Progressivism and WWI
advertisement

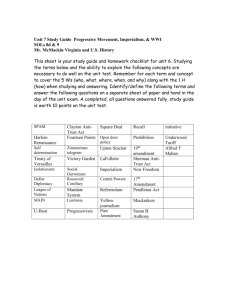
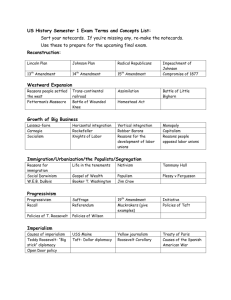
Progressivism to World War I (1890-1920) Study guide – AP U.S. History Main ideas / changes over time: Progressivism - Between 1900 and 1917, Progressivism pushed for and achieved some active reform of U.S. society with the aid of the government. Progressivism and politics - Between 1902 and 1920, Progressives expanded the authority of the government to attempt to reform corrupt business and politics in the U.S. U.S. imperialism - Between 1867 and 1917 the United States expanded overseas through imperialism, resulting in territorial acquisition, political and economic control, and resentment of East Asia and Latin America. U.S. and World War I - By 1917, the U.S. eventually entered World War I, stimulating economic opportunities and manipulating American public support. The End of World War I - Between 1917 and 1920, the U.S. helped the Allies win World War I but refused its peace treaty, then struggled in its own transition from war to peace. SFI names and terms – remember to make connections, understand significance, recognize cause and effect, and group with patterns and categories 1. Progressivism 24. Trust-busting 46. Annexation of Hawaii 2. Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire 25. Northern Securities 47. Teller Amendment 3. Muckraking 26. Pure Food and Drug Act 48. Spanish-American War 4. Upton Sinclair – The Jungle 27. William Howard Taft 49. Rough Riders 5. Ida Tarbell 28. 16th Amendment – income tax 50. Treaty of Paris 1898 6. American Federation of Labor 29. Woodrow Wilson 51. Platt Amendment 7. Industrial Workers of the World 30. Progressive “Bull Moose” Party 52. Anti-Imperialist League 8. Socialism 31. Eugene Debs 53. William McKinley 9. Techniques to combat unions 32. Federal Reserve Act 54. Filipino-American War 10. “Old Guard” Republicans 33. Keating-Owen Act 55. Open Door Policy 11. State child labor laws 34. Imperialism 56. Sphere of influence 12. Margaret Sanger 35. “Scramble for Africa” 57. Panama Canal 13. Prohibition – 18th Amendment 36. Motives for imperialism 58. Monroe Doctrine 14. Niagara Movement 37. Anglo-Saxonism superiority / 59. Roosevelt Corollary 15. Carrie Chapman Catt 16. National American Woman Suffrage White Man’s Burden 60. Big Stick Policy 38. Alfred Mahan & Mahanism 61. Dollar Diplomacy 39. Commodore Matthew Perry 62. Pancho Villa 17. 19th Amendment – woman suffrage 40. Cuban Revolution 63. Causes of World War I 18. Initiative, referendum, and recall 41. Yellow press/journalism 64. Franz Ferdinand 19. 17th Amendment – direct election 42. William Randolph Hearst 65. Central Powers 20. Theodore “Teddy” Roosevelt 43. Joseph Pulitzer 66. Allies (a.k.a. Entente) 21. Coal Strike of 1902 44. U.S.S. Maine 67. American neutrality 22. “Square Deal” 45. Queen Liliuokalani 68. Lusitania Association (NAWSA) 23. Conservation 69. Sussex Pledge 70. Unrestricted submarine warfare 76. “Doughboys” 71. Self-determination 77. American Expeditionary Force 72. Causes of U.S. entering war 78. Russian Revolution 84. Irreconcilables & Reservationists 85. Spanish Flu Pandemic 73. Zimmerman telegram/note 79. Vladimir Lenin 86. First Red Scare 74. Committee on Public Information 80. Armistice Day/Veterans Day 87. Palmer Raids 81. Fourteen Points 88. F.B.I. – J. Edgar Hoover 82. League of Nations 89. Warren G. Harding 83. Treaty of Versailles 90. “Return to normalcy” (Creel Committee) 75. Espionage and Sedition Acts Dates: 1890-1920 – gen. time period of Progressivism, imperialism 1898 – Spanish-American War Presidential terms 1896-1920 1914-1918 – World War I 1917 – U.S. enters World War I 1920 – 18th, 19th Amendment, end of Progressive Era Document-Based Question (DBQ) essay question possibilities: 1. Evaluate the effectiveness of Progressive Era reformers and the federal government in bringing about reform to the United States. Be sure to analyze the successes and limitations of these efforts in the period 1900-1920. 2. Evaluate the degree to which United States imperialism during the period 1865 to 1920 was or was not justified. 3. To what extent did the United States achieve the objectives that led it to enter the First World War?