Hypernatremia - Lectures For UG-5
advertisement

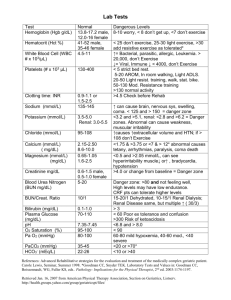
Lecture 9 Definition Serum Na concentration above reference range. (135- 145 mmol/L). Water loss Sodium gain Water loss Pure water loss Decreased intake (elderly, unconscious) Excessive loss (decreased AVP secretion diabetes inspidus, nephrogenic) Water and sodium loss Water loss exceeds sodium loss Osmotic diuresis (DM, excessive sweating or diarrhoea) Sodium gain (salt poisoning) Sodium bicarbonate (for correction of acidosis) Near drowning in salt water Infants fed on high salt diet (1 tbs of salt raises upto 70 mmol/L of sodium. Primary hyperaldosteronism Cushing’s disease. (150 mmol/L) Clinical Manifestations Confusion Neuromuscular excitability Hyperreflexia Seizures coma Treatment Free water 5% dextrose Diuretics or natriuresis Other osmolality diordres Increased urea in renal diseases Hyperglycemia Ethanol Osmolal gap Common cause is presence of ethanol Comatosed patients Hyperkalemia Important IC electrolyte Maintain resting membrane potential of the cells like nerve and muscle cells. Heart arrythmias 3.5- 5.5 mmol/L 30 -100 mmol/L is intake 5 mmol loss through GIT 20-100 mmol/L through kidneys ˃ 7 mmol/L is life threatening Cardiac arrest ECG changes Muscle weakness Parsthesias Causes of hyperkalemia Increased intake Redistribution Decreased excretion Increased intake Patients with impaired renal functions Drugs as potassium salts Intra venous (20 mmol/hr) Blood products Redistribution out of cell Metabolic acidosis Potassium release from damaged cells Insulin deficiency (insulin stimulates cellular uptake of potassium) Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis Rare familial disorder autosomal dominance Recurrent attacks of muscle weakness or paralysis Rest after exercise Pseudohyperkalemis Pseudohyperkalemia Sampling errors Hemolysis (rbc, wbc and platlets) Check potassium in serum and plasma Decreased excretion Renal failure Potassium can not be excreted out when GFR is low Hypoaldosteronism ACE inhibitors Potassium sparing diuretics Treatment Insulin infused along with glucose Calcium gluconate Cation exchage resins orally Dialysis in refractory hyperkalemia