Chapter 22: Sect. 1 Solutions
advertisement

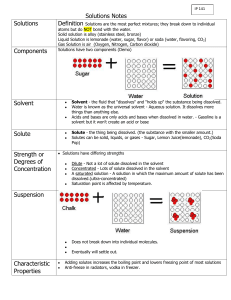
A mixture is 2 or more substances that are combined together that can be separated by physical means (not chemically bonded together) Heterogeneous mixtures – unevenly mixed mixtures, “different” composition throughout Homogeneous mixtures– evenly mixed mixtures, “same” composition throughout Which type of mixture are solutions? Homogenous mixtures Solutions have the same composition, color, and density throughout them We call solutions the “best mixed mixtures” If a solution is made from a substance dissolved in water, it is called an aqueous solution To create a solution, one substance must dissolve in another substance Solute – the substance being dissolved When solids or gases are dissolved in liquids, they are considered to be the solutes Solvent – the substance that does the dissolving When a liquid dissolves another liquid, the liquid that has the largest amount is considered to be the solvent As a general rule of thumb, there is LESS solute and MORE solvent in a solution Solutions do not always involve a solid or gas dissolving in a liquid Solid dissolved in solid Gas dissolved in gas i.e. air (78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% other gases) Liquids dissolved in gas i.e. Alloys - brass (Melted metal solute mixed with melted metal solvent and cooled) i.e. clouds Gas dissolved in solid i.e. marshmallows For each example, identify the solute and the solvent: Kool-Aid Sterling Silver (92.5% silver, 7.5% copper) copper Solute: _____________________ silver Solvent: _____________________ Styrofoam sugar/ Kool-Aid powder Solute: _____________________ water Solvent: _____________________ air (gas) Solute: _____________________ foam (solid) Solvent: _____________________ Mountain Dew sugar, carbon dioxide (gas) Solute: _____________________ Solvent: _____________________ water 1. Moving solvent molecules cluster around the solute They are attracted to each other because they have opposite charges (like a magnet) 2. The solvent molecules pull the solute molecules into the solution 3. The solvent and solute molecules spread out to form a homogeneous mixture Dissolving Animation What can you do to increase the rate at which solutes dissolve in solvents? Stir it! Decrease crystal size By stirring, you are bringing more solvent in contact with the solutes, which cause the particles to dissolve more quickly If you make larger solutes smaller, you are increasing the surface area of the crystals which allows the solvent to surround it more easily Increase temperature Increasing the temperature speeds up the movement of the particles which causes more of the solvent particles to bump into the solute particles Review Song: http://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=3G472AA3SEs