Grade 7 MS Science Midterm Review
advertisement
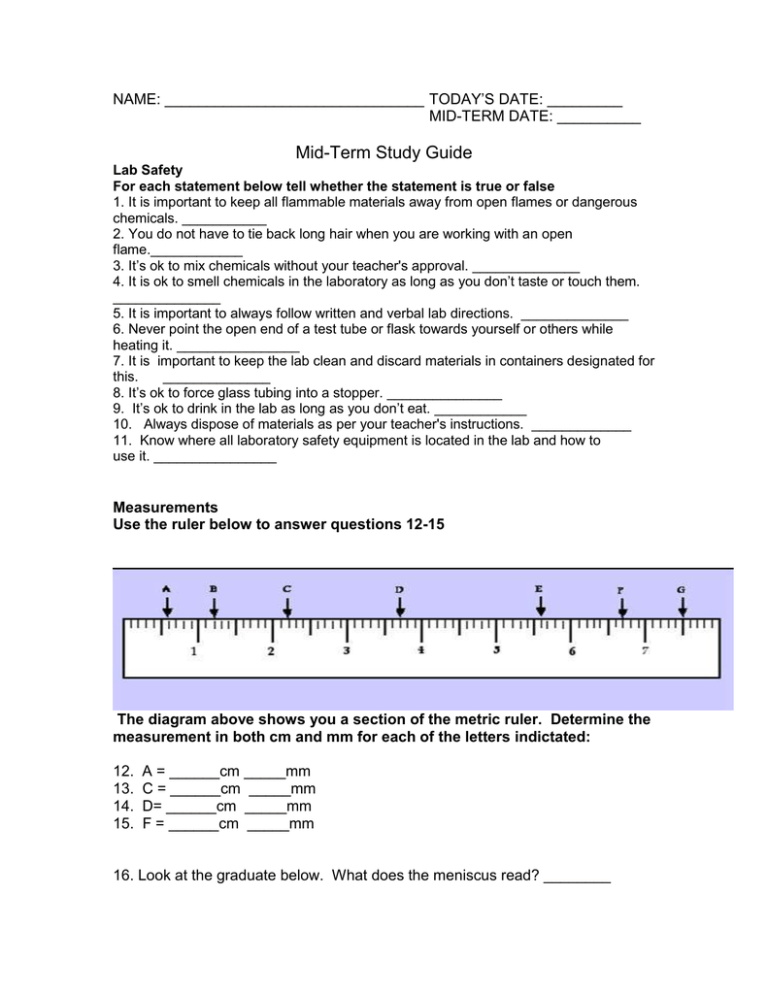
NAME: _______________________________ TODAY’S DATE: _________ MID-TERM DATE: __________ Mid-Term Study Guide Lab Safety For each statement below tell whether the statement is true or false 1. It is important to keep all flammable materials away from open flames or dangerous chemicals. ___________ 2. You do not have to tie back long hair when you are working with an open flame.____________ 3. It’s ok to mix chemicals without your teacher's approval. ______________ 4. It is ok to smell chemicals in the laboratory as long as you don’t taste or touch them. ______________ 5. It is important to always follow written and verbal lab directions. ______________ 6. Never point the open end of a test tube or flask towards yourself or others while heating it. ________________ 7. It is important to keep the lab clean and discard materials in containers designated for this. ______________ 8. It’s ok to force glass tubing into a stopper. _______________ 9. It’s ok to drink in the lab as long as you don’t eat. ____________ 10. Always dispose of materials as per your teacher's instructions. _____________ 11. Know where all laboratory safety equipment is located in the lab and how to use it. ________________ Measurements Use the ruler below to answer questions 12-15 The diagram above shows you a section of the metric ruler. Determine the measurement in both cm and mm for each of the letters indictated: 12. 13. 14. 15. A = ______cm _____mm C = ______cm _____mm D= ______cm _____mm F = ______cm _____mm 16. Look at the graduate below. What does the meniscus read? ________ 17. Using the water displacement method determine the volume of the object. What is the volume of the object? ______________ Initial Volume Final Volume ____________ ____________ 18. Look at the triple beam balance. What is the mass of the object?_______ Interpret Data Tables and Graphs Use the data table below to answer questions 19-23. Week Baseball Team Performance Games Won Games Lost 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 6 5 5 8 4 3 1 2 3 2 1 2 3 5 Total # of Games Played 8 16 23 32 38 44 50 19. How many games did the team win during the first 7 weeks? 20. What percent of the games did the team win? 21. According to the table which week was the worst for the team? 22. What week was the best for the team? 23. From the data on the table what can you conclude? 24. What purpose do data tables and graphs serve? Use the data displayed on the line graph below to answer questions 25-27 25. During what month(s) did the individual weigh the least?________ 25b. What was the individuals weight?__________ 26. During what month(s) did the individual weigh the most? ________ 26b. What was the individuals weight?____________ 27. What do you predict the weight of the individual will be in January? ______________ Scientific Method 28. In order, identify the steps in the scientific method. 29. How is the hypothesis proven or disproven? Identifying Parts of An Experiment A student wishes to test how caffeine affects the heart rate of mice. The student feeds 20 mice 6mL of coffee along with their meal. A second group of 20 mice is fed 6mL of water along with their meal. Each day in the evening (7pm) the heart rate of each mouse is monitored for one minute and recorded. The average heart rate is calculated for each group. The experiment is run for a period of 7 days. 30. What problem is the student trying to investigate? 31. Which group in the experiment is the control group? 32. What is the independent variable in the experiment? 33. What is the dependent variable in the experiment? Life Characteristics 34.What is the basic unit of life?_______________________ 35. The scientific term for a living thing is a(n) ______________________ 36. What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms? Give an example of each. 37. Organisms can reproduce (produce offspring) one of two ways. Name and define the two basic types of reproduction. 38. What is the difference between growth and development? 39. Circle the graphic below that illustrates both growth and development. 40. Organisms respond to environmental factors (stimuli) to help maintain homeostasis. Define homeostasis and give two examples of how living things respond to changes in their environment to maintain homeostasis Interpreting Food Chains, Food Webs and Energy Pyramids 41.What do the arrows on the food web above represent? 42. Where does the initial source of energy come from? 43. From the food chain above, which organism(s) are classified as an herbivore? 44. From the food chain above, which organism(s) are classified as a carnivore? 45. Which the food web above is a producer? organism(s) in 46. Which organism(s) in the food web above are consumers? 47. Which organism(s) in the food web above are omnivores? 48. Which organism(s) in the food web above are carnivores? 49. Which organism(s) in the food web above are herbivores? 50. What happens move up the energy pyramid? 51. At which level would you find the most organisms? 52. At which level would you find the primary consumers? 53. At which level would you find the producers? to energy as you 54. At which level would you find the secondary consumers? Classification 55. Identify the 7 levels of classification from least specific (largest) to most specific (smallest) 56. Ailuropoda melanoleuca, is the scientific name for the panda bear. What two levels in the classification system does this name refers to? 57. When are a species considered to be different? 58. How many kingdoms are there in taxonomy? Name them. 59. Define prokaryote. Define eukaryote. 60. Which kingdom(s) contain the prokaryotes? The eukaryotes? 61. What 4 characteristics do scientists look for when placing organisms into a specific kingdom? 62. Suppose a scientist observes a uni-celled organism under the microscope and notices that the one celled creature has a nucleus. In what kingdom would this specimen belong to? The Microscope 63. What is the difference between a simple microscope and a compound microscope? 64. If the eyepiece of a microscope is marked at 10X and the objective lens is marked at 50X, what is the total magnification? 65. While observing a specimen under low power you notice that the specimen moves down then to the left. In what direction was the specimen really moving? 66. A teacher tells her students to sketch the specimen as it appears under the high power objective lens only. Why should the specimen be viewed under low power first? 67. When should the course adjustment knob be used? 68. When should the fine adjustment knob be used? 69. Give the steps for preparing a wet mount slide. 70. Label all of the microscope parts numbered below: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ 71. Which part of the microscope provides light?_________ 72. Which part of the microscope allows you to select how much light you want shining through the opening of the stage? ______ 73. Which part of the microscope brings a specimen in to a clear, crisp view under high power? _______ 74. Which parts of the microscope magnifies the specimen being viewed? __________ Cells (Animal & Plant) Parts and Function 75. Identify the 3 statements in the cell theory. A) _____________________________________________________________________________________________ B) _____________________________________________________________________________________________ C) _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 76. Label the parts of the animal cell below: 77. Label the parts of the plant cell below: Read each statement below. Tell whether the statement is true or false. 78. The vacuole produces enzymes. _________ 79. The Golgi body stores excess water, food and waste. _________ 80. Vacuoles are larger in plant cells than in animal cells. ________ 81. Two organelles found in plant cells that are not found in animal cells are the cell wall and the chloroplasts.______ 82. The nucleus is the organelle commonly called the control center of the cell. ______ 83. The cell wall is flexible and thin __________ 84. In plant and animal cells the DNA floats freely in the cytoplasm. _______ 85. Ribosomes produce proteins. _______ 86. The cell membrane is a thin structure that controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell. _______ 87. The mitochondria is often referred to as the “power house” of the cell. _______ 88. In plant cells, photosynthesis takes place in the cell wall. ________ 89. Lysosome are the “clean up” crew of the animal cell. __________ 90. Lysosome are found in both plant and animal cells. ___________




