Chapter09 File I/O and Looping
advertisement

Chapter 9
File I/O and Looping
1
Chapter 9 Topics
Using Data Files for I/O
While Statement Syntax
Count-Controlled Loops
Event-Controlled Loops
Using the Peek Method
Using a While Statement for Summing and
Counting
Nested While Loops
Loop Testing and Debugging
2
9.1 File Input and Output
File(檔案)
Store
data on an auxiliary storage device,
such as a disk.
Reading
Writing
file pointer
end-of-file (EOF)
3
To Use File I/O, you must
Import System.IO namespace
Use declaration statements to declare the file
variable identifiers we are going to use.
Associate a file object with each variable.
use methods associated with the file objects
to read or write data. (using available
methods such as Read, ReadLine, Write,
WriteLine)
Call a method to close the files when we are
through with them.
4
1. Import System.IO namespace
Imports System.IO
In namespace Sustem.IO, VB defines many
classes
File
– Provide methods for opening files
StreamReader
– Represents streams of characters coming from an input
file
StreamWriter
– Represents streams of characters going to an output file
5
2. declare the file identifiers
Dim theFile As File
Dim outFile As StreamingWriter
Dim inFile As StreamReader
StreamReader is for input files only
StreamingWriter is for output files only
Allow us to read or write both individual
characters and whole lines of text from or to files.
6
3. Associate a file object with each variable
Tell operating system(作業系統) the name of
the file on the disk.
We pass a file name on the disk to a method
that creates a StreamReader or
StreamWriter object.
outFile = theFile.CreateText(“outfile.dat”)
inFile = theFile.OpenText(“infile.dat”)
inFile = theFile.OpenText(“c:\myfile.dat”)
outFile = theFile.CreateText(“c:\outfile.dat”)
7
outFile
inFile
File pointer
File pointer
File name:
infile.dat
File name:
outfile.dat
outFile = theFile.CreateText(“outfile.dat”)
inFile = theFile.OpenText(“infile.dat”)
8
What does instantiating a file do?
associates the Visual Basic identifier for your
file with the physical (disk) name for the file
places a file pointer at the very beginning of
the file, pointing to the first character in it
if the output file does not exist on disk, an
empty file with that name is created
if the output file already exists, it is erased
9
4. use methods associated with the file
objects to read or write data
Imports System.IO
input data
disk file
“myInfile.dat”
your variable
(of type
StreamReader)
output data
executing
program
disk file
“myOutfile.dat”
your variable
(of type
StreamWriter)
10
5. Call a method to close the file
inFile.Close()
outFile.Close()
11
class StreamWriter
Write
WriteLine
Private data
and
Flush
methods
Close
12
Write( ) method
Write( ) method of StreamWriter class can be
passed a value of type Integer or a String
object as parameter.
An Integer parameter is first converted using
Unicode and then written to the file as a character.
EXAMPLE
Dim theFile As File
Dim outFile As StreamWriter
outFile = theFile.CreateText ("outfile.dat")
outFile.Write (“X"c)
outFile.Write(Chr(88))
outFile.Write("This is a string value.")
13
Write( ) method
EXAMPLE
outFile.Write (“X"c)
outFile.Write (“ ")
outFile.Write(Chr(88))
outFile.Write (“ ")
outFile.Write("This is a string value.")
outFile.Write (“X"c)
outFile.Write (Chr(13) & Chr(10))
outFile.Write(Chr(88))
outFile.Write (Chr(13) & Chr(10))
outFile.Write("This is a string value.")
14
class StreamReader
Peek
Read
Private data
and
ReadLine
methods
Close
15
Read( ) method
Read( ) method is a value-returning method.
It is called with no parameters and returns an Integer value
containing the code for a single character Unicode.
Read return -1, which is not a valid character code.
EXAMPLE
Dim theFile As File
Dim inFile As StreamReader
Dim outFile As StreamWriter
inFile = theFile.CreateText (“infile.dat")
outFile = theFile.CreateText ("outfile.dat")
datum = infile.Read()
letter = Chr(datum)
outFile.Write(datum)
16
WriteLine() Method
WriteLine( ) automatically adds the EOL mark to the end of
whatever it writes to the file
println( ) automatically adds the EOL mark to the end of
whatever it writes to the file.
EXAMPLE
payFile.WriteLine(“X”)
payFile.WriteLine()
payFile.WriteLine(88)
payFile.WriteLine()
payFile.Write("This is a string value.")
payFile.Write(“X” & Chr(13) & Chr(10) & Chr(13) & Chr(10) & 88 &
Chr(13) & Chr(10) & Chr(13) & Chr(10) & "This is a string value.")
17
ReadLine( ) method
ReadLine( ) method of StreamReader class can be used
to input a numeric value from a file.
ReadLine( ) method of StreamReader class uses no
parameters and returns a String Object
It reads a line of input from the file, including the end-of-line
mark, but discards the EOL mark and stores the rest of the
input line in the returned String.
EXAMPLE
Dim dataLine As String
dataLine = dataFile.ReadLine()
payFile.WriteLine(dataLine)
18
ReadLine( ) method
EXAMPLES
dataLine = dataFile.ReadLine()
dataLine = dataLine & “***”
payFile.WriteLine(dataLine)
number = CDbl(inputBox.Text)
Dim floatNumber As Double
floatNumber = CDbl(dataFile.ReadLine())
Dim intNumber As Double
intNumber = CDbl(dataFile.ReadLine())
19
ReadLine( )
ReadLine reads successive characters (including
blanks) into the string, and stops when it reaches
the linefeed character or the carriage return
character followed by the linefeed character.
Either or both of the carriage return and linefeed
characters are consumed by ReadLine, but they
are not stored in the returned string
20
Examples
'Using Files
Imports System.IO
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim inFile As StreamReader
Dim outFile As StreamWriter
Dim txtLine As String
'File classes
'input data file
'output data file
inFile = File.OpenText("infile.dat")
outFile = File.CreateText ("outfile.dat")
txtLine = inFile.ReadLine()
outFile.WriteLine(txtLine)
inFile.Close()
outFile.Close()
End Sub
End Module
21
Examples
Public Sub New()
MyBase.New()
...
InitializeComponent()
inFile = theFile.OpenText("c:\infile.dat")
outFile = theFile.CreateText("c:\outfile.dat")
txtLine.Text = inFile.ReadLine()
inFile.Close()
End Sub
Protected Overloads Overrides Sub()
outFile.WriteLine(txtLine.Text)
outFile.Close()
...
MyBase.Dispose(disposing)
End
22
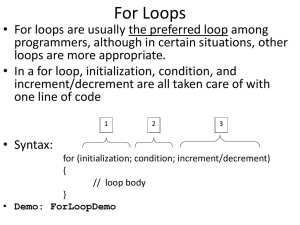
9.2 What is a loop(迴圈)?
A loop is a repetition(重覆) control
structure.
It causes a single statement or block
to be executed repeatedly while an
expression is true.
23
while Statement
SYNTAX
While ( Expression )
.
Statement
.
End While
' Loop body
NOTE: Loop body can be a single statement, a null
statement, or a statement sequence.
24
When the expression is tested and found to be false,
the loop is exited and control passes to the statement
that follows the loop body.
WHILE LOOP
Expression
Statement
True
False
End While
25
While loop Example
Dim loopCount As Integer
Count = 1
While (loopCount <= 25)
Count = Count + 1
End While
' Initialize loop variable
' test expression
' Repeated action
' update loop variable
26
Comparison of If and While
If (then) Statement
Expression
While Statement
Statement
Expression
Statement
True
True
False
False
End If
End While
27
Two types of loops
count controlled loops (以次數控制)
repeat a specified number of times
event-controlled loops (以事件控制)
something happens inside the loop body
and this causes the repeating to stop
28
Count-controlled loop contains
an initialization(初始化)of the
loop control variable(控制變數)
an expression to test for
continuing the loop
an update of the loop control
variable to be executed with each
iteration of the body
29
Count-controlled loop
Dim loopCount As Integer
loopCount = 1
' Initialize loop variable
While (loopCount <= 10)
' test expression
.
' Repeated action
.
.
loopCount = loopCount + 1 ' update loop variable
End While
30
Count-controlled loop
Dim loopCount As Integer
loopCount = 1
While (loopCount <= 10)
' Initialize loop variable
' test expression
' repeated action
loopCount += 1
End While
31
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
' Initialize loop variable
' test expression
' repeated action
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine("Done")
32
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
OUTPUT
33
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
1
OUTPUT
34
Count–controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4) TRUE
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
1
OUTPUT
35
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
1
OUTPUT
count is 1
36
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
2
OUTPUT
count is 1
37
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
TRUE
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
2
OUTPUT
count is 1
38
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
2
OUTPUT
count is 1
count is 2
39
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
3
OUTPUT
count is 1
count is 2
40
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
TRUE
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
3
OUTPUT
count is 1
count is 2
41
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
3
OUTPUT
count is 1
count is 2
count is 3
42
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
4
OUTPUT
count is 1
count is 2
count is 3
43
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
TRUE
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
4
OUTPUT
count is 1
count is 2
count is 3
44
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
4
OUTPUT
count is 1
count is 2
count is 3
count is 4
45
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
5
OUTPUT
count is 1
count is 2
count is 3
count is 4
46
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
FALSE
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
5
OUTPUT
count is 1
count is 2
count is 3
count is 4
47
Count-controlled loop
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
While (count <= 4)
Console.WriteLine("count is" & count)
count += 1
End While
Console.WriteLine ("Done")
count
5
OUTPUT
count is 1
count is 2
count is 3
count is 4
Done
48
Count-Controlled Loop Example
dataFile contains 100 blood pressures,
one to a line.
Use a while loop to read the 100 blood
pressures and find their total.
49
' Count-controlled loop
Dim thisBP As Integer
Dim total As Integer
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
' Initialize
total = 0
While (count <= 100)
' Test expression
thisBP = Integer.Parse(dataFile.ReadLine())
total = total + thisBP
count +=1
' update
End While
Console.WriteLine("The total = " & total)
50
Event-controlled loops
Sentinel (衛兵、守衛)controlled
keep processing data until a special value
which is not a possible data value is entered
to indicate that processing should stop.
End-of-file controlled
keep processing data as long as there is more
data in the file.
Flag controlled
keep processing data until the value of a flag
changes in the loop body.
51
Examples of kinds of loops
Count controlled loop
Read exactly 100 blood
pressures from a file.
End-of-file controlled
loop
Read all the blood
pressures from a file
no matter how many
are there.
Flag controlled
loop
Read blood pressures(血壓)
until a dangerously high BP
(200 or more) is read.
52
Sentinel-controlled Loops
Loops often are used to read in and
process long lists of data.
Each time the loop body is executed,
a new piece if data is read and
processed.
Reading sentinel or trailer value
Used to signal the program that there
is no more data to be processed.
53
A Sentinel-controlled loop
Requires a “priming read”
“Priming read” means you read one
set of data before entering the while
loop
54
Sentinel Value
date = dataFile.ReadLine()
While (Not(date.Equals(“0231”) ))
...
outFile.WriteLine(date)
date = dataFile.ReadLine()
End While
date = ChrW(inFile.ReadLine())
While Not (date <> “0231”)
...
outFile.WriteLine(date)
date = ChrW(inFile.ReadLine())
End While
55
Using Return Mark As Sentinel Value
inChar = ChrW(inFile.Read())
While Not (lastChar = Chr(13) And inChar = Chr(10))
outFile.Write(inChar)
lastChar = inChar
inChar = ChrW(inFile.Read())
End While
56
A Sentinel Value
data = dataFile.ReadLine()
sentinel = data.Substring(0,1)
While (sentinel.Equals(“Y”))
value = CDbl(data.Substring(1, data.Length() - 1))
…
data = dataFile.ReadLine()
sentinel = data.Substring(0,1)
End While
57
End-of-File controlled loop
Depends on fact that the Peek
method from the StreamReader
class returns the sentinel value –1
when the end of the file has been
reached
58
' End-of-file controlled loop
Dim thisBP As Integer
Dim total As Integer
Dim count As Integer
count = 1
' Initialize
total = 0
line = dataFile.ReadLine()
While(dataFile.Peek <> -1)
thisBP = Integer.Parse(line)
total = total + thisBP
count += 1
line = dataFile.ReadLine()
End While
Console.WriteLine('The total = " & total)
59
Flag-controlled loops
Use meaningful name for the flag
You initialize flag (to true or false)
Test for the flag in the loop test
expression
A condition in the loop body changes
the value of the flag
60
Using a flag-controlled loop
to count and sum the first 10 odd
numbers in a data file
flag notDone is initialized to True
loop test will be While (notDone)
flag value will be changed to False
if 10 odd numbers have been read,
or if EOF is reached unexpectedly
61
Examples
Count = 0
'Initialize event counter
Sum = 0
'Initialize sum
notDone = True
'Initialize loop control flag
While(notDone)
If (dataFile.Peek() <> -1 Then
number = CInt(dataFile.ReadLine())
If (number Mod 2 = 1) Then 'Is number odd?
count += 1
'Increment count
sum = sum + number
'add number to sum
notDone = (count <10)
End If
Else
msgbox("EOF reached before ten add values.")
notDone = False
End If
62
End While
Loops often used to:
Count all data values
Count special data values
Sum data values
63
'Flag and EOF controlled loop
countGoodReadings = 0
isSafe = True
While (isSafe And dataFile.Peek <> -1)
line = dataFile.ReadLine()
thisBP = Integer.Parse(line)
If (thisBP >= 200) Then
isSafe = False
Else
countGoodReadings += 1
End If
End While
Console.WriteLine("There were "& countGoodReadings & " _
safe blood pressure readings.")
64
Nested loops
Initialize outer loop
While (outer loop condition)
...
Initialize inner loop
While (inner loop condition)
Inner loop processing and update
End While
...
End While
65
To design a nested loop
Begin with outer loop.
When you get to where the inner loop
appears, make it a separate module and
come back to its design later.
66
Algorithm uses Nested Loops
While the end of data file has not been reached
Get a data line from the data file
obtain starCount from the data line
use a count-controlled loop to print
starCount asterisks to the output file
print a newline character to the output file
read next data line from the data file
print “End” to the output file
67
' Using nested loops
While (dataFile.Peek <> -1)
line = dataFile.ReadLine()
starCount = Integer.Parse(line)
loopCount = 1
While (loopCount <= starCount)
outFile. Write (" * ")
loopCount += 1
End While
outFile.WriteLine()
End While
' While not EOF
' Get data line
' loop to print asterisks
68
Information about 20 books in file
Hardback or
Paperback?
bookfile.dat
Price of book
P 3.98
H 7.41
P 8.79
.
.
.
WRITE A PROGRAM TO FIND TOTAL VALUE OF ALL BOOKS
69
Loop to read information about 20 books
from a file
Dim line As String
' Declarations
Dim kind As String
Dim price As Double
Dim total As Double
Dim count As Double = 0.0
While (dataFile.Peek <> -1 And count <= 20)
line = dataFile. ReadLine()
kind = line.Substring(0,1)
price = Double.Parse(line.Substring(1, line.Length() –1))
total = total + price
count += 1
End While
70
Trace of Program Variables
count
1
2
3
4
20
21
kind
“P”
“H”
“P”
etc.
price
total
3.98
7.41
8.79
0.0
3.98
11.39
20.18
so loop terminates
71
Loop Testing and Debugging
Test data should test all sections of program
Beware of infinite loops -- program doesn’t stop.
Check loop termination condition, and watch for “off-by-1”
problem.
Use Read method for loops controlled by detection of EOL
character.
Use algorithm walk-through to verify that appropriate
conditions occur in the right places.
Trace execution of loop by hand with code walk-through.
Use a debugger (if available) to run program in “slow motion”
or use debug output statements.
72
Case Study
73
incomes.dat
A file contains income data for different
people.
Each line has an M or F for gender,
followed by the salary amount for that
person
gender
M
F
F
M
amount
38119.29
24345.23
32933.73
31820.04
74
results.dat
For 6 females, the average income is 37097.99667.
For 2 males, the average income is 47067.51250.
75
imports system
imports system.io
imports microsoft.visualbasic
module RainFall
'This program reads a file of income amounts classified by
'gender and computes the average income for each gender
sub main
Dim femaleCount as Integer
Dim femaleSum as Double
Dim femaleAvg as Double
Dim maleCount as Integer
Dim maleSum as Double
Dim maleAvg as Double
Dim inLine as String
Dim gender as Char
Dim amountString as String
'Keeps count of females
'Keeps total of salaries
'Holds average salary
'Keeps count of males
'Keeps total of salaries
'Holds average salary
'A line from the file
'Indicate gender
'Amount part of input line
76
Dim
Dim
Dim
Dim
amount as Double
theFile as File
inFile as StreamReader
outFile as StreamWriter
'Salary amount
'Generic file object
'Input data file
'Output data file
'Prepare files for reading and writing
inFile = theFile.OpenText("gender.dat")
outFile = theFile.CreateText ("results.dat")
'Calculate averages
'Initialize process
femaleCount = 0
femaleSum = 0.0
malecount = 0
maleSum = 0.0
77
while (inFile.Peek() <> -1)
'Read line of data, update process
'Extract gender code and amount from input line
inLine = inFile.ReadLine()
gender = inLine.Chars(0)
amountString = inLine.Substring(2)
amount = Cdbl(amountString)
'Process amount based on gender code
If (gender = "F"c) then
'female
femaleCount += 1
femaleSum += amount
Else
'male
maleCount += 1
maleSum += amount
end If
end While
78
'Compute average incomes
femaleAvg = femaleSum / Cdbl(femaleCount)
maleAvg = maleSum / Cdbl(maleCount)
'Write results
outFile.WriteLine("For "
average income is
outFile.WriteLine("For "
average income is
inFile.Close()
outFile.Close()
end sub
end module
&
"
&
"
femaleCount
& femaleAvg
maleCount &
& maleAvg &
& " females, the _
& ".")
" males, the _
".")
79
Exercises
Chapter9
Exam
preparation exercises: 1, 7,11, 12,16,
19
Programming warm-up exercises: 2,4,7,12
Due Date: 12/6 (一)
請寫在A4報表紙上,勿使用電腦列印
80
Programming
由鍵盤輸入人數,然後依次輸入每個人的身高,並將每
個人的身高顯示在螢幕上,依序將身高加總,最後顯示
平均身高在螢幕上。
可使用Windows應用程式或主控制台。
主控制台由鍵盤輸入之語法:x = Console.ReadLine()
由檔案讀入10個人之姓名,再將個人成績讀入(0~100)
,然後將每個人的成績除以10,以一符號畫出橫條圖
及分數,並寫入一檔案。
Due Date: 12/8 (三)
程式不可與他人相同
請將程式及結果畫面列印,並交程式磁片。
81