Chapter Three The Biological Basis of Life
advertisement

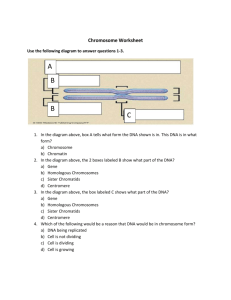
Chapter 3 The Biological Basis of Life Key Terms Nucleus A structure (organelle) found in all eukaryotic cells. The nucleus contains chromosomes (nuclear DNA). Molecules Structures made up of two or more atoms. Molecules can combine with other molecules to form more complex structures. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) The double-stranded molecule that contains the genetic code. DNA is a main component of chromosomes. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) A single stranded molecule, similar in structure to DNA. The three forms of RNA are essential to protein synthesis. Cytoplasm The portion of the cell contained within the cell membrane, excluding the nucleus. The cytoplasm consists of a semifluid material and contains numerous structures involved with cell function. Proteins Three-dimensional molecules that serve a wide variety of functions through their ability to bind to other molecules. Protein synthesis The assembly of chains of amino acids into functional protein molecules. The process is directed by DNA. Mitochondria Structures contained within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that convert energy, derived from nutrients, into a form that is used by the cell. Ribosomes Structures composed of a specialized form of RNA and protein. Ribosomes are found in the cell’s cytoplasm and are essential to the manufacture of proteins. Somatic cells Basically, all the cells in the body except those involved with reproduction. Gametes Reproductive cells (eggs and sperm in animals) developed from precursor cells in ovaries and testes. Zygote A cell formed by the union of an egg and a sperm cell. It contains the full complement of chromosomes (in humans, 46) and has the potential of developing into an entire organism. Nucleotides Basic units of the DNA molecule, composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of four DNA bases. Complementary Referring to the fact that DNA bases form base pairs in a precise manner. For example, adenine can bond only to thymine. Thus, these two bases are said to be complementary because one requires the other to form a complete DNA base pair. Enzymes Specialized proteins that initiate and direct chemical reactions in the body. Replicate To duplicate. The DNA molecule is able to make copies of itself. Hemoglobin A protein molecule that occurs in red blood cells and binds to oxygen molecules. Hormones Substances (usually proteins) that are produced by specialized cells and that travel to other parts of the body, where they influence chemical reactions and regulate various cellular functions. Amino acids Small molecules that are the components of proteins. Messenger RNA (mRNA) A form of RNA that is assembled on a sequence of DNA bases. It carries the DNA code to the ribosome during protein synthesis. Codons The triplets of messenger RNA bases that correspond to specific amino acids during protein synthesis. Transfer RNA (tRNA) The type of RNA that binds to specific amino acids and transports them to the ribosome during protein synthesis. Gene Sequence of DNA bases that specifies the order of amino acids in an entire protein or, in some cases, a portion of a protein. A gene may be made up of hundreds or thousands of DNA bases. Mutation A change in DNA. Technically, mutation refers to changes in DNA bases (specifically called point mutations); also refers to changes in chromosome number and/or structure. Chromosomes Discrete structures composed of DNA and protein found only in the nuclei of cells. Visible only under magnification during certain stages of cell division. Centromere The constricted portion of a chromosome. After replication, the two strands of a doublestranded chromosome are joined at the centromere. Homologous Referring to members of chromosome pairs. Homologous chromosomes carry genes that govern the same traits. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair and exchange segments of DNA. Autosomes All chromosomes except the sex chromosomes. Sex chromosomes In mammals, the X and Y chromosomes. Mitosis Simple cell division; the process by which somatic cells divide to produce two identical daughter cells. Meiosis Cell division in specialized cells in ovaries and testes. Meiosis involves two divisions and results in four daughter cells, each containing only half the original number of chromosomes. These cells can develop into gametes. Recombination The exchange of DNA between homologous chromosomes during meiosis; also called “crossing over.” Nondisjunction The failure of homologous chromosomes or chromosome strands to separate during cell division. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) A method of producing thousands of copies of a DNA segment using the enzyme DNA polymerase. Recombinant DNA technology A process in which genes from the cell of one species are transferred to somatic cells or gametes of another species. Clone An organism that is genetically identical to another organism. The term may also be used to refer to genetically identical DNA segments and molecules. Human Genome Project An international effort aimed at sequencing and mapping the entire human genome. Genome The entire genetic makeup of an individual or species. In humans, it is estimated that each individual possesses approximately 3 billion DNA nucleotides.