The Middle East Conflict
advertisement

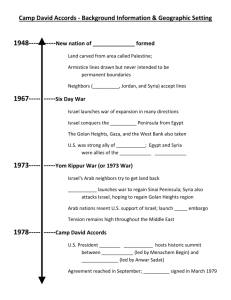
The Middle East Conflict “A Troubled Past” The Middle East Conflict What caused the conflict between the Israelis and the Arabs? Israel was created by a United Nations action in 1947. The Middle East Conflict Why can’t a lasting peace be reached? The Palestinian Arabs demand an independent state in Israel. The Middle East Conflict Middle East Leaders - Egypt Gamal Nasser Pres. of Egypt 1956-1970 * Overthrew King Farouk •Modernizes Egypt Aswan Nile Dam Project Nile River The Middle East Conflict Middle East Leaders - Egypt Gamal Nasser Pres. of Egypt 1956-1970 * Overthrew King Farouk •Modernizes Egypt Aswan Nile Dam Project The Middle East Conflict Middle East Leaders – Egypt Anwar Sadat President of Egypt 1970-1981 Goal: to get the Sinai Peninsula back Goal: make peace with Israel, breaks ties with USSR Assassinated by own countryman for trying to make peace with Israel The Middle East Conflict Middle East Leaders - Egypt Hosni Mubarak Pres. of Egypt 1981-present The Middle East Conflict Middle East Leaders – Israel Golda Meir Prime Minister 1969-1974 Yitzak Rabin Prime Minister 1974-1977 Menachem Begin Prime Minister 1977-1983 The Middle East Conflict Middle East Leaders – Israel Ariel Sharon Prime Minister, 2001-2006 goes into coma in January 2006 Ehud Olmert Prime Minister since April 14, 2006 The Middle East Conflict Middle East Leaders – P.L.O. Palestinian Liberation Organization (established 1964) Yasser Arafat Leader 1964-2004 Goal: Regain the Palestinian State Method: TERRORISM The Middle East Conflict Middle East Leaders – P.L.O. Palestinian Liberation Organization Mahmoud Abbas Leader 2004-present The Middle East Conflict What is O.P.E.C.? Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries It controls the production (amount) and price of most of the oil produced in the world. The Middle East Conflict O.P.E.C. Member Nations The Middle East Conflict Since the UN Partition Plan was put into place, there have been several major wars and many more intermittent battles. 1st Arab- Israeli War When: 1948-1949 Who: Israel vs. Palestinians, Jordan, Egypt, Saudi Arabia Causes: UN Partition Plan – creates State of Israel Results: 1) Israel doubles in size 2) Palestine disappears 3) Divided Jerusalem – Israel/Jordan 4) Palestinian refugees (fled to Gaza & West Bank) The Middle East Conflict 2nd Arab- Israeli War Suez –Sinai War When: 1956 Who: Israel , Britain, France vs. Egypt Causes: Nasser takes control of the Suez Canal - had been under control of Britain/France Results: 1) Egypt gets Suez Canal 2) UN troops move into Sinai (along Egypt/Israel border) 3) Straits of Tiran now open to Israeli shipping The Middle East Conflict 3rd Arab- Israeli War (6 Day War) When: 1967 (June 5 – starts) Who: Israel vs. Egypt, Jordan, Iraq, Syria Causes: Egypt closes the Straits of Tiran – Israel attacks Syria, Egypt, Jordan, and Iraq Results: 1) Israel gets Occupied Territories (Gaza, Sinai, Golan Heights, West Bank) 2) PLO becomes stronger and more prevalent 3) Arabs bitter: NO negotiations, NO recognition, NO peace The Middle East Conflict 4th Arab- Israeli War (October War) (Yom Kippur War – highest of Jewish Holidays) When: 1973 (lasts only 3 weeks) Who: Israel vs. Egypt & Syria Causes: Egypt and Syria, supported by USSR, attack Israel to get land back Results: 1) Ends in cease-fire 2) OPEC oil embargo against U.S.A. 3) UN troops to Sinai to watch border 4) Egypt showed they could fight and regained half of Sinai The Middle East Conflict Camp David Summit When: September 1978 (finalized in April 1979) Who: Israeli President Begin, Egyptian President Sadat, U.S. President Carter Where: Camp David, Maryland (Presidential Retreat) Results: 1) Israel agreed to withdraw its armed forces from the Sinai 2) Evacuate civilians and restore it to Egypt 3) normal diplomatic relations between Israel & Egypt 4) Israel gained free passage through the Suez Canal and other nearby waterways ( Straits of Tiran) 5) Egypt gained free passage between Egypt and Jordan 6) Israel also lost the Abu-Rudeis oil fields in western Sinai their only long term commercially productive wells The Middle East Conflict Operation “Peace for Galilee” When: June 1982 Who: Israel vs. PLO in Lebanon Causes: PLO attacks on Israeli settlements along border Israel launches full-scale invasion of Lebanon to destroy PLO bases The Middle East Conflict Operation “Peace for Galilee” Results: 1) Israel reaches Beirut (capital) within a week, by end of June has captured most of southern Lebanon and besieged PLO and Syrian forces 2) US intervenes to end siege in August Israel agrees to withdraw provided PLO and Syrian forces do also 3) Sept. 15 – Lebanese Pres. Gemayel assassinated, Israel re-occupies Beirut and gives orders to “cleanse” Palestian Refugee Camps – hundreds are killed The Middle East Conflict Oslo Accords When: August - September 1993 Who: Israeli President Rabin, PLO Leader Arafat Where: Oslo Norway Results: 1) Israel agrees to recognize PLO 2) PLO will renounce terrorism 3) Agree to a 5-year plan of Israeli withdrawal of Gaza and West Bank and self-governance by PLO in those areas 4) Creation of Palestinian National Authority (PNA) The Middle East Conflict What is the current status? Sinai: part of Egypt since Camp David Summit 1978 Gaza: Israel has withdrawn, but threatens to intervene as Hamas continues to strike Israeli settlements across the border Hamas Golan Heights: (Arabic: stillحماس needs ;حركة to be acronym: resolved between Arabic: حركة االسالمية Syria/Israel, المقاومة,but or Israel Harakat considers al-Muqawama it to “annexed”alIslamiyya or "Islamic Resistance West Bank: agreed to be shared with the PNA governing all Movement,"[1]) is a Palestinian Sunni Muslim Palestinians – Israel began construction of the Israeli West militant organization Bank barrier in 2000 The Middle East Conflict U.S. Involvement 1991 – US puts together a coalition of countries to protect Saudi Arabia from attack by Iraq – they had already invaded Kuwait “DESERT SHIELD” The operation to liberate Kuwait was called “DESERT STORM” The Middle East Conflict U.S. Involvement 2001 – Terrorists attack the World Trade Towers and the Pentagon The Middle East Conflict U.S. Involvement 2001 – Terrorists attack the World Trade Towers and the Pentagon 2003 – US invades Iraq for the second time Mission: capture Iraqi President Saddam Hussein WMD’s: Reasons: nuclear, biological, and chemical 1)Iraq supports terrorist activities 2)US govt. believes Iraq has weapons of mass destruction (WMD’s) The Middle East Conflict Mideast Today- Iraq In 2003, the United States invaded Iraq to prevent the continued production of weapons of mass destruction. The U.S. claimed that Iraq was supporting terrorism and that it was important to attack before Hussein got nuclear weapons. Ultimately, they wanted to remove Saddam Hussein from office. The U.S. involvement with Iraq spans many decades. In 1990 Iraq invaded the neighboring country of Kuwait. They claimed Kuwait was part of their territory. They claimed that Kuwait was cross drilling and stealing their oil. Furthermore, they claimed that Kuwait was exceeding OPEC quotas driving down prices, hurting Iraq’s economy. The U.S. engaged in a military action called Operation Desert Shield to protect Saudi Arabia’s oil. Operation Desert Storm was a coalition of nations that aimed to drive Iraq out of Kuwait under UN direction. The coalition was very successful. Under a cease-fire, Iraq had to destroy all weapons of mass destruction and allow UN weapons inspectors to investigate. They were not to build weapons of mass destruction. They were limited with two no fly zones to protect the Kurds in the North and the Shiites in the South. Finally they were faced with punishments that limited their oil sales and limited their imports and exports to necessities. Hussein kicked out the UN weapons inspectors in 1998, which prompted the U.S. to take action. In 2003, the U.S. wanted to invade. The U.S. had no major allies because nations were afraid that an invasion would further destabilize the Mideast. The U.S. has sent in over 200,000 troops and experienced over 3000 casualties. The war in Iraq has cost the U.S. between $30-50 billion. Now that the U.S. has ousted Hussein from office, it is unclear who will replace him and what should be done with the imprisoned dictator. The Middle East Conflict War on Terrorism The U.S. is currently engaged in a so-called War on Terrorism. Terrorism is the act of violence for a political goal. One of the major terrorist groups in the Mideast is Hamas, which is a radical break off group of the PLO. They are involved in an intifada with the goal of driving Israel out of Gaza and the West Bank. As of 2003, the leader of the PLO was Yassar Arafat and the leader of Israel was Ariel Sharon. Neither of these men remains in office. On September 11, 2001 terrorists attacked the Pentagon in New York City, the World Trade Center in Washington D.C. and aimed for other targets. Investigation found that Al Quida, led by Osama bin Laden was responsible for the attacks. Bin Laden, is a Saudi whose whereabouts are currently unknown. Al Quida is also responsible for the first attack on the WTC in 1993 and the 1998 bombing of U.S. embassies in Kenya and Tanzania, and the 2000 bombing of the USS Cole in Yemen. Since 2001, Al Quida has carried out many other attacks throughout the world. In 1995, these terrorists called for a jihad or holy war against the U.S. They are against the U.S. because of our support of Israel and our continued presence in the Mideast. Furthermore, they are against the American capitalist system that has yielded our country great wealth. Since 2001, the U.S. has been engaged in a war on terrorism. In response, there has been tighter airport security and the government has tied to better organize itself to protect against terrorism. After the attacks, the President created a new Cabinet position for Homeland Security.