Research Methodology
advertisement

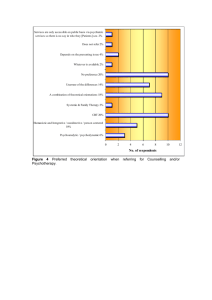
Research Methodology EPH 7112 LECTURE 2: CHARACTERISTICS AND TYPES OF RESEARCH Contents Characteristics of Scientific Research Types of Research Basic Research Applied Research Academic Research Industrial Research Scientific Research How is it different from non-scientific research? Focuses on solving problems and pursues a step-by-step logical, organized, and rigorous method to identify the problems collect data analyze and draw valid conclusions Scientific Research Non-scientific research based on hunches, experience and intuition Pilot study, exploratory Characteristics of Scientific Research Aim Rigor Testability Replicability Precision and Confidence Objectivity Generalizability Parsimony Characteristics of Scientific Research Aim The purpose of scientific research is clear eg to increase gain of EDFA to reduce Optical Beat Interference to reduce Noise Figure Characteristics of Scientific Research Rigorous Based on good theoretical base and sound methodology Careful and scrupulous eg all design parameters concerning the gain in EDFA must be considered; EDF length and concentration, pump power, input signal power and wavelength. eg resolution of OSA, stability of current source for pump laser Characteristics of Scientific Research Testability Test theoretical model by simulation or experiment Analysis of performance parameter against design parameter eg EDFA theoretical model show low gain with high input signal power. Experiment to test this relationship while other design parameters are fixed can be carried out. Gain is measured against input signal power Characteristics of Scientific Research Replicability The same relationship stands repeatedly under the same design parameters Characteristics of Scientific Research Precision and Confidence Precision refers to closeness of the findings to reality Confidence refers to the probability that our estimations are correct Characteristics of Scientific Research Objectivity Conclusions drawn from the analysis of data must be objective Proven from trend in data Supported by theoretical model Characteristics of Scientific Research Generalizability Scope of applicability The wider, the better Eg. Rate Equation Model applicable for lasers and fiber amplifiers Characteristics of Scientific Research Parsimony Simplicity in explaining the phenomena or problem Assumptions are critical Minimize the dependant variable Types of Research Basic Research Applied Research Academic Research Industrial Research Basic Research Also known as pure or fundamental research Objective: Advancement of knowledge Understanding of theoretical relationship between variables Basic Research Exploratory in nature Without any practical end in mind Basic Research Examples of questions asked in basic research: Which aspects of genomes explain organismal complexity? Is it possible to prove or disprove Goldbach's conjecture? (i.e. that every even integer greater than 2 can be written as the sum of two (not necessarily distinct) primes) Applied Research Solve specific, practical questions Can be exploratory, but descriptive Involves precise measurement of the characteristics and describes relationships between variables of a studied phenomenon Applied Research Can be carried out by academic or industrial institutions Investigation directed “to discovering new scientific knowledge that has specific commercial objectives with respect to products, processes or services Applied Research Examples of question asked in applied research: How can Canada's wheat crops be protected from grasshoppers? What is the most efficient and effective vaccine against influenza? How can the Great Lakes be protected against the effects of greenhouse gas? Academic research carried out in universities and research institutes expanding the extant levels of knowledge and technology does not have any limits as it does not have any bounds in terms of tangible goals or outputs Industrial Research carried out in commercial organizations a goal or a set of outputs that apply to the sector or industry focuses on application of knowledge Defining MSc and PhD UG One is ready to learn MSc One is ready to explore PhD One is ready to create MSc, a process of Identifying a research area of interest Learning to carry out a research project Identifying problems Analyzing/ dissecting problems Designing/developing solutions Proving/Substantiating solution Reporting Outcome of MSc program Understand the issues of concerns within the area of specialization Update with the latest development in the area of specialization Master some of the tools (analytical, programming, simulation) required within the scope of study Master some of the test and measurement skills Outcome of MSc program Be able to analyze results Be able to report results ; oral and written Have published papers Know the primary references for the area of specialization Outcome of MSc program Know the leading researchers/research groups in the area of study Know the relevant industries/companies Identify his/her research strength and weaknesses (theoretical, experimental; materials, processes, components/devices, system) Conduct research with minimal guidance Smile..