NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Exemplar
Module Analysis
Grade 9 – Module 1
Grade 11 – Module 1
Grade 12 – Module 1
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
AGENDA
• G9-M1
• Topic Exploration – a Sampling of Exercises and Key Concepts
• Exercise: Assessment & Scoring Rubric
• Overview of Other G9 Modules
• Summary of Key Shifts of Instruction
• G11-M1
• G12-M1
2
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
What’s in G9-M1?
• Topic A: Explore the main functions of the year (linear, exponential
and quadratic) through graphing stories (making graphs of
situations)
• Topic B: Study the structure of expressions, define what it means for
expressions to be equivalent
• Topic C: Precisely explain each step in the process of solving an
equation
• Topic D: The modeling cycle – solving problems using equations and
inequalities in one variable, systems of equations in two variables
3
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic A
Introduction to Functions Studied this Year: Graphing Stories
Sample Exercise:
• Describe the motion of the man in the video
4
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
The Video:
• http://mrmeyer.com/graphingstories1/graphingstories2.mov
(watch only the first 1:08 minutes)
5
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic A
Introduction to Functions Studied this Year: Graphing Stories
Sample Exercise:
• Describe the motion of the man in the video
6
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
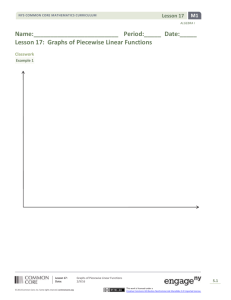
Piecewise Defined Functions (cont.)
A Follow-On Activity:
• Here is an elevation vs.. time graph of a person’s motion, can we
describe what the person might have been doing?
7
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic A
Introduction to Functions Studied this Year: Piecewise Defined
Functions
Define Real piece-wise defined linear function:
• Given a finite number of non-overlapping intervals on the real
number line, a real piecewise-linear function is a function from the
union of the intervals, to the real number line, such that the function
is defined by (possibly different) linear functions on each interval.
8
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic B
The Structure of Expressions
Sample Exercises from Lesson 7:
• Use this diagram to build an expression using these symbols and operators.
9
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic B
The Structure of Expressions
DEFINE VARIABLE:
A variable symbol is a symbol that is a placeholder for a number from a
specified set of numbers. The set of numbers is called the domain of
variability.
If a variable symbol represents a number from a set of numbers with
more than one element, it is typically just called a variable. If the
domain of variability is exactly one element, then the variable
symbol is called a constant.
10
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic B
The Structure of Expressions
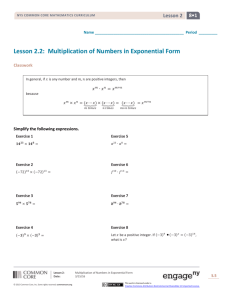
DEFINE ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSION:
An algebraic expression is either
a numerical symbol or a variable symbol, or
the result of placing previously generated algebraic expressions into the
two blanks of one of the four operators (__+__, __-__, __×__,
__÷__) or into the base blank of an exponentiation with an
exponent that is a rational number.
A numerical expression is a algebraic expression that does not have any
variables in it and that evaluates to a real number value.
11
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic C
Solving Equations and Inequalities
ALGEBRAIC EQUATION:
An algebraic equation is a statement of equality between two algebraic
expressions.
NUMBER SENTENCE. A number sentence is a statement of equality between
two numerical expressions.
TRUTH VALUES OF A NUMBER SENTENCE. A number sentence is said to be
true if both numerical expressions evaluate to the same number; it is said
to be false otherwise.
12
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic C
Solving Equations and Inequalities
The vocabulary of Solution Sets:
• An equation with variables is often viewed as a question asking
for which values of the variables is the equation true.
• The equation serves as a filter that sifts through all the
numbers in the domain of the variability and sorts those into
two disjoint sets: The Solution Set and the set of values for
which the equation is false.
13
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic C
Solving Equations and Inequalities
Key concepts and definitions:
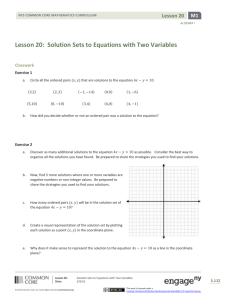
• “Solve”– identifying all the values of the solution set for a given
system of one or more equations.
• Solving an equation:
… starts with the assumption that the original equation has a
solution, example: x + 5 = x - 3
… and then strategically uses the associative, commutative and
distributive properties and “If-then” moves that apply the
properties of equalities (or inequalities).
14
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
A Story of Functions
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
Topic D
Creating Equations to Solve Problems
Sample exercise:
• Create a piecewise defined function to represent the total effective Federal
Income tax due for a married couple filing jointly.
Schedule Y-1 — Married filing Jointly or Qualifying Widow(er)
If taxable income is
over--
But not over--
The tax is:
of the amount over--
$0
$17,000
10%
$0
$17,000
$69,000
$1,700.00 + 15%
$17,000
$69,000
$139,350
$9,500.00 + 25%
$69,000
$139,350
$212,300
$27,087.50 + 28%
$139,350
$212,300
$379,150
$47,513.50 + 33%
$212,300
$102,574.00 + 35%
$379,150
$379,150
15
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
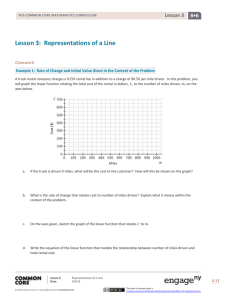
Sample from the Assessments:
1. Jacob lives on a street that runs east and west. The grocery store is to the
east and the post office is to the west of his house. Both are on the same
street as his house. Answer the questions below about the following story:
At 1:00 p.m., Jacob hops in his car and drives at a constant speed of 25 mph
for 6 minutes to the post office. After 10 minutes at the post office, he
realizes he is late, and drives at a constant 30 mph to the grocery store,
arriving at 1:28 p.m. He then spends 20 minutes buying groceries.
a. Draw a graph that shows the distance Jacob’s car is from his house with
respect to time. Remember to label your axes with the units you chose
and any important points (home, post office, grocery store).
16
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Other Grade 9 Modules:
G9-M2: Descriptive Statistics
• Distributions and their shapes
• Measures of center and spread
• Modeling relationships of numerical data on two variables
17
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Other Grade 9 Modules:
G9-M3: Linear and Exponential Relationships
• Formal function notation – a study of arithmetic and geometric
sequences
• Rates of change – contrasting linear and exponential
• Interpreting graphs of functions – domain, range, maxima, minima
• Relating equation notation to function notation
• Absolute value function – studying transformations – how graphs
change when equations change
• Applying functions to real world contexts – systems of equations
18
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Other Grade 9 Modules:
G9-M4: Expressions and Equations
• Explaining properties of quantities represented by an expression
based on contextual situation
• Identify ways to rewrite quadratics and the usefulness of each
• Operations with polynomials
• Symmetry in quadratic graphs
• Solving quadratic equations, deriving the quadratic formula
POLYNOMIAL. A polynomial is any algebraic expression generated in the following
way: (1) declare all variable symbols and all numerical expressions to
be polynomials. (2) any algebraic expression created by substituting two
polynomials into the blanks of an addition operator or multiplication operator is also
a polynomial.
19
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Other Grade 9 Modules:
G9-M5: Quadratic Functions
• Key features of quadratic and non-quadratic graphs
• Exponential vs.. quadratic growth
• Modeling with quadratic functions
20
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Key Shifts of G9 Curriculum:
• A focus on the solution set.
• How does the solution set stay the same or change as we modify the
equation.
• Graphs of equations are pictorial representations of solution sets.
• The graph of the function, f, is a pictorial representation of the solution
set of y = f(x).
• How does the graph of the function stay the same or change as we
modify the function.
• Students experience learning and modeling: Start with an intuitive notion -> play with examples and look for structure --> find rogue examples and
figure out what to do with them ---> arrive at a nice definition.
21
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
AGENDA
• G9-M1
• G11-M1
• Topic Exploration – a Sampling of Exercises and Key Concepts
• Summary of Key Shifts of Instruction
• G12-M1
22
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
What’s in G11-M1?
• Topic A: POLYNOMIALS: extending from, and analogous to, base 10
arithmetic; division with polynomials
• Topic B: FACTORING: Its use and its obstacles, leading to modeling
with polynomials
• Topic C: Solving and applying polynomial and rational equations
• Topic D: A surprise from geometry: complex numbers overcome all
obstacles; radical equations
23
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic A
Polynomials from Base Ten to Base X
Exercise:
• Write the number 8943 in base 20
• Let’s be as general as possible – not identify which base we are in,
just call it x.
1 x x3 + 2 x x2 + 7 x x + 3 x 1
24
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic A
Polynomials from Base Ten to Base X
• Two models for division with polynomials:
• Long division algorithm that is analogous to the division
algorithm in base 10 arithmetic.
• Reverse Galley method that is analogous to the area model
• Extensive exploration with division serves as a precursor to
factoring:
What happens when we divide x2 – a2 by x – a?
25
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic B
Factoring: Its Use and Its Obstacles
• Exercise: Write 501 as a product of prime numbers.
• 1st Obstacle: What if a factor is not given to us first… how can we
achieve factored form when we don’t know what to divide by?
• Motivated by graphing (A-APR.3):
Can we write an equation whose graph would look like this?
26
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic C
Solving and Applying Equations: Polynomial and Rational
• Rational Expressions are analogous to rational numbers
• Solving rational equations in one variable – IF there is an
answer, what must the answer be?
1
=0
𝑥
• Solving systems of equations in real-world contexts
• Deriving the equation of a parabola
27
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic D
A Surprise from Geometry—Complex Numbers Overcome All
Obstacles
• Some quadratic equations do not have solutions, why?
• Does every cubic have a solution?
• A surprising boost from geometry – transformations on the
number line:
• What is the geometric effect of adding 2 to all the numbers
on the number line?
• … to multiplying all the numbers by -1?
• What transformation would create a 90°rotation?
28
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Summary of Key Shifts in G11-M1
• Polynomials are analogous to the integers (foundational from G9M4’s A-APR.1)
• Rational expressions are analogous to rational numbers (precursor
to G12-M3’s A-APR.7)
• Graphs of equations are pictorial representations of solution sets.
• The graph of the function, f, is a pictorial representation of the
solution set of y = f(x).
• Students experience learning and modeling: Start with an intuitive
notion --> play with examples and look for structure --> find rogue
examples and figure out what to do with them ---> arrive at a nice
definition.
29
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
AGENDA
• G9-M1
• G11-M1
• G12-M1
• Topic Exploration – a Sampling of Exercises and Key Concepts
• Supporting content from grades 8-11
• Summary of Key Shifts of Instruction
30
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
By the end of G12-M1 students:
• Use matrix notation to define and interpret
transformations of the coordinate plane
31
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
How do they get there?
Topic A: A Question of Linearity
• Investigate the qualities of linear transformations (from reals
to the reals)
Topic B: Complex Number Operations as Transformations
• Geometric representations of complex numbers and
operations thereon (in the complex plane)
• Extend linearity to transformations from coordinate plane to
coordinate the plane (aka, functions that take an (x, y) pair as
an input and produce another (x, y) pair as an output.)
• Connect to the geometric effect of dilation and/or rotation
Topic C: The Power of the Right Notation
32
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic A
A Question of Linearity
Wouldn’t it be lovely if functions were “nice” and just did what we expected
them to do? Exercise: Here are some common student mistakes:
(𝑎 + 𝑏)2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2
1
1 1
= +
𝑎+𝑏 𝑎 𝑏
log 2𝑎 = 2 log 𝑎
a. Substitute in some values to show these statements are not in general true.
b. Are there any values for which these statements, by coincidence, happen to
work? Find all such values a and b for which these statements are true.
33
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic A
A Question of Linearity
• If only all functions behaved in this way:
𝐿 𝑥 + 𝑦 = 𝐿 𝑥 + 𝐿(𝑦)
𝐿 𝑘𝑥 = 𝑘 𝐿(𝑥)
• Functions that behave in this way are called:
LINEAR TRANFORMATIONS
• Are all linear functions also linear transformations?
• No, but functions of the form 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑚𝑥 are linear
transformations.
34
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic B
Complex Number Operations as Transformations
What ‘happens’ in the geometric representation
• When we add two complex numbers?
• When we multiply a complex number by -1?
• When we subtract one complex number from another?
• When we multiply two complex numbers?
• When we divide a complex number by another?
35
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic B
Complex Number Operations as Transformations
Can we come up with a function that takes any point in the
complex plane and transforms it to another point in the
complex plane based on the rule of the function?
YES!
We have seen that 𝑇 𝑥 + 𝑖𝑦 = 𝑥 + 𝑖𝑦 + (𝑎 + 𝑏𝑖) translates
in the plane. We could write this as 𝑇 𝑧 = 𝑧 + 𝑤.
And that 𝑇 𝑥 + 𝑖𝑦 = (𝑥 + 𝑖𝑦)(𝑎 + 𝑏𝑖) rotates and dilates in the
plane. We could write this as 𝑇 𝑧 = 𝑤𝑧.
36
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Topic B
Complex Number Operations as Transformations
Can we agree that complex numbers, can be matched with or thought
of as 𝑥, 𝑦 points?
Consider our function that rotates and dilates about the origin:
𝑇 𝑧 = 𝑤𝑧,
𝑜𝑟 𝑇 𝑥 + 𝑖𝑦 = (𝑥 + 𝑖𝑦)(𝑎 + 𝑏𝑖)
What are the coordinates of the resulting point in the complex plane in
terms of a, b, x and y?
( 𝑎𝑥 − 𝑏𝑦 , 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑎𝑦 )
37
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
A Story of Functions
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
Topic C
The Power of the Right Notation
Doesn’t this look ugly?
𝐿 𝑥, 𝑦 = (𝑎𝑥 − 𝑏𝑦, 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑎𝑦)
After 70 years of struggle, they came up with this:
𝑥
𝑎
𝐿
=
𝑏
𝑦
We know that:
𝑎
𝑏
−𝑏
𝑎
Can we decipher what
𝑥
𝑦
2
3
−𝑏
𝑎
𝑥
𝑦
has to end up as: (𝑎𝑥 − 𝑏𝑦, 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑎𝑦)
1
−2
𝑥
𝑦
would end up as?
38
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Supporting Content of Grade 9-11:
Grade 11
• Motivates a discovery of complex numbers as students graph
polynomials and thus look for their zeros (G11-M1)
• Complex numbers are connected to the complex plane via, “If
multiplying by -1 has the effect of rotating the number line 180degrees, what could I multiply by to rotate 90-degrees” (G11-M1)
• Provides a study of the trigonometric functions (G11-M2)
39
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Supporting Content of Grade 9-11:
Grade 10
• In depth study of basic rigid motions: rotations, translations,
reflections (G10-M1)
• In depth study of similarity transformations (dilations) (G10-M2)
Grade 9
• Introduces function notation;
• Gives focused attention to interpreting the structure of expressions
40
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
A Story of Functions
Key Shifts of G12-M1:
• Introduction motivation for use of matrices:
• The need for notation of transformations in the plane (their
primary mathematical use) – every type of 3 dimensional game
uses this type of rotation and dilation matrices.
• Introduces the idea of an inverse function.
41
© 2012 Common Core, Inc. All rights reserved. commoncore.org