Unit 3: Exploration & Colonization of Georgia (1540
advertisement

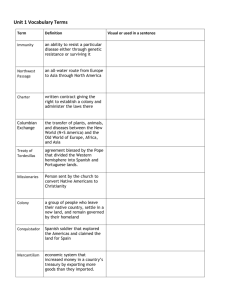
Georgia Performance Standards: SS8H1b: Evaluate the impact of European contact on Native American culture; include Spanish missions along the barrier islands and the explorations of Hernando DeSoto. 1 Unit 3 Vocabulary Terms 1. Azilia: A proposed colony on the land between Spanish Florida and English Carolina. 2. Charter: A written contract issued by a government that grants special rights and privileges. 3. Colony: A group of people who leave their native country to form in a new land a settlement subject to, or connected with, the parent nation. 4. Conquistador: A Spanish explorer and conqueror who sought to destroy and take over existing cultures in the Americas in the 1500s. 5. Indentured Servant: A person who sold his or her labor to a person in return for passage to the New World. 2 Unit 3 Vocabulary Terms 6. Malcontent: Not satisfied or content with current conditions or circumstances. 7. Mercantilism: An economic theory in which government controls trade and attempts to transfer wealth from colonies to the parent country. 8. Mission: A group of people sent to a foreign country to conduct negotiations, establish relationships, provide scientific and technical assistance. 9. Monopoly: A company that eliminates it competition and controls an industry. 10. Trustee: A person who is appointed to take care of business or property for the benefit of someone else. 3 Spanish Explorers Chart, pp. 40-44 4 Exploration • The Renaissance (time of rebirth in Europe) brought about changes in learning, religion, and trade. • Business owners wanted to make bigger profits. • Customers wanted exotic spices and fabrics from Asia. • Therefore, a shortcut was needed to get merchandise from Asia to Europe (Supply & Demand). 5 European Explorers • Spices were in great demand by Europeans. • Before refrigeration, meat and fish spoiled too quickly. • People used spices such as pepper, cinnamon, nutmeg, and cloves to help preserve food and to help improve its flavor. • Transporting spices across great distances cost too much money. 6 Exploration • The 3 main reasons that kings and queens financed expeditions to the New World: A. God: To spread Christianity to more people. B. Gold: To find riches (Gold, silver, precious C. stones, & exotic trinkets). Glory: To become historically famous and to add more territory to their kingdom. 7 European Exploration • European kings and queens, monarchs, were Christians. • They sent missionaries and religious officials to help convert conquered people to Christianity. • They wanted to make Christianity the most powerful religion in the world. 8 Comprehension Check Questions (1) What are the 3 Gs of Exploration and what was the purpose for each “G”? (2) What was Hernando De Soto searching for in the southeastern area of North America? (3) De Soto’s army became famous for being the 1st Europeans to cross the _____________ in North America. (4) What were the purpose of Spanish missions? 9 European Explorers • Portuguese explorers continued to travel farther down the coast of Africa. • 1488-Bartolomeu Dias traveled around the southern tip of Africa. The Portuguese named the tip the Cape of Good Hope. • 1497-Vasco da Gama and his sailors were the 1st Europeans to discover a sea route to Asia. became the leader of exploration. 10 11 European Exploration • Spain and England wanted to compete to discover new sea routes, too! -If you controlled the seas, then you controlled trade with Asia= Power & Wealth 12 Conquistadors • Spanish explorers were known for being conquerors. • They sought to destroy and take over native cultures. • As they explored the Americas, they used guns and swords to defeat Native Americans. 13 European Exploration • Without knowing it, the explorers carried diseases with them (smallpox, malaria, and measles). • These diseases killed many of the natives in the Americas. 14 European Exploration • August 1492-Italian Christopher Columbus and his convoy of ships (Santa Maria, Pinta, & Niña) left Spain to find spices and gold for King Ferdinand & Queen Isabella. • October 12, 1492- He found islands which he thought were part of the Caribbean (A.K.A. West Indies). • He brought back Native Americans (mistakenly calling them “Indians”). • He did not find much gold. • The King and Queen of Spain named him, Admiral of the Ocean Sea. 15 16 Spanish Explorers • Due to Christopher Columbus’s success in the New World, Spain began to finance more voyages to the Americas. began to claim more territory and riches than England and France. • Juan Ponce de León was determined to find the “Fountain of Youth” in Florida (claimed for Spain). • Ponce de León discovered a powerful ocean current called the Gulf Stream. • This current flows from the Gulf of Mexico north along the eastern coast before turning east toward Europe…This helped explorers get back home to Europe quicker! 17 18 Spanish Explorers • 1540-Hernando De Soto and his army were the 1st Europeans to enter what is now known as Georgia. • They were also the 1st Europeans to cross the Appalachian Mountains. • De Soto and his men were searching for cities of gold. • They brutally killed many Native Americans. • Four years later, De Soto died after sustaining injuries during battle and his men never found cities of gold. 19 Spanish Missions in Georgia • Spain built missions, churches, with small communities around them. • They were built along the Atlantic coast in an attempt to bring Christianity to the Indians. • Also, the missions helped to keep French explorers and army off the coast. • Guale (mission) covered the Outer Coastal Plain and barrier islands of Georgia. • 1566-Pedro Menéndez de Avilés started a mission on St. Catherine’s Island. • Spain controlled the coast and southern part of Georgia for 100+ years with missions and military posts. • By 1700, Spain controlled much of the Americas (South America, Central America, and Mexico). 20 21 Georgia Performance Standards: SS8H1c: Explain reasons for European exploration and settlement of North America, with emphasis on the interests of the French, Spanish, and the British in the southeastern area. 22 French Exploration in North America • They were looking for riches and fame and some were searching for religious freedom. • The French treated the Native Americans kindly…They wanted to create communities and live peacefully with the Indians. • However, the French wanted to create a colony on the Atlantic coast. • From the Atlantic coast, they could attack Spanish ships that were traveling back to Europe with treasure back to Spain. 23 French Explorers in North America Explorer Area Explored End Results Jean Ribault René de Laudonniére 24 French Explorations in North America • The official religion of France was Catholicism, but the Huguenots wanted religious freedom. • In 1562, Jean Ribault brought French Protestants called Huguenots to settle in present day South Carolina and created Fort Charlesfort. • The French Huguenots and the Spanish Roman Catholics constantly fought in South Carolina. • Three years later, the Huguenots back to France. 25 French Exploration in North America • In 1564, René de Laudonniére took more Huguenots back to North America. • They settled in Florida (present day Jacksonville) and created Fort Caroline. • The Huguenots ran out of supplies and Jean Ribault was sent to Florida to bring more supplies and soldiers. • The Huguenots and the Spanish settlers of St. Augustine fought each other over territory. • Spanish conquistador Pedro Menéndez de Avilés and his men fought/conquered Ribault and the Huguenots. 26 French Claims in North America • By the 1600s, French explorers had claimed: A. Ohio River Valley B. Mississippi River Valley C. the entire Great Lakes region • By 1760, the French colony of New France had 80,000 people • Also, the French controlled most of the land in the interior of North America. 27 Map of New France in 1750 28 Georgia Performance Standards: SS8H1c: Explain reasons for European exploration and settlement of North America, with emphasis on the interests of the French, Spanish, and the British in the southeastern area. 29 English Colonies in North America • People from England wanted to find a new home in America because of: 1. Population= Overcrowded cities 2. Food Shortage = The English countryside could not produce enough food for all the people. 3. Religious Freedom = Some people did want to practice the religion of the Church of England (Anglican Church) 4. Mercantilism = Wanted new economic opportunities 30 English Colonies in North America • Spain and England were enemies and competitors. • Spain’s official religion was Catholicism and England’s was Protestant. • During the reign of Queen Elizabeth I, their navies fought a major battle at sea and England won…ENGLAND BECOMES THE MOST POWERFUL COUNTRY IN THE WORLD! • Now, England wanted to create its own colonies in North America. 31 English Colonies in North America • 1585-Queen Elizabeth I gave Sir Walter Raleigh permission to start a colony in Virginia, at Roanoke Island. • This colony was not successful, because the settlers ran out of food and supplies. • The colonist disappeared without a trace; therefore, it is known as the “Lost Colony.” 32 English Colonies in North America • 1607-King James I granted two charters for the owners of the Virginia Company of London and the Virginia Company of Plymouth to create colonies. • The colony named Jamestown was started in Virginia with 100 people. • John Smith was the leader of Jamestown. • 1612-A new type of tobacco was developed at Jamestown and became popular in England. • Indentured servants came to Jamestown for a better life. • 1619-The 1st African slaves were brought to Jamestown. • This was England’s 1st successful colony! 33 English Colonies in North America • 1663-Carolina became a colony. • 1670-English settlers created Charlestown (name was changed to Charleston). • 1685-The English settlers of Charlestown allows the French Huguenots to move in (wanted religious freedom). • 1700s-The English and Spanish fought over land from South Carolina to Georgia. 34 English Colonies in North America • Both the French and Spanish had lost power. • The English controlled all the supplies of guns and manufactured goods the Native Americans wanted (Monopoly). • English traders began to cheat and mistreat the Native Americans. • 1715-The Yamasee tribe (Creek Indians) led an attack against the English traders of Carolina. • The English settlers were able to beat the Yamasees and force them to move to the area known as Alabama. 35 The Creation of Georgia SS8H2: The student will analyze the colonial period of Georgia History. Explain the importance of James Oglethorpe, the Charter of 1732, reasons settlement (charity, economics, and defense), Tomochichi, Mary Musgrove, and the city of Savannah. 36 The Creation of Georgia • Leaders in England wanted to form a buffer between the Spanish colonies in Florida to protect the English colonists in Carolina. • 1717-Sir Robert Montgomery proposed a new colony to be built in the area that is known as Georgia. • This proposed colony was to be called the Magravate of Azilia. • Due to fears of attacks from the local Native Americans and the Spanish located in Florida, this proposed colony was never created (unsuccessful). 37 The Creation of Georgia • Due to overcrowding in England’s prisons, a proposal for creating a new colony was considered (debtors were the targeted prison population). • Also, this proposed colony would ease: 1. Overcrowding population in England 2. Solve the homeless problem in England 3. Provide work opportunities for the unemployed people of England. 38 The Creation of Georgia • 1730-James Oglethorpe and 20 other important men became trustees of Georgia (named in honor of King George II). • 1732-the trustees decided to only allow “worthy poor” people with good character to move to Georgia. James Edward Oglethorpe King George II 39 The Creation of Georgia • The 21 trustees created Georgia’s charter with 3 purposes: 1. Charitable: This land would be settled by poor people of London. 2. Economic: a self-supporting colony that would provide cheap natural resources for Great Britain. 3. Defensive: a protective barrier between the English colony of Charlestown from attacks by Spanish Florida. 40 Primary Document 41 The Creation of Georgia • 1. 2. 3. 4. Georgia’s 21 trustees established rules: Colonists could not own land in Georgia No liquor Slavery was not allowed Only man heirs could inherit land • 115 settlers and James Oglethorpe traveled to Georgia on a ship named Ann, which took 2 months. • First stop in North America was in Charlestown. • James Oglethorpe, members of the Georgia militia, and two leaders from Charlestown then traveled to Georgia. 42 The Creation of Georgia • They reached Yamacraw Bluff (modern day Savannah) and met John & Mary Musgrove (trading post owners & interpreters for the Creek Indian), Yamacraw Indians, & Chief Tomochichi. • Oglethorpe formed a treaty with Chief Tomochichi in order to settle at Yamacraw Bluff. • Oglethorpe and others went back to Charlestown to bring the colonists to Georgia. • February 12, 1733-They arrive at Yamacraw Bluff (colonists named it Savannah). • Treaty of Savannah was signed by Oglethorpe and group of Creek Chiefs…The Creek Indians gave the colonists the land and the colonists agreed to trade with the Creeks at set prices. 43 44 45