CHAPTER 3
advertisement

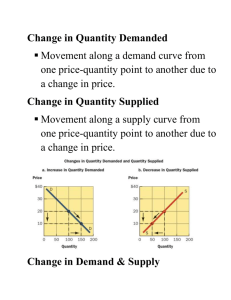
CHAPTER 3 SUPPLY AND DEMAND The Situation: Demand for Tea • -The CEO of Global Food has asked to his VP of Marketing, Nicole Goodman to provide him with a report on the elements that are driving the demand for tea. “How responsive will people be to price changes in the price of competing products such as bottled water and carbonated soft drinks? Is tea a ‘luxury’ good, or is it a necessity? The answers to these questions will help us better understand how to price and position our brand in the marketplace”. Market Demand • The demand for a good is the quantity of a good people are ready to buy at various prices with a time period, while other factors held constant. • There is an inverse relationship between Price and Quantity demand, which is called the “law of demand”. • • • • • • • P$ 10 9 8 7 6 5 Qd 0 80 120 160 200 250 Non-Price Determinants of Demand • • • • • Tastes and Preferences Income Price of Related Goods Future Expectations Number of buyers • Changes in price result in changes in the quantity demanded (movement along demand curve) • Changes in the non-price determinants result in changes in demand (shifts in the demand curve) Market Supply • Supply is the quantity of a good that people are ready to sell at various prices within a period, while other factors held constant. Changes in price result in the quantity supplied. Changes in non-price determinants result in change in the supply.-i.e. shifts of the supply curve Non-price Determinants: • • • • • Costs and technology Price of other goods Future expectations Number of sellers Weather conditions Market Equilibrium • It takes place where Qd=Qs • Draw a Figure over here. • • • • • Show: Equilibrium price Equilibrium quantity Shortage Surplus Comparative Statics Analysis • Market analysis is made through changes in other determinants of demand and supply. • Comparative statics analysis is a form of sensitivity analysis often referred as “what if”. It refers to the comparison of the various points of equilibrium, resulting from shifts in Supply or Demand curves. Supply, Demand and Managerial Decision Making: • While Supply and Demand establish the overall framework in which prices established, individual firm exist market power (some control over price) over their price because of their dominant size in the market or because of their ability to differentiate their product through advertising, brand names and special features. • It is important for managers to understand market demand on two levels: One is the overall demand for the product which is offered by all sellers. Second, there is the demand by buyers for the product offered by the particular firm. This is called company demand. International application: world sugar market • While our situation indicates the importance of corn syrup as a sweetener, sugar is still the primary sweetener of soft drinks around the world. • World sugar price, like corn prices are governed by forces of supply and demand. In 1998, world sugar price were lowest in a decade. This is caused by non-price determinant of supply and demand. Non-price determinants of supply and demand • Non-price determinants of supply: – Costs and technology – Price of other products offered – Future expectations of sellers – Number of sellers – Weather conditions particularly for agricultural products Ie. Favorable weather condition in Brazil, Thailand and Australia – Brazil supplied more cane syrup to the sugar market from alcohol production • Non-price determinants of demand: – Tastes and preferences – Income – Price of related products – Future expectations among buyers – Number of buyers Ie. Economic crisis in Asia reduced the demand for sugar in this region. – China and India increased domestic production, thus less imported sugar. – Russia imposed substantial tariff on imported sugar from 1% to 15% All above factors caused a world surplus of 1-2 million tons of sugar in 1998. leading to 215 dollars per ton from high of 500 dollars in 1980ties. • Draw Figures: • 3.5, 3.6, 3.7, 3.8 Short-run vs Long-run changes • Class Exercise • Case 3.1 (Coffee) and Case 3.2 (Air travel) • The Solution (Tea)