • Potential difference, voltage (V) – 1Joule/coulomb (1J/C) • Unit for Current (I) = Ampere (amp-A) • Unit for Resistance (R) = Ohm Ω – Formula : Resistance = Volts/Current – Formula with symbols: Ω = V / I • Unit for Electric Power (P) = Watts (Watts) --- Formula: Power = Volts x Current --- Formula with symbols: P= V x I Amps vs volts: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9iKD7vuq-rY