Unit Two (Chapters 4-7) Vocabulary: demand, supply, ceteris
advertisement

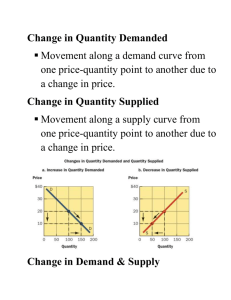
Unit Two (Chapters 4-7) Vocabulary: demand, supply, ceteris paribus, complementary goods, substitute goods, substitution effect, income effect, elasticity, excise tax, price ceiling, price floor, equilibrium, disequilibrium, shortage, surplus, perfect competition, monopolistic competition, monopoly, oligopoly, Sherman Anti-Trust Act, conglomerate What is the law of demand? How does the law of demand affect the quantity demanded? What are the non-price determinants of demand? Why do these determinants cause the demand curve to shift? o If there are a lot of substitutes for a good, what will happen to demand? o If there is an increase in the price for orange juice, what would happen to the demand for apple juice (a substitute good)? o If there is an increase in the price for ski boots, what happens to the demand for skis (a complimentary good)? What does it mean if a good has an “elastic demand”? What does it mean if a good has an “inelastic demand”? What factors affect elasticity of demand? What is the law of supply? How does the law of supply affect the quantity supplied? How can a producer maximize profits? What are the non-price determinants of supply? o If China exports more goods to the United States, what happens to the supply of goods in the United States? Why do the determinants of supply cause the supply curve to shift? What is shown on a supply/demand graph? o What happens when the government imposes a price ceiling that is below the market equilibrium price? o Why might the government impose a price ceiling? A price floor? What factors affect prices? o How do changes in supply and demand affect the equilibrium price and quantity? If the price of bricks in America decreases, what would happen to the price of new homes (bricks represent a production cost) What roles do price play in a free market economy? What are the characteristics of perfect competition? What is non-price competition, and why do businesses use it? How does competition impact the price, quantity, variety of goods? What are the characteristics of monopoly? Why might the government try to limit monopolies from forming? When does the government regulate competition? How does government intervention (through regulations) sometimes hinder economic growth? Why do patents encourage people to invent?